Abstract
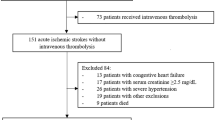
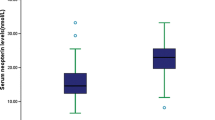
While a number of studies have reported an association between apelin-13 and ischemic stroke, few have verified its clinical effect. We investigated the prognostic value of serum apelin-13 levels in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS). We prospectively recruited 244 AIS patients within 24 h after stroke onset, and 167 healthy controls. We assessed the serum apelin-13 levels using ELISA, and the severity of AIS using the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS). The primary outcomes included death or major disability (modified Rankin Scale score, 3–6) and major disability (modified Rankin Scale score, 3–5). Secondary outcomes included recurrent stroke and combined events (all-cause death, or cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events). We found that the serum apelin-13 levels in the patients (38.63 ng/mL (interquartile range [IQR], 29.86–50.99)) were lower than those in the healthy controls (42.50 ng/mL [IQR, 31.25–59.17]) (P = 0.017). Patients with a NIHSS score ≤ 3 had higher apelin-13 levels than those with a NIHSS score > 3 (P = 0.048). At the 3-month follow-up, multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated an association between apelin-13 and death or major disability (OR 0.31; 95% CI 0.11–0.86; P = 0.024) and major disability (OR 0.32; 95% CI 0.11–0.90; P = 0.030). At the 1-year follow-up, the patients with high apelin-13 levels showed a lower incidence of stroke and combined events (Log-rank test P < 0.05). Our findings indicate that serum apelin-13 may be a potential prognostic biomarker for AIS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou M, Wang H, Zhu J, Chen W, Wang L, Liu S, et al. Cause-specific mortality for 240 causes in China during 1990-2013: a systematic subnational analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2016;387(10015):251–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00551-6.
Collaborators GBDCoD. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1151–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9.
Writing Group M, Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133(4):e38–360. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000350.
Vadakkan C, Siddiqui W. Claustrophobia. StatPearls. Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2019.
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R, Kakegawa T, Zou MX, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;251(2):471–6. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1998.9489.
Lee DK, Cheng R, Nguyen T, Fan T, Kariyawasam AP, Liu Y, et al. Characterization of apelin, the ligand for the APJ receptor. J Neurochem. 2000;74(1):34–41. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0740034.x.
Kawamata Y, Habata Y, Fukusumi S, Hosoya M, Fujii R, Hinuma S, et al. Molecular properties of apelin: tissue distribution and receptor binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1538(2–3):162–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-4889(00)00143-9.
Zhong JC, Zhang ZZ, Wang W, McKinnie SMK, Vederas JC, Oudit GY. Targeting the apelin pathway as a novel therapeutic approach for cardiovascular diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(8):1942–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.11.007.
Opatrilova R, Caprnda M, Kubatka P, Valentova V, Uramova S, Nosal V, et al. Adipokines in neurovascular diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;98:424–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.074.
Chu H, Yang X, Huang C, Gao Z, Tang Y, Dong Q. Apelin-13 protects against ischemic blood-brain barrier damage through the effects of aquaporin-4. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;44(1–2):10–25. https://doi.org/10.1159/000460261.
Khaksari M, Aboutaleb N, Nasirinezhad F, Vakili A, Madjd Z. Apelin-13 protects the brain against ischemic reperfusion injury and cerebral edema in a transient model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci. 2012;48(1):201–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9808-3.
Amani H, Habibey R, Shokri F, Hajmiresmail SJ, Akhavan O, Mashaghi A, et al. Selenium nanoparticles for targeted stroke therapy through modulation of inflammatory and metabolic signaling. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):6044. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42633-9.
Amani H, Mostafavi E, Alebouyeh MR, Arzaghi H, Akbarzadeh A, Pazoki-Toroudi H, et al. Would colloidal gold nanocarriers present an effective diagnosis or treatment for ischemic stroke? Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:8013–31. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s210035.
Stroke--1989. Recommendations on stroke prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. Report of the WHO Task Force on Stroke and other Cerebrovascular Disorders. Stroke. 1989;20(10):1407–31.
Kelly PJ, Albers GW, Chatzikonstantinou A, De Marchis GM, Ferrari J, George P, et al. Validation and comparison of imaging-based scores for prediction of early stroke risk after transient ischaemic attack: a pooled analysis of individual-patient data from cohort studies. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(12):1238–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(16)30236-8.
Song B, Fang H, Zhao L, Gao Y, Tan S, Lu J, et al. Validation of the ABCD3-I score to predict stroke risk after transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2013;44(5):1244–8. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.113.000969.
Song B, Hu R, Pei L, Cao Y, Chen P, Sun S, et al. Dual antiplatelet therapy reduced stroke risk in high-risk patients with transient ischaemic attack assessed by ABCD3-I score. Eur J Neurol. 2019;26(4):610–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13864.
Hurford R, Li L, Lovett N, Kubiak M, Kuker W, Rothwell PM. Prognostic value of “tissue-based” definitions of TIA and minor stroke: population-based study. Neurology. 2019;92(21):e2455–e61. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000007531.
Strambo D, Zambon AA, Roveri L, Giacalone G, Di Maggio G, Peruzzotti-Jametti L, et al. Defining minor symptoms in acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;39(3–4):209–15. https://doi.org/10.1159/000375151.
Ferrari J, Knoflach M, Kiechl S, Willeit J, Schnabl S, Seyfang L, et al. Early clinical worsening in patients with TIA or minor stroke: the Austrian Stroke Unit Registry. Neurology. 2010;74(2):136–41. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181c9188b.
Han Y, Rajah GB, Hussain M, Geng X. Clinical potential of pre-reperfusion hypothermia in ischemic injury. Neurol Res. 2019;41(8):697–703. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2019.1609160.
Ran YC, Zhu M, Li SJ, Zhang ZX, Wang X, Zhang Y, et al. Related research and recent progress of ischemic penumbra. World Neurosurg. 2018;116:5–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.193.
Wu F, Qiu J, Fan Y, Zhang Q, Cheng B, Wu Y, et al. Apelin-13 attenuates ER stress-mediated neuronal apoptosis by activating Galphai/Galphaq-CK2 signaling in ischemic stroke. Exp Neurol. 2018;302:136–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.01.006.
Wu Y, Wang X, Zhou X, Cheng B, Li G, Bai B. Temporal expression of apelin/apelin receptor in ischemic stroke and its therapeutic potential. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00001.
Aminyavari S, Zahmatkesh M, Farahmandfar M, Khodagholi F, Dargahi L, Zarrindast MR. Protective role of apelin-13 on amyloid beta25-35-induced memory deficit; involvement of autophagy and apoptosis process. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019;89:322–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.10.005.
Chen D, Lee J, Gu X, Wei L, Yu SP. Intranasal delivery of apelin-13 is neuroprotective and promotes angiogenesis after ischemic stroke in mice. ASN Neuro. 2015;7(5). https://doi.org/10.1177/1759091415605114.
Yu M, Yuan HS, Li Q, Li Q, Teng YF. Combination of cells-based therapy with apelin-13 and hyperbaric oxygen efficiently promote neovascularization in ischemic animal model. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(6):2630–9. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201903_17413.
Huang C, Dai C, Gong K, Zuo H, Chu H. Apelin-13 protects neurovascular unit against ischemic injuries through the effects of vascular endothelial growth factor. Neuropeptides. 2016;60:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2016.08.006.
Fraga-Silva RA, Seeman H, Montecucco F, da Silva AR, Burger F, Costa-Fraga FP, et al. Apelin-13 treatment enhances the stability of atherosclerotic plaques. Eur J Clin Investig. 2018;48(3). https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.12891.
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Qiao S. Apelin: a potential marker of coronary artery stenosis and atherosclerotic plaque stability in ACS patients. Int Heart J. 2014;55(3):204–12.
Lago F, Dieguez C, Gomez-Reino J, Gualillo O. Adipokines as emerging mediators of immune response and inflammation. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007;3(12):716–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0674.
Xin Q, Cheng B, Pan Y, Liu H, Yang C, Chen J, et al. Neuroprotective effects of apelin-13 on experimental ischemic stroke through suppression of inflammation. Peptides. 2015;63:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2014.09.016.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the participants of the study and acknowledge the contribution from Jian Chai in statistical analysis.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81571158) and the Education Department of Henan Province (16A320054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Tian, X., Pei, Ll. et al. The Association Between Serum Apelin-13 and the Prognosis of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 11, 700–707 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-019-00769-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-019-00769-w