Abstract
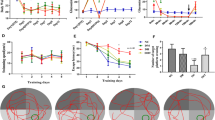
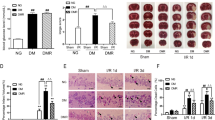
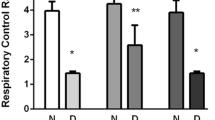
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of stroke and post-stroke mortality. Recurrent hypoglycemia (RH) is common among diabetes patients owing to glucose-lowering therapies. Earlier, we showed that RH in a rat model of insulin-dependent diabetes exacerbates cerebral ischemic damage. Impaired mitochondrial function has been implicated as a central player in the development of cerebral ischemic damage. Hypoglycemia is also known to affect mitochondrial functioning. The present study tested the hypothesis that prior exposure of insulin-treated diabetic (ITD) rats to RH exacerbates brain damage via enhanced post-ischemic mitochondrial dysfunction. In a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes, we evaluated post-ischemic mitochondrial function in RH-exposed ITD rats. Rats were exposed to five episodes of moderate hypoglycemia prior to the induction of cerebral ischemia. We also evaluated the impact of RH, both alone and in combination with cerebral ischemia, on cognitive function using the Barnes circular platform maze test. We observed that RH exposure to ITD rats leads to increased cerebral ischemic damage and decreased mitochondrial complex I activity. Exposure of ITD rats to RH impaired spatial learning and memory. Our results demonstrate that RH exposure to ITD rats potentially increases post-ischemic damage via enhanced post-ischemic mitochondrial dysfunction.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
cornus ammonis
- ETC:
-
electron transport chain
- ITD:
-
insulin-treated diabetic
- MMP:
-
mitochondrial membrane potential
- MPTP:
-
mitochondrial permeability transition pores
- RH:
-
recurrent hypoglycemia
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- STZ:
-
streptozotocin
- s.c.:
-
subcutaneous
- T1D:
-
type 1 diabetes
- T2D:
-
type 2 diabetes
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor α
References
Amador-Alvarado L, Montiel T, Massieu L. Differential production of reactive oxygen species in distinct brain regions of hypoglycemic mice. Metab Brain Dis. 2014;29:711–9.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2011. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(Suppl 1):S11–61.
Anderson MF, Sims NR. Mitochondrial respiratory function and cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem. 1999;73:1189–99.
Baregamian N, Song J, Bailey CE, Papaconstantinou J, Evers BM, Chung DH. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 control reactive oxygen species release, mitochondrial autophagy, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase/p38 phosphorylation during necrotizing enterocolitis. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2009;2:297–306.
Barone FC, Arvin B, White RF, Miller A, Webb CL, Willette RN, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke. 1997;28:1233–44.
Barrientos A, Moraes CT. Titrating the effects of mitochondrial complex I impairment in the cell physiology. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:16188–97.
Beckman, J., Libby, P., Creager, M., Diabetes mellitus, the metabolic syndrome, and atherosclerotic vascular disease, 2008.
Boland E, Monsod T, Delucia M, Brandt CA, Fernando S, Tamborlane WV. Limitations of conventional methods of self-monitoring of blood glucose: lessons learned from 3 days of continuous glucose sensing in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1858–62.
Borutaite V, Morkuniene R, Brown GC. Release of cytochrome c from heart mitochondria is induced by high Ca2+ and peroxynitrite and is responsible for Ca(2+)-induced inhibition of substrate oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1453:41–8.
Brainin M, Tuomilehto J, Heiss WD, Bornstein NM, Bath PM, Teuschl Y, et al. Post-stroke cognitive decline: an update and perspectives for clinical research. Eur J Neurol. 2015;22(229–238):e213–26.
Canevari L, Kuroda S, Bates TE, Clark JB, Siesjo BK. Activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain enzymes after transient focal ischemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:1166–9.
Cardoso S, Correia SC, Santos RX, Carvalho C, Candeias E, Duarte AI, et al. Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia and dementia: role of mitochondria and uncoupling proteins. Curr Mol Med. 2013;13:586–601.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention 2016 http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/statsreport14/national-diabetes-report-web.pdf (Retrieved on September 25th, 2016).
Chan PH. Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:2–14.
Chauvin C, De Oliveira F, Ronot X, Mousseau M, Leverve X, Fontaine E. Rotenone inhibits the mitochondrial permeability transition-induced cell death in U937 and KB cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41394–8.
Choi BY, Kim JH, Kim HJ, Yoo JH, Song HK, Sohn M, et al. Pyruvate administration reduces recurrent/moderate hypoglycemia-induced cortical neuron death in diabetic rats. PLoS One. 2013;8:e81523.
Cohan CH, Neumann JT, Dave KR, Alekseyenko A, Binkert M, Stransky K, et al. Effect of cardiac arrest on cognitive impairment and hippocampal plasticity in middle-aged rats. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124918.
Corda S, Laplace C, Vicaut E, Duranteau J. Rapid reactive oxygen species production by mitochondria in endothelial cells exposed to tumor necrosis factor-alpha is mediated by ceramide. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001;24:762–8.
Cryer PE. Hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001;281:E1115–21.
Cryer PE. Diverse causes of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2272–9.
Cuzzocrea S, Riley DP, Caputi AP, Salvemini D. Antioxidant therapy: a new pharmacological approach in shock, inflammation, and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:135–59.
Dave KR, Lange-Asschenfeldt C, Raval AP, Prado R, Busto R, Saul I, et al. Ischemic preconditioning ameliorates excitotoxicity by shifting glutamate/gamma-aminobutyric acid release and biosynthesis. J Neurosci Res. 2005;82:665–73.
Dave KR, Saul I, Busto R, Ginsberg MD, Sick TJ, Perez-Pinzon MA. Ischemic preconditioning preserves mitochondrial function after global cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:1401–10.
Dave KR, Tamariz J, Desai KM, Brand FJ, Liu A, Saul I, et al. Recurrent hypoglycemia exacerbates cerebral ischemic damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Stroke. 2011;42:1404–11.
Davis EA, Jones TW. Hypoglycemia in children with diabetes: incidence, counterregulation and cognitive dysfunction. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1998;11:177–82.
Davis SN, Fowler S, Costa F. Hypoglycemic counterregulatory responses differ between men and women with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2000a;49:65–72.
Davis SN, Shavers C, Costa F. Gender-related differences in counterregulatory responses to antecedent hypoglycemia in normal humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000b;85:2148–57.
DCCT Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–86.
Doll DN, Engler-Chiurazzi EB, Lewis SE, Hu H, Kerr AE, Ren X, et al. Lipopolysaccharide exacerbates infarct size and results in worsened post-stroke behavioral outcomes. Behav Brain Funct. 2015a;11:32.
Doll DN, Rellick SL, Barr TL, Ren X, Simpkins JW. Rapid mitochondrial dysfunction mediates TNF-alpha-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem. 2015b;132:443–51.
Donnelly LA, Morris AD, Frier BM, Ellis JD, Donnan PT, Durrant R, et al. Frequency and predictors of hypoglycaemia in type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a population-based study. Diabet Med. 2005;22:749–55.
EDIC group. Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC). Design, implementation, and preliminary results of a long-term follow-up of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Cohort. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:99–111.
Endres M, Wang ZQ, Namura S, Waeber C, Moskowitz MA. Ischemic brain injury is mediated by the activation of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:1143–51.
Feng ZC, Sick TJ, Rosenthal M. Oxygen sensitivity of mitochondrial redox status and evoked potential recovery early during reperfusion in post-ischemic rat brain. Resuscitation. 1998;37:33–41.
Fiskum G, Murphy AN, Beal MF. Mitochondria in neurodegeneration: acute ischemia and chronic neurodegenerative diseases. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:351–69.
Geddes J, Schopman JE, Zammitt NN, Frier BM. Prevalence of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2008;25:501–4.
Gehlaut RR, Dogbey GY, Schwartz FL, Marling CR, Shubrook JH. Hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes—more common than you think: a continuous glucose monitoring study. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2015;9:999–1005.
Giachin G, Bouverot R, Acajjaoui S, Pantalone S, Soler-Lopez M. Dynamics of human mitochondrial complex I assembly: implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 2016;3:43.
Goossens V, Grooten J, De Vos K, Fiers W. Direct evidence for tumor necrosis factor-induced mitochondrial reactive oxygen intermediates and their involvement in cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:8115–9.
Goossens V, Stange G, Moens K, Pipeleers D, Grooten J. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor-induced, mitochondria- and reactive oxygen species-dependent cell death by the electron flux through the electron transport chain complex I. Antioxid Redox Signal. 1999;1:285–95.
Guo C, Sun L, Chen X, Zhang D. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8:2003–14.
Harrison FE, Reiserer RS, Tomarken AJ, McDonald MP. Spatial and nonspatial escape strategies in the Barnes maze. Learn Mem. 2006;13:809–19.
Hattori K, Lee H, Hurn PD, Crain BJ, Traystman RJ, DeVries AC. Cognitive deficits after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke. 2000;31:1939–44.
Hershey T, Perantie DC, Warren SL, Zimmerman EC, Sadler M, White NH. Frequency and timing of severe hypoglycemia affects spatial memory in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2372–7.
Herzog RI, Chan O, Yu S, Dziura J, McNay EC, Sherwin RS. Effect of acute and recurrent hypoglycemia on changes in brain glycogen concentration. Endocrinology. 2008;149:1499–504.
Higuchi M, Proske RJ, Yeh ET. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I by TNF results in cytochrome c release, membrane permeability transition, and apoptosis. Oncogene. 1998;17:2515–24.
Hodges H, Nelson A, Virley D, Kershaw TR, Sinden JD. Cognitive deficits induced by global cerebral ischaemia: prospects for transplant therapy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1997;56:763–80.
Iijima T. Mitochondrial membrane potential and ischemic neuronal death. Neurosci Res. 2006;55:234–43.
Iijima T, Mishima T, Tohyama M, Akagawa K, Iwao Y. Mitochondrial membrane potential and intracellular ATP content after transient experimental ischemia in the cultured hippocampal neuron. Neurochem Int. 2003;43:263–9.
International Diabetes Federation, IDF diabetes atlas. 2015.
Isaev NK, Stelmashook EV, Dirnagl U, Plotnikov EY, Kuvshinova EA, Zorov DB. Mitochondrial free radical production induced by glucose deprivation in cerebellar granule neurons. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2008;73:149–55.
Isenberg JS, Klaunig JE. Role of the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition (MPT) in rotenone-induced apoptosis in liver cells. Toxicol Sci. 2000;53:340–51.
Janssen MM, Snoek FJ, de Jongh RT, Casteleijn S, Deville W, Heine RJ. Biological and behavioural determinants of the frequency of mild, biochemical hypoglycaemia in patients with type 1 diabetes on multiple insulin injection therapy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2000;16:157–63.
Jing L, Mai L, Zhang JZ, Wang JG, Chang Y, Dong JD, et al. Diabetes inhibits cerebral ischemia-induced astrocyte activation—an observation in the cingulate cortex. Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9:980–8.
Jing L, Wang JG, Zhang JZ, Cao CX, Chang Y, Dong JD, et al. Upregulation of ICAM-1 in diabetic rats after transient forebrain ischemia and reperfusion injury. J Inflamm (Lond). 2014;11:35.
Kauppinen RA, Nicholls DG. Synaptosomal bioenergetics. The role of glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation and responses to hypoglycaemia. Eur J Biochem. 1986;158:159–65.
Kiprianova I, Sandkuhler J, Schwab S, Hoyer S, Spranger M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor improves long-term potentiation and cognitive functions after transient forebrain ischemia in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1999;159:511–9.
Kissela B, Air E. Diabetes: impact on stroke risk and poststroke recovery. Semin Neurol. 2006;26:100–7.
Kowaltowski AJ, Vercesi AE, Fiskum G. Bcl-2 prevents mitochondrial permeability transition and cytochrome c release via maintenance of reduced pyridine nucleotides. Cell Death Differ. 2000;7:903–10.
Lee C, Sciamanna M, Peterson P. Intact rat brain mitochondria from a single animal: preparation and properties. Methods Toxicology. 1993;2:41–50.
Levine DA, Galecki AT, Langa KM, Unverzagt FW, Kabeto MU, Giordani B, et al. Trajectory of cognitive decline after incident stroke. JAMA. 2015;314:41–51.
Lincoln NB, Faleiro RM, Kelly C, Kirk BA, Jeffcoate WJ. Effect of long-term glycemic control on cognitive function. Diabetes Care. 1996;19:656–8.
Liu P, Yang X, Hei C, Meli Y, Niu J, Sun T, et al. Rapamycin reduced ischemic brain damage in diabetic animals is associated with suppressions of mTOR and ERK1/2 signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12:1032–40.
Liu Y, Rosenthal RE, Haywood Y, Miljkovic-Lolic M, Vanderhoek JY, Fiskum G. Normoxic ventilation after cardiac arrest reduces oxidation of brain lipids and improves neurological outcome. Stroke. 1998;29:1679–86.
McCrimmon RJ, Frier BM. Hypoglycaemia, the most feared complication of insulin therapy. Diabete Metab. 1994;20:503–12.
McGowan JE, Chen L, Gao D, Trush M, Wei C. Increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in newborn brain during hypoglycemia. Neurosci Lett. 2006;399:111–4.
McNally PG, Dean JD, Morris AD, Wilkinson PD, Compion G, Heller SR. Using continuous glucose monitoring to measure the frequency of low glucose values when using biphasic insulin aspart 30 compared with biphasic human insulin 30: a double-blind crossover study in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:1044–8.
McNay E. Recurrent hypoglycemia increases anxiety and amygdala norepinephrine release during subsequent hypoglycemia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015;6:175.
McNay EC, Sherwin RS. Effect of recurrent hypoglycemia on spatial cognition and cognitive metabolism in normal and diabetic rats. Diabetes. 2004;53:418–25.
McNay EC, Williamson A, McCrimmon RJ, Sherwin RS. Cognitive and neural hippocampal effects of long-term moderate recurrent hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 2006;55:1088–95.
McNeilly AD, Gallagher JR, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Hayes JD, Sharkey J, Ashford ML, et al. Nrf2-mediated neuroprotection against recurrent hypoglycemia is insufficient to prevent cognitive impairment in a rodent model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2016;65:3151–60.
Moro MA, Almeida A, Bolanos JP, Lizasoain I. Mitochondrial respiratory chain and free radical generation in stroke. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005;39:1291–304.
Moulaert VR, Verbunt JA, van Heugten CM, Wade DT. Cognitive impairments in survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a systematic review. Resuscitation. 2009;80:297–305.
Murakami K, Kondo T, Kawase M, Li Y, Sato S, Chen SF, et al. Mitochondrial susceptibility to oxidative stress exacerbates cerebral infarction that follows permanent focal cerebral ischemia in mutant mice with manganese superoxide dismutase deficiency. J Neurosci. 1998;18:205–13.
Myers KM, Fiskum G, Liu Y, Simmens SJ, Bredesen DE, Murphy AN. Bcl-2 protects neural cells from cyanide/aglycemia-induced lipid oxidation, mitochondrial injury, and loss of viability. J Neurochem. 1995;65:2432–40.
Nathan DM. The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: overview. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:9–16.
Nawashiro H, Tasaki K, Ruetzler CA, Hallenbeck JM. TNF-alpha pretreatment induces protective effects against focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:483–90.
Niatsetskaya ZV, Sosunov SA, Matsiukevich D, Utkina-Sosunova IV, Ratner VI, Starkov AA, et al. The oxygen free radicals originating from mitochondrial complex I contribute to oxidative brain injury following hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal mice. J Neurosci. 2012;32:3235–44.
Nicholls DG, Budd SL. Mitochondria and neuronal survival. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:315–60.
Okada M, Tamura A, Urae A, Nakagomi T, Kirino T, Mine K, et al. Long-term spatial cognitive impairment following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. A behavioral study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1995;15:505–12.
Ormstad H, Aass HC, Amthor KF, Lund-Sorensen N, Sandvik L. Serum cytokine and glucose levels as predictors of poststroke fatigue in acute ischemic stroke patients. J Neurol. 2011;258:670–6.
Pastorino JG, Simbula G, Yamamoto K, Glascott PA Jr, Rothman RJ, Farber JL. The cytotoxicity of tumor necrosis factor depends on induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:29792–8.
Patockova J, Marhol P, Tumova E, Krsiak M, Rokyta R, Stipek S, et al. Oxidative stress in the brain tissue of laboratory mice with acute post insulin hypoglycemia. Physiol Res. 2003;52:131–5.
Pedersen-Bjergaard U, Pramming S, Heller SR, Wallace TM, Rasmussen AK, Jorgensen HV, et al. Severe hypoglycaemia in 1076 adult patients with type 1 diabetes: influence of risk markers and selection. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2004;20:479–86.
Perez CA, Samudra N, Aiyagari V. Cognitive and functional consequence of cardiac arrest. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016;16:70.
Piantadosi CA, Zhang J. Mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species after brain ischemia in the rat. Stroke. 1996;27:327–31.
Prut L, Belzung C. The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;463:3–33.
Puente EC, Silverstein J, Bree AJ, Musikantow DR, Wozniak DF, Maloney S, et al. Recurrent moderate hypoglycemia ameliorates brain damage and cognitive dysfunction induced by severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 2010;59:1055–62.
Rath PC, Aggarwal BB. TNF-induced signaling in apoptosis. J Clin Immunol. 1999;19:350–64.
Rovet J, Alvarez M. Attentional functioning in children and adolescents with IDDM. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:803–10.
Schopman JE, Geddes J, Frier BM. Frequency of symptomatic and asymptomatic hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: effect of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia. Diabet Med. 2011;28:352–5.
Schulze-Osthoff K, Beyaert R, Vandevoorde V, Haegeman G, Fiers W. Depletion of the mitochondrial electron transport abrogates the cytotoxic and gene-inductive effects of TNF. EMBO J. 1993;12:3095–104.
Shafiee G, Mohajeri-Tehrani M, Pajouhi M, Larijani B. The importance of hypoglycemia in diabetic patients. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2012;11:17.
Shoji Y, Uedono Y, Ishikura H, Takeyama N, Tanaka T. DNA damage induced by tumour necrosis factor-alpha in L929 cells is mediated by mitochondrial oxygen radical formation. Immunology. 1995;84:543–8.
Shukla, V., Rehni, A., Dave, K., Dysregulated cytokine released by activated microglia in the hippocampus of diabetes associated recurrent hypoglycemic rat brain exacerbate ischemic damage, Society for Neuroscience, 45th Annual Meeting, Chicago. 2015. 499.419.
Sims NR, Anderson MF. Mitochondrial contributions to tissue damage in stroke. Neurochem Int. 2002;40:511–26.
Singh P, Jain A, Kaur G. Impact of hypoglycemia and diabetes on CNS: correlation of mitochondrial oxidative stress with DNA damage. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004;260:153–9.
Suh SW, Gum ET, Hamby AM, Chan PH, Swanson RA. Hypoglycemic neuronal death is triggered by glucose reperfusion and activation of neuronal NADPH oxidase. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:910–8.
Tamborlane WV, Beck RW, Bode BW, Buckingham B, Chase HP, Clemons R, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1464–76.
UK Hypoglycaemia Study Group. Risk of hypoglycaemia in types 1 and 2 diabetes: effects of treatment modalities and their duration. Diabetologia. 2007;50:1140–7.
Unachukwu C, Ofori S. Diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risk. the internet. J Endocrinol. 2012;7:1–10.
Weber KK, Lohmann T, Busch K, Donati-Hirsch I, Riel R. High frequency of unrecognized hypoglycaemias in patients with type 2 diabetes is discovered by continuous glucose monitoring. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2007;115:491–4.
Won SJ, Yoo BH, Kauppinen TM, Choi BY, Kim JH, Jang BG, et al. Recurrent/moderate hypoglycemia induces hippocampal dendritic injury, microglial activation, and cognitive impairment in diabetic rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:182.
Yamada KA, Rensing N, Izumi Y, De Erausquin GA, Gazit V, Dorsey DA, et al. Repetitive hypoglycemia in young rats impairs hippocampal long-term potentiation. Pediatr Res. 2004;55:372–9.
Yeoh E, Choudhary P, Nwokolo M, Ayis S, Amiel SA. Interventions that restore awareness of hypoglycemia in adults with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1592–609.
Ying W, Wei G, Wang D, Wang Q, Tang X, Shi J, et al. Intranasal administration with NAD+ profoundly decreases brain injury in a rat model of transient focal ischemia. Front Biosci. 2007;12:2728–34.
Zaidan E, Sims NR. Reduced activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex but not cytochrome c oxidase is associated with neuronal loss in the striatum following short-term forebrain ischemia. Brain Res. 1997;772:23–8.
Zoratti M, Szabo I. The mitochondrial permeability transition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1241:139–76.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Brant Watson for critical reading of this manuscript.
Funding
The present study is supported by NIH grant NS073779 and the Evelyn F. McKnight Brain Institute. The funding agency had no role in study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the National Institute of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by an institutional animal care and use committee.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 119 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, V., Fuchs, P., Liu, A. et al. Recurrent Hypoglycemia Exacerbates Cerebral Ischemic Damage in Diabetic Rats via Enhanced Post-Ischemic Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Transl. Stroke Res. 10, 78–90 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-018-0622-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-018-0622-2