Abstract
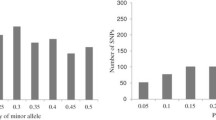
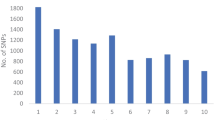
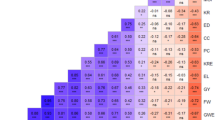
Knowledge about the genetic diversity within a germplasm allows for a more effective and efficient use of resources for crop improvement programs. Diversity assessment of 48 tropical drought-tolerant maize inbreds, 24 each from CIMMYT and IITA, was carried out with microsatellite markers to determine the genetic divergence between the two groups of maize inbred lines. Eighty-one polymorphic SSR markers were used for the assessment. Results showed that the average number of alleles per locus was 3.7. The mean polymorphic information content (PIC) was 0.51 whereas the average modified Roger’s genetic distance (MRD) was 0.49. The mean genetic distance estimates between the CIMMYT and IITA lines were higher than the mean genetic distance among IITA lines or among CIMMYT lines. The average linkage cluster analysis separated the lines into two broad groups along institutional lines. The observed sub-groups within each main group were reflections of the relationships of the lines based on pedigree records. The F ST value of 19.5% reflects a high level of genetic differentiation between the two groups of lines. The results highlighted the presence of appreciable genetic divergence between CIMMYT and IITA lines that can be exploited for superior hybrid maize development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebayo MA. 2012. Genetic analyses of drought tolerance in crosses of adapted and exotic maize (Zea mays L.) inbred lines. Ph. D. thesis. West Africa Centre for Crop Improvement, University of Ghana, Legon
Adebayo MA, Menkir A, Blay E, Gracen V, Danquah E, Hearne S. 2014. Genetic analysis of drought tolerance in adapted x exotic crosses of maize inbred lines under managed stress conditions. Euphytica 196: 261–270
Adetimirin VO, Vroh-Bi I, The C, Menkir A, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S. 2008. Diversity analysis of elite maize inbred lines IITA to West and Central Africa using SSR markers. Maydica 53: 143–149
Aguiar CG, Schuster I, Amaral Junior AT, Scapim CA, Vieira ESN. 2008. Heterotic groups in tropical maize by test crosses and simple sequence repeat markers. Genet Mol. Res. 7: 1233–1244
Barata C, Carena MJ. 2006. Classification of North Dakota maize inbred lines into heterotic groups based on molecular and testcross data. Euphytica 151: 339–349
Betran FJ, Ribaut JM, Beck D, Gonzalez de LD. 2003. Genetic diversity, specific combining ability, and heterosis In tropical maize under stress and non-stress environments. Crop Sci. 43: 797–806
Dellaporta SL, Wood J. Hicks JB. 1983. A plant DNA minipreparation: Version II. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1: 19–21
Dhliwayo T, Pixley K, Menkir A, Warburton M. 2009. Combining ability, genetic distances, and heterosis among elite CIMMYT and IITA tropical maize inbred lines. Crop Sci. 49: 1201–1210
Enoki H, Sato H, Koinuma K. 2002. SSR analysis of genetic diversity among maize inbred lines adapted to cold regions of Japan. Theor. Appl. Genet. 104: 1270–1277
Excoffer L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM. 1992. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131: 479–491
Goodman MM, Stuber CW. 1983. Races of maize: VI. Isozyme variation among races of maize in Bolivia. Maydica 28: 169–187
Guei RG, Wassom CE. 1996. Genetic analysis of tassel size and leaf senescence and their relationships with yield in two tropical lowland maize populations. Afr. Crop Sci. J. 4: 275–281
Hallauer AR, Carena MJ, Miranda-Filho JB. 2010. Quantitative Genetics in Maize Breeding. 3rd ed. Handbook of Plant Breeding vol. 6. Springer, NewYork, pp 383–423
Legesse BM, Myburg AA, Pixley K, Botha AM. 2007. Genetic diversity of African maize inbred lines revealed by SSR markers. Hereditas 144: 10–17
Liu K, Goodman M, Muse S, Smith JS, Buckler E, Doebley J. 2003. Genetic structure and diversity among maize inbred lines as inferred from DNA microsatellites. Genetics 165: 2117–2128
Lu H, Bernardo R. 2001. Molecular marker diversity among current and historical maize inbreds. Theor. Appl. Genet. 103: 613–617
Lu Y, Yan J, Guimara˜es CT, Taba S, Hao Z et al. 2009. Molecular characterization of global maize breeding germplasm based on genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms. Theor. Appl. Genet. 120: 93–115
Matsuoka Y, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Goodman M, Doebley J. 2002. Microsatellites in Zea-variability, patterns of mutations, and use for evolutionary studies. Theor. Appl. Genet. 104: 436–450
Melchinger AE, Gumber RK. 1998. Overview of heterosis and heterotic groups in agronomic crops. In: KR Lambey, JE Staub, eds, Concepts and Breeding of Heterosis in Crop Plants, CSSA, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 29–44
Menkir A, Melake-Berhan A, The C, Ingelbrecht I, Adepoju A. 2004. Grouping of tropical mid-altitude maize inbred lines on the basis of yield data and molecular markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 108: 1582–1590
Mir RR, Zaman-Allah M, Sreenivasulvu N, Trethowan R, Varshney RK. 2012. Intregrated genomics, physiology, and breeding approaches for improving drought tolerance in crops. Theor. Appl. Genet. 125: 625–645
Pejic I, Ajmone-Marsn P, Morgante M, Kozuumplick V, Castiglioni P, Taramino G, Motto M. 1998. Comparative analysis of genetic similarity among maize inbred lines detected by RFLPs, RAPDs, SSRs, and AFLPs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97: 1248–1255
Reif JC, Melchinger AE, Xia XC, Warburton ML, Hoisington DA, Vasal SK, Beck D, Bohn M, Frisch M. 2003. Use of SSRs for establishing heterotic groups in subtropical maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 107: 947–957
Rohlf FJ. 1998. NTSYS-PC. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2. 0. Exeter Software, Setauket, NY
Semagn K, Magorokosho C, Vivek BS, Makumbi D, Beyene Y, Mugo S, Prasanna BM, Warburton ML. 2012. Molecular characterization of diverse CIMMYT maize inbred lines from eastern and southern Africa using single nucleotide polymorphic marker. BMC Genomics 13: 113 doi 10. 1186/1471-2164-13-113
Senior ML, Murphy JP, Goodman MM, Stuber CW. 1998. Utility of SSRs for determining genetic similarities and relationships in maize using an agarose gel system. Crop Sci. 38: 1088–1098
Senior ML, Heun M. 1993. Mapping maize microsatellites and polymerase chain reaction confirmation of the targeted repeats using a CTprimer. Genome 36: 884–889
Smith JSC, Chin ECL, Shu H, Smith OS, Wall SJ, Senior ML, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Ziegle J. 1997. An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L.): Comparisons with data from RFLPs and pedigree. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95: 163–173
Taramino G, Tingey S. 1996. Simple sequence repeats for germplasm analysis and mapping in maize. Genome 39: 277–287
Tivang JG, Nienhuis J, Smith OS. 1994. Estimation of sampling variance of molecular marker data using the bootstrap procedure. Theor. Appl. Genet. 89: 259–264.
Vaz Patto MC, Satovic Z, Pego S, Fevereiro P. 2004. Assessing the genetic diversity of Porguese maize germplasm using microsatellite markers. Euphytica 137: 63–72
Wang D, Shi J, Carlson SR, Cregan PB, Ward RW, Diers BW. 2003. A low-cost, high-throughput polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis system for genotyping with microsatellite DNA markers. Crop Sci. 43: 1828–1832
Warburton ML, Ianchun XX, Crossa J, Franco J, Melchinger AE, Frisch M, Bohn M, Hoisington D. 2002. Genetic characterization of CIMMYT inbred lines and open-pollinated populations using large-scale fingerprinting methods. Crop Sci. 42: 1822–1840
Wen W, Araus JL, Shah T, Cairns J, Mahuku G, Banziger M, Torres JL, Sanchez C, Yan J. 2011. Molecular characterization of a diverse maize inbred line collection and its potential utilization for stress tolerance improvement. Crop Sci. 51: 2569–2581
Xia XC, Reif JC, Melchinger AE, Frisch M, Hoisington DA, Beck D, Pixley K, Warburton ML. 2005. Genetic diversity among CIMMYT maize inbred lines investigated with SSR markers: II. subtropical, tropical midaltitude, and highland maize inbred lines and their relationships with elite U. S. and European maize. Crop Sci. 45: 2573–2582
Xia XC, Reif JC, Hoisington DA, Melchinger AE, Frisch M, Warburton ML. 2004. Genetic diversity among CIMMYT maize inbred lines investigated with SSR markers:I. lowland tropical maize. Crop Sci. 44: 2230–2237
Xiao YN, Li XH, George ML, Li MS, Zhang SH, Zheng YL. 2005. Quantitative trait locus analysis of drought tolerance and yield in maize in China. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 23: 155–165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adebayo, M.A., Menkir, A., Gedil, M. et al. Diversity assessment of drought tolerant exotic and adapted maize (Zea mays L.) inbred lines with microsatellite markers. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 18, 147–154 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-014-0076-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-014-0076-3