Abstract
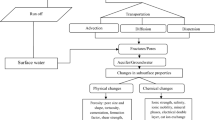
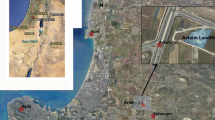
Coal washing operation is now being carried out in the Alborz-Sharghi plant, located in northeast of Iran. This can in effect create a number of environmental problems. In this research, different geophysical surveys were conducted to investigate the leachate flow pathways and time-dependent transportation of contaminants in downstream of the plant which is situated between a coal waste pile and tailings impoundments. The very low frequency survey identified the most likely contamination zones and flow pathways. Furthermore, two-dimensional resistivity models obtained by the inversion of geoelectrical data (measured with the use of a dipole–dipole array incorporating a time-laps technique) showed the contaminated plumes with low resistivity values (<1 Ω m). To carry out a time-laps technique, 2-D geoelectrical surveys were repeated at same profiles by a time interval of 6 months. The results distinguished a time-dependent movement of the plume in a lateral and longitudinal form as well as its further extension to the deeper layers towards the groundwater table. This was also verified by the results obtained by the induced polarization measurements.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackil A, Koldas S (2006) Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. J Clean Prod 14:1139–1145
Al-Tarazi E, El-Naqa A, El-Waheidi M, Abu Rajab J (2006) Electrical geophysical and hydrogeological investigations of groundwater aquifers in Ruseifa municipal landfill, Jordan. Environ Geol 50:1095–1103. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0283-4
Amirkhani Shiraz F, Doulati Ardejani F, Moradzadeh A, Arab-Amiri AR (2013) Investigating the source of contaminated plumes downstream of the Alborz Sharghi coal washing plant using EM34 conductivity data, VLF-EM and DC-resistivity geophysical methods. Explor Geophys 44(1):16–24
Aristodemou E, Thomas-Betts A (2000) DC resistivity and induced polarization investigations at a waste disposal site and its environments. J Appl Geophys 44:275–302
Atekwana EA, Sauck WA, Werkema DD Jr (2000) Investigations of geoelectrical signatures at a hydrocarbon contaminated site. J Appl Geophys 44:167–180
Benson AK, Payne KL, Stubben MA (1997) Mapping groundwater contamination using dc resistivity and VLF geophysical methods—a case study. Geophysics 62(1):80–86
Bernstone C, Dahlin T, Ohlsson T, Hogland W (2000) DC-resistivity mapping of internal landfill structures: two pre-excavation surveys. Environ Geol 39:360–370
Buselli G, Lu K (2001) Groundwater contamination monitoring with multichannel electrical and electromagnetic methods. J Appl Geophys 48:11–23
Carlson NR, Mayerle CM, Zonge KL (1999) Extremely fast IP used to delineate buried landfills. In: Proceedings of the 5th meeting of the environmental and engineering geophysical society European section, Budapest, Hungary
Carpenter PJ, Kaufman RS, Price B (1990) Use of resistivity soundings to determine landfill structure. Ground Water 28:569–575
Cheng W, Zhang Q, Yang R, Tian Y (2014) Occurrence modes and cleaning potential of sulfur and some trace elements in a high-sulfur coal from Pu’an coalfield, SW Guizhou, China. Environ Earth Sci 72(1):35–46. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2934-6
DeVos KJ, Pehme P, Greenhouse JP (1997) Ground geophysical surveys for mine wastes. In: Gubbins AG (ed) Proceedings of exploration ‘97, fourth decennial international conference on mineral exploration, 917-26. Toronto: Prospectors and Developers Association of Canada
Doulati Ardejani F, Jodieri Shokri B, Moradzadeh A, Soleimani E, Ansari Jafari MA (2008) Combined mathematical-geophysical model for prediction of pyrite oxidation and pollutant leaching associated with a coal washing waste dump. Int J Environ Sci Technol 5(4):517–526
Doulati Ardejani F, Jodieri Shokri B, Bagheri M, Soleimani E (2010) Investigation of pyrite oxidation and acid mine drainage characterization associated with Razi active coal mine and coal washing waste dumps in the Azad Shahr–Ramian region, northeast Iran. Environ Earth Sci 61:1547–1560
Doulati Ardejani F, Jodieri Shokri B, Moradzadeh A, Shafaei SZ, Kakaei R (2011) Geochemical characterisation of pyrite oxidation and environmental problems related to release and transport of metals from a coal washing low grade waste dump, Shahrood, northeast Iran. Environ Monit Assess 183:41–55
Ebraheem MW, Bayless ER, Krothe NC (1990) A study of acid mine drainage using earth resistivity measurements. Ground Water 28:361–368
Ellia RG, Oldenburg W (1994) Applied geophysical inversion. Geophys J Int 119:5–11
Fahringer P (2002) Shallow EM investigations of AMD at an abandoned coal mine in northern west Virginia, the Leding Edge, 478- 481
Farooq M, Park S, Kim JH, Song YS, Sabir MA, Umar M, Tariq M, Muhammad S (2014) Time-lapse electrical resistivity investigations for imaging the grouting injection in shallow subsurface cavities. Sci World J. Article ID 178203. doi:10.1155/2014/178203
Gómez E, Parviainen A, Hokkanen T, Ruskeeniemi KL (2010) Integrated geophysical and geochemical study on AMD generation at the Haveri Au–Cu mine tailings, SW Finland. Environ Earth Sci 61:1435–1447
Grellier S, Guerin R, Robain H, Bobachev A, Vermeersch F, Tabbagh A (2008) Monitoring of leachate recirculation in a bioreactor landfill by 2-D electrical resistivity imaging. J Environ Eng Geophy 13(4):351–359
Jaynes DB, Rogowski AS, Pionke HB (1984) Acid mine drainage from reclaimed coal strip mines, 1, model description. Water Resour Res 20(2):233–242
Jodeiri Shokri B, Ramazi H, Doulati Ardejani F, Moradzadeh A (2014a) Integrated time-lapse geoelectrical–geochemical investigation at a reactive coal washing waste Pile in Northeastern Iran. Mine Water Environ 33:256–265
Jodeiri Shokri B, Ramazi H, Doulati Ardejani F, Moradzadeh A (2014b) A statistical model to relate pyrite oxidation and oxygen transport within a coal waste pile: case study, Alborz Sharghi, northeast of Iran. Environ Earth Sci 71:4693–4702
Jodeiri Shokri B, Ramazi H, Doulati Ardejani F, Sadeghiamirshahidi M (2014c) Prediction of pyrite oxidation in a coal washing waste pile applying artificial neural networks (ANNs) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems (ANFIS). Mine Water Environ 33:146–156
Karlik G, Kaya MA (2001) Investigation of groundwater contamination using electric and electromagnetic methods at an open waste-disposal site: a case study from Isparta, Turkey. Environ Geol 40:725–731
Kaya MA, Ozurlan G, Sengul E (2007) Delineation of soil and groundwater contamination using geophysical methods at an open waste-disposal site in Canakkale, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 135:441–446
Kim JY, Chon HT (2001) Pollution of a water course impacted by acid mine drainage in the Imgok creek of the Gangreung coal field, Korea. Appl Geochem 16:1387–1396
Li Y, Oldenburg DW (1992) Approximate inverse mappings in DC resistivity problems. Geophys J Int 109:343–362
Loke MH (2001) Constrained time‐lapse resistivity imaging inversion. In: Symposium on the application of geophysics to engineering and environmental problems, pp EEM7–EEM7. doi:10.4133/1.2922877
Merkel RH (1972) The use of resistivity techniques to delineate acid mine drainage in ground water. Ground Water 10:38–42
Mondelli G, Giacheti HL, Boscov MEG, Elis VR, Hamada J (2007) Geoenvironmental site investigation using different techniques in a municipal solid waste disposal site in Brazil. Environ Geol 52(5):871–887
Moradzadeh A, Zare M, Doulati Ardejani F (2012) Recognition of the pollution zone related to acid mine drainage using three dimensional modelling of geoelectrical data at Alborz-e-Sharghi coal washing plant area, Semnan Province, Iran. Iran Geophys J 6(2):95–111
Moreau S, Bouye JM, Barina G, Oberty O (2003) Electrical resistivity survey to investigate the influence of leachate recirculation in a MSW landfill. In: 9th international waste management and landfill symposium, Calgliari, Italy
Morris JWF, Vasuki NC, Baker JA, Pendleton CH (2003) Findings from long-term monitoring studies at MSW landfill facilities with leachate recirculation. Waste Manag 23(7):653–666
Olofsson B, Jernberg H, Rosenqvist A (2006) Tracing leachates at waste sites using geophysical and geochemical modelling. Environ Geol 49(5):720–732
Poisson J, Chouteau M, Aubertin M, Campos D (2009) Geophysical experiments to image the shallow internal structure and the moisture distribution of a mine waste rock pile. J Appl Geophys 67:179–192
RAMAG Instruction manual, Ver. 2.2. (2002) VLF survey planning and interpretation software. Encinitas, California
RES2DINV Manual, Ver. 3.5. (2002) Rapid 2D resistivity and ip inversion. Geotomo software
Rogowski AS, Pionke HB, Broyan JG (1977) Modelling the impact of strip mining and reclamation processes on quality and quantity of water in mined areas: a review. J Environ Qual 6(3):237–244
Rucker DF, Glaser DR, Osborne T, Maehl WC (2009) Electrical resistivity characterization of a reclaimed gold mine to delineate acid rock drainage pathways. Mine Water Environ 28:146–157
Sadeghiamirshahidi MH, Eslam Kish T, Doulati Ardejani F (2012) Application of image processing for modeling pyrite oxidation in a coal washing waste pile. Environ Model Assess. doi:10.1007/s10666-012-9350-2
Sadeghiamirshahidi MH, Eslam Kish T, Doulati Ardejani F (2013) Application of artificial neural networks to predict pyrite oxidation in a coal washing refuse pile. Fuel 104:163–169
Santos FA, Mateus A, Figueiras J, Gonçalves MA (2006) Mapping ground water contamination around a landfill facility using the VLF-EM method—a case study. J Appl Geophys 60:115–125
Selim ESI, Abdel-Raouf O (2013) The use of magnetic and geo-electrical data to delineate the subsurface structures and groundwater potentiality in Southeastern Sinai, Egypt. Environ Earth Sci 70(4):1479–1494
Singer PC, Stumm W (1970) Acidic mine drainage: the rate determining, step. Science 167:1121–1123
Soupios P, Manios T, Sarris A, Vallianatos F, Maniadakis K, Papadopoulos N, Makris JP, Kouli M, Gidarakos, E., Saltas, V., Kourgialas, N (2005a) Integrated environmental investigation of a municipal landfill using modern techniques. In: Paper presented at the international workshop in geoenvironment and geotechnics, 12–14 September 2005, Milos Island, Greece, 75–82
Soupios P, Vallianatos F, Papadopoulos I, Makris JP, Marinakis M (2005b) Surface-geophysical investigation of a landfill in Chania, Crete. In: Paper presented at the international workshop in geoenvironment and geotechnics, 12–14 September 2005, Milos Island, Greece, 149–156
Yuval D, Oldenburg W (1996) DC resistivity and IP methods in acid mine drainage problems: results from the Copper Cliff mine tailings impoundments. J Appl Geophys 34:187–198
Zhao F, Cong Zh, Sun H, Ren D (2007) The geochemistry of rare earth elements (REE) in acid mine drainage from the Sitai coal mine, Shanxi Province, North China. Int J Coal Geol 70:184–192
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the technical and financial supports made by Shahrood University of Technology. The authors are also grateful to Alborz-Sharghi Coal Company for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jodeiri Shokri, B., Doulati Ardejani, F. & Moradzadeh, A. Mapping the flow pathways and contaminants transportation around a coal washing plant using the VLF-EM, Geo-electrical and IP techniques—A case study, NE Iran. Environ Earth Sci 75, 62 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4776-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4776-x