Abstract
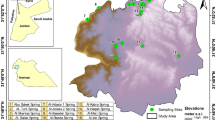
A yearly survey in a piezometric network was realized in the Litorale Romano Natural Reserve (Rome, Central Italy), collecting water table and chemo-physical data. Monthly chemo-physical surveys highlighted a groundwater salinization variability in a coastal unconfined aquifer. The aquifer is mostly composed by aeolian sands of a still preserved dune ridge environment, on which a pine forest develops. The groundwater salinity variability resulted is connected to the wind pattern and rainfalls. In fact, wind speed higher than 4 m/s is responsible for generating sea salt aerosols (SSA) from sea surface. A statistical analysis was performed for wind with a speed higher than 4 m/s, to detect wind orientation. The dry deposition of SSA on the tree foliage appeared correlated to the westerly winds, blowing in the springtime. When the rainy season occurs, the SSA is washed out from the trees and it is directed to groundwater, where an enhancement of the Electrical Conductivity (EC) values is noticed. Whenever rain events occur and winds are not westerly, a dilution of groundwater salinity takes place and consequently a reduction of EC. Chemical analyzes were realized as well. They confirmed that groundwater of piezometers located close to the coast line is enriched of SSA elements.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MA, Samie SGA, Badawy HA (2013) Factors controlling mechanisms of groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in the Quaternary aquifer of the Eastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ Earth Sci 68(2):369–394. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1744-6
Amenduni G (1884) Sulle opere di bonificazione della plaga litoranea dell’Agro Romano che comprende le paludi e gli stagni di Ostia, Porto, Maccarese e delle terre vallive di Stracciacappa, Baccano, Pantano e Lago dei Tartari. Relazione del progetto generale 15 Jul 1880, Ministero Lavori Pubblici
Antonellini M, Mollema P, Giambastiani B, Bishop K, Caruso L, Minchio A, Pellegrini L, Sabia M, Ulazzi E, Gabbianelli G (2008) Salt water intrusion in the coastal aquifer of the southern Po Plain, Italy. Hydrogeol J 16(8):1541–1556. doi:10.1007/s10040-008-0319-9
Bellotti P, Tortora P, Valeri P (1989) La piana deltizia del Tevere: analisi di facies ed ipotesi evolutiva dall'ultimo low stand glaciale all'attuale. Giornale di Geologia 51(1):71–91
Bellotti P, Calderoni G, Carboni MG, Di Bella L, Tortora P, Valeri P, Zernitskaya V (2007) Late Quaternary landscape evolution of the Tiber River delta plain (Central Italy): new evidence from pollen data, biostratigraphy and C-14 dating. Zeitschrift Fur Geomorphol 51(4):505–534. doi:10.1127/0372-8854/2007/0051-0505
Capelli G, Salvati R (2003) Studi per la riforestazione della Pineta di Castelfusano. Comune di Roma, Dipartimento X-Politiche Ambientali e Agricole & Università di Roma Tre, Dipartimento di Scienze Geologiche
Capelli G, Mazza R, Gazzetti C (2005) Strumenti e strategie per la tutel e l’uso compatibile della risorsa idrica nel Lazio, vol 78. Quaderni di Tecniche di Protezione Ambientale, Bologna
Capelli G, Mazza R, Papiccio C (2007) Saline intrusion in the Tiber Delta Geology, hydrology and hydrogeology of the coastal plain of the roman sector. Giornale di Geologia Appl 5:13–28
Capelli G, Mastrorillo L, Mazza R, Petitta M, Baldoni T, Banzato F, Cascone D, Di Salvo C, La Vigna F, Taviani S, Teoli P (2012) Carta Idrogeologica del Territorio della Regione Lazio. Scala 1:100.000 (4 Fogli). S.EL.CA., Firenze
Civano A, Morini M, Sodi R (2004) Caratteristiche del vento all’aeroporto di Genova in base all’analisi dei dati anemometrici raccolti su due punti. ENAV
Cruz JV, Coutinho R, Pacheco D, Cymbron R, Antunes P, Freire P, Mendes S (2011) Groundwater salinization in the Azores archipelago (Portugal). Environ Earth Sci 62(6):1273–1285. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0615-2
Di Salvo C, Di Luzio E, Mancini M, Moscatelli M, Capelli G, Cavinato GP, Mazza R (2012) GIS-based hydrostratigraphic modeling of the city of Rome (Italy): analysis of the geometric relationships between a buried aquifer in the Tiber Valley and the confining hydrostratigraphic complexes. Hydrogeol J 20(8):1549–1567. doi:10.1007/s10040-012-0899-2
Drabbe J, Badon Ghyben W (1889) Nota in verband met de voorgenomen puboring nabij Amsterdam. Amsterdam
Edmunds WM (2001) Paleowater in European coastal aquifers—the goals and main conclusions of the PALAEAUX project. In: Edmunds WM, Milne CJ (eds) Paleowaters in Coastal Europe, vol 189., Geological Society Special PublicationThe Geological Society, Bath, pp 1–16
Erickson DJ, Duce RA (1988) On the global flux of the armospheric sea salt. J Geophys Res Oceans 93(C11):14079–14088. doi:10.1029/JC093iC11p14079
ESRI (2008) ArcGIS—a complete integrated system. http://www.esri.com/software/arcgis. Accessed June 2012
Fuentes E, Coe H, Green D, de Leeuw G, McFiggans G (2010) Laboratory-generated primary marine aerosol via bubble-bursting and atomization. Atmos Meas Tech 3(1):141–162. doi:10.5194/amt-3-141-2010
Gong SL, Barrie LA, Lazare M (2002) Canadian aerosol module (CAM): a size-segregated simulation of atmospheric aerosol processes for climate and air quality models-2. Global sea-salt aerosol and its budgets. J Geophys Res Atmos 107(D24):AAC 13-1. doi:10.1029/2001jd002004
Gustafsson MER, Franzen LG (2000) Inland transport of marine aerosols in southern Sweden. Atmos Environ 34(2):313–325. doi:10.1016/s1352-2310(99)00198-3
Hasselrot B, Grennfelt P (1987) Deposition of air-pollutants in a wind-exposed forest edge. Water Air Soil Pollut 34(2):135–143. doi:10.1007/bf00184756
Herzberg B (1901) Die wasserversorgundeinigerNordseebâder. J Gasbeleuchtung Und Wasserversorgung 44(815–819):824–844
Kelly D (2005) Seawater intrusion topic paper, vol 6. WRIA, Island County
La Vigna F, Ciadamidaro S, Mazza R, Mancini L (2010) Water quality and relationship between superficial and ground water in Rome (Aniene River basin, central Italy). Environ Earth Sci 60(6):1267–1279. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0267-2
La Vigna F, Demiray Z, Mazza R (2013) Exploring the use of alternative groundwater models to understand hydrogeological flow processes in an alluvial context (Tiber River, Rome, Italy). Environ Earth Sci 71(3):1–7. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2515-8
Lewis ER, Schwartz S (2004) Sea salt aerosols production; mechanism, methods. Measurement and Models, Washington DC, USA
Manca F, Capelli G, La Vigna F, Mazza R, Pascarella A (2014a) Wind-induced salt-wedge intrusion in the Tiber river mouth (Rome–Central Italy). Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-3024-5
Manca F, Capelli G, La Vigna F, Mazza R (2014b) Pascarella A (2014) Salt-wedge intrusion in river mouths: assessment of the wind effect. Paper presented at Flowpath Congress. National Meeting on Hydrogeology, Viterbo, pp 18–20
Martensson EM, Nilsson ED, de Leeuw G, Cohen LH, Hansson HC (2003) Laboratory simulations and parameterization of the primary marine aerosol production. J Geophys Res Atmos 108(D9):AAC15. doi:10.1029/2002jd002263
Mikhailova MV, Bellotti P, Valeri P, Tortora P (1999) Intrusion of seawater into the River Part of the Tiber Mouth. Water Resour 26(6):679–686
Milli S, D’Ambrogi C, Bellotti P, Calderoni G, Carboni MG, Celant A, Di Bella L, Di Rita F, Frezza V, Magri D, Pichezzi RM, Ricci V (2013) The transition from wave-dominated estuary to wave-dominated delta: the Late Quaternary stratigraphic architecture of Tiber River deltaic succession (Italy). Sed Geol 284:159–180. doi:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.12.003
Moller D (1990) The Na/Cl ratio in rainwater and the seasalt chloride cycle. Tellus 42B:254–262. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0889.1990.t01-1-00004.x
O’Dowd CD, De Leeuw G (2007) Marine aerosol production: a review of the current knowledge. Philosophical transactions of the royal society. Math Phys Eng Sci 365(1856):1753–1774. doi:10.1098/rsta.2007.2043
Panno SV, Hackley KC, Hwang HH, Greenberg SE, Kaprac IG, Landsberger S (2006) O’Kelly DJ (2006) Characterization and identification of Na-Cl sources in ground water (vol 44, pg 176. Ground Water 44(2):129. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.2006.00200.x
Reinap A, Wiman BLB, Svenningsson BLUG, Gunnarsson S (2012) Forest-edge effects on sea-salt aerosol deposition: a wind-tunnel study using living oak leaves. Boreal Environ Res 17(3–4):193–209
Schofield R, Thomas DSG, Kirkby MJ (2001) Causal processes of soil salinization in Tunisia, Spain and Hungary. Land Degrad Dev 12:163–181. doi:10.1002/ldr.446
Smedema LK, Shiati K (2002) Irrigation and salinity: a perspecive review of the salinity hazards of irrigation development in the arid zone. Irrigat Drain Syst 16:161–174
Tho N, Merckx R, Ut VN (2014) Impacts of saline water irrigation and shrimp pond discharges on the surrounding waters of a coastal district in the Mekong delta of Vietnam. Environ Earth Sci 71(5):2015–2027. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2603-9
Toth G, Adhikari K, Varallyay GY, Toth T, Bodis K, Stolbovoy V (2008) Updated map of salt affected soils in the european union. In: Tóth G, MaER L (eds) Threats to soil quality in Europe. European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Environment and Sustainability Luxemburg, pp 65–78. doi:10.2788/8647
Tuccimei P, Salvati R, Delitala MC, Capelli G, Amorini E, Cutini A, Manetti MC (2003) Studi sulle relazioni tra assetto idro-geochimico e copertura forestale nella pineta costiera di Castelfusano (Roma). Paper presented at the FIST, Geoitalia, Bellaria, pp 16–18 Settembre 2003
Tuccimei P, D’Angelantonio M, Manetti MC, Cutini A, Amorini E, Capelli G (2010) The chemistry of precipitation and groundwater in a coastal Pinus Pinea forest (Castel Fusano area, Central Italy) and its relation to stand and canopy structure. In: Szigethy BVaJ (ed) Horizons in Earth Science Research, vol 4. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., pp 1–17
UNESCO (1991) Guidelines on the study of seawater intrusion into rivers. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Paris
Ward J, Werner AD, Howe B (2009) Saltwater intrusion in Southern Eyre Peninsula. Eyre Peninsula Groundwater, Allocation and Planning Project
Wunderground (2012) Dati anemometrici della stazione della Lega Navale di Ostia relativi al periodo maggio 2011-maggio 2012. http://www.wunderground.com/cgi-bin/findweather/getForecast?query=41.71937561,12.30211830&sp=IROMELID3
Wunderground (2012) Dati anemometrici della stazione di Fiumicino relativi al periodo maggio 2011-maggio 2012. http://www.wunderground.com/cgi-bin/findweather/getForecast?query=zmw:00000.1.16242
Wunderground (2012) Piogge relative al pluviometro di Ostia nel periodo 1/05/2011-31/05/2012. http://www.wunderground.com/weatherstation/WXDailyHistory.asp?ID=IROMELID3&day=23&month=07&year=2013
Yu J, Li Y, Han G, Zhou D, Fu Y, Guan B, Wang G, Ning K, Wu H, Wang J (2013) The spatial distribution characteristics of soil salinity in coastal zone of the Yellow River Delta. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2980-0
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Environmental and Civil Protection Dept. of ROMA CAPITALE (Municipality of Rome). This department was led before by Romano Maria Delli Santi and after by Tommaso Profeta. Emanuele Ruta and Barbara Zaccaria offered an important contribution during the hydrogeological surveys. Moreover, the authors want to thank the referees a lot for their precious comments and suggestion to improve the manuscript. Finally, special thanks to Duccio Patanè for the illuminating suggestions provided throughout the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manca, F., Capelli, G. & Tuccimei, P. Sea salt aerosol groundwater salinization in the Litorale Romano Natural Reserve (Rome, Central Italy). Environ Earth Sci 73, 4179–4190 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3704-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3704-9