Abstract
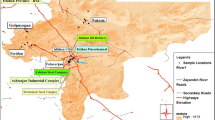
Heavy metal pollution in vegetable-growing soils is of increasing concern due to the potential health risk via food chain. The present study aimed at assessing the potential ecological risk (RI) of heavy metals (HMs) in the vegetable-growing soils collected from Fujian Province, China, and identifying the potential sources with multivariable methods including correlation matrix and principal component analysis (PCA). The concentrations of HMs including Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr, As, Cu, Zn, and Ni in 160 soils collected from 25 sites of vegetable-growing land in Fujian Province, China, are measured with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and hydrogen generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometer, respectively. Results show that most of the soil samples have been seriously contaminated with HMs, especially the metals of Hg, Cd, and Pb, compared with both of the background values of soils in Fujian Province and the limitation of total HMs in soil environmental quality for edible agricultural products set in China (HJ 332-2006). The indexes of RI indicate that only 8% of the 25 sites are environmentally safe, whereas according to the present study 28% of the sampling sites are heavily contaminated with HMs with 628–1,076 of the RI values. Based on PCA analysis, Zn, Cd, and Pb associated with PC1 are found to derive from anthropogenic sources, especially the local industrial activities, such as porcelain plants in Dehua, zinc metallurgical plants in Nan’an, and sewage irrigation from industrial estate in Taijiang. The concentrations of As, Ni, and Cu loaded in PC2 are found to be mainly controlled by natural factors (i.e., the lithogenic process of natural parent soils). Hg in PC3 is also found to originate from the anthropogenic sources, such as local coal combustion in Longhai and industrial activities in Cangshan. However, Cr in PC3 is mainly derived from the lithogenic sources.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander PD, Alloway BJ, Dourado AM (2006) Genotypic variations in the accumulation of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn exhibited by six commonly grown vegetables. Environ Pollut 144(3):736–745
Castellano M, Ruiz-Filippi G, González W, Roca E, Lema JM (2007) Selection of variables using factorial discriminant analysis for the state identification of an anaerobic UASB–UAF hybrid pilot plant, fed with winery effluents. Water Sci Technol 56(2):139–145
Chen M, Ma LQ, Harris WG (1999) Baseline concentrations of 15 trace elements in Florida surface soils. J Environ Qual 28:1173–1181
Chojnacka K, Chojnacki A, Górecka H, Górecki H (2005) Bioavailability of heavy metals from polluted soils to plants. Sci Total Environ 337(1–3):175–182
De Meeûs C, Eduljee GH, Hutton M (2002) Assessment and management of risks arising from exposure to cadmium in fertilizer. Sci Total Environ 291(1–3):167–187
Deng PY, Shu WS, Lan CY, Liu W (2008) Metal contamination in the sediment, pondweed, and snails of a stream receiving effluent from a lead/zinc mine in southern China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81(1):69–74
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114(3):313–324
Finster ME, Gray KA, Binns HJ (2004) Lead levels of edibles grown in contaminated residential soils: a field survey. Sci Total Environ 320(2–3):245–257
Franco-Uría A, López-Mateo C, Roca E, Fernández-Marcos ML (2009) Source identification of heavy metals in pastureland by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. J Hazard Mater 165(1–3):1008–1015
Gimeno-García E, Andreu V, Boluda R (1996) Heavy metals incidence in the application of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides to rice farming soils. Environ Pollut 92(1):19–25
Gupta UC, Gupta SC (1998) Trace element toxicity relationships to crop production and livestock and human health: implication for management. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 29(11–14):1491–1522
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
Huang SS, Liao QL, Hua M, Wu XM, Bi KS, Yan CY, Chen B, Zhang XY (2007) Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong district, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 67(11):2148–2155
Jinadasa KBPN, Milham PJ, Hawkins CA, Cornish PS, Williams PA, Kaldor CJ, Conroy JP (1997) Survey of Cadmium levels in vegetables and soils of Greater Sydney, Australia. J Environ Qual 26:924–933
Karim RA, Hossain SM, Miah MMH, Nehar K, Mubin MSH (2008) Arsenic and heavy metal concentrations in surface soils and vegetables of Feni district in Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 145(1–3):417–425
Kirkham MB (2006) Cadmium in plants on polluted soils: Effects of soil factors, hyperaccumulation, and amendments. Geoderma 137(1–2):19–32
Li J, Xie ZM, Xu JM, Sun YF (2006a) Risk assessment for safety of soils and vegetables around a lead/zinc mine. Environ Geochem Health 28(1–2):37–44
Li JT, Qiu JW, Wang XW, Zhong Y, Lan CY, Shu WS (2006b) Cadmium contamination in orchard soils and fruit trees and its potential health risk in Guangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 143(1):159–165
Li JH, Lu Y, Yin W, Gan HH, Zhang C, Deng XL, Lian J (2009) Distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soils near a petrochemical complex in Guangzhou, China. Environ Monit Assess 153(1–4):365–375
Luo W, Lu YL, Giesy JP, Wang TY, Shi YJ, Wang G, Xing Y (2007) Effects of land use on concentrations of metals in surface soils and ecological risk around Guanting Reservoir, China. Environ Geochem Health 29(6):459–471
Manta DS, Angelone M, Bellanca A, Neri R, Sprovieri M (2002) Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci Total Environ 300(1–3):229–243
McBride MB (2003) Toxic metals in sewage sludge-amended soils: has promotion of beneficial use discounted the risks? Adv Environ Res 8:5–19
Micó C, Recatalá L, Peris M, Sánchez J (2006) Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 65(5):863–872
Navas A, Machín J (2002) Spatial distribution of heavy metals and arsenic in soils of Aragón (northest Spain): Controlling factors and environmental implications. Appl Geochem 17(8):961–973
Nziguheba G, Smolders E (2008) Inputs of trace elements in agricultural soils via phosphate fertilizers in European countries. Sci Total Environ 390(1):53–57
Peris M, Recatalá L, Micó C, Sánchez R, Sánchez J (2008) Increasing the knowledge of heavy metal contents and sources in Agricultural Soils of the European Mediterranean Region. Water Air Soil Pollut 192(1–4):25–37
Qiu XX, Huang DF, Cai SX, Chen F, Ren ZG, Cai YC (2000) Investigation on Fuzhou vegetable pollution and pollutant sources and its control. Chin J Agric Sci 15(1):16–21
Sun YF, Xie ZM, Li J, Xu JM, Chen ZL, Naidu R (2006) Assessment of toxicity of heavy metal contaminated soils by the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure. Environ Geochem Health 28(1–2):73–78
Svendsen ML, Steinnes E, Blom HA (2007) Vertical and horizontal distributions of Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu, and Hg in uncultivated soil in the vicinity of a zinc smelter at Odda, Norway. Soil Sediment Contam 16:585–603
Upadhyay AK, Gupta KK, Sircar JK, Deb MK, Mundhara GL (2006) Heavy metals in freshly deposited sediments of the river Subernarekha, India: an example of lithogenic and anthropogenic effects. Environ Geol 50(3):397–403
Wang HY, Stuanes AO (2003) Heavy metal pollution in air-water-soil-plant system of Zhuzhou City, Hunan Province, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 147(1–4):79–107
Wang XS, Qin Y, Sang SX (2005) Accumulation and sources of heavy metals in urban topsoils: A case study from the city of Xuzhou, China. Environ Geol 48(1):101–107
Wang G, Su MY, Chen YH, Lin FF, Luo D, Gao SF (2006) Transfer characteristics of cadmium and lead from soil to the edible parts of six vegetable species in southeastern China. Environ Pollut 144(1):127–135
Wei WX (2007) On the influence of heavy metals in the soil of major vegetable bases in Fuzhou City. Chin J Geol Fujian 26(2):100–107
Yan S, Ling QC, Bao ZY (2007) Metals contamination in soils and vegetables in metal smelter contaminated sites in Huangshi, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79(4):361–366
Zhou J, Ma DS, Pan JY, Nie WM, Wu K (2008) Application of multivariate statistical approach to identify heavy metal sources in sediment and waters: a case study in Yangzhong, China. Environ Geol 54(2):373–380
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40771185), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (2009J01034), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Fujian Province, China (2007Y0028), the Foundation of the Key Laboratory of Urban Environment and Health, Institute of Urban Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences (KLUEH201006), and the Foundation for Innovative Research Team of Jimei University (2010A007) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Huang, Z., Chen, T. et al. Evaluation of ecological risk and source of heavy metals in vegetable-growing soils in Fujian province, China. Environ Earth Sci 65, 29–37 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1062-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1062-4