Abstract
Introduction
Orthognathic surgery involves making several osteotomies. Any osteotomies leads to varying degrees of post-operative swelling. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of anti-edema drugs for the control of edema, using Digitizer 3D™ for measuring soft-tissue thickness, in patients who underwent bimaxillaryorthognathic surgery.
Materials and Methods
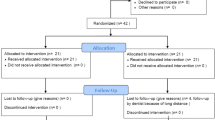
In this double-blinded, randomized, control trial, 24 patients (study group: 12 patients, control group: 12 patients) in whom bimaxillary orthognathic surgery was indicated, were included in this study. All swelling measurements were expressed as total 3-D area of the landmarks (cm2) in T0 pre-operative, T1 first day after surgery, T2 fourth day after surgery, T3 4 months after surgery. For each patient we compared, by adding left and right area, the increase of swelling between T1–T0, T2–T0 and T1–T3.
Results
The differences T0–T1 are highly significant (p < 0.01) between group 1 or study group (treated with Venoplant®) and group 2 (control group); the differences T0–T2 are significant (p < 0.05) between group 1 (treated with Venoplant®) and group 2 (control group). The differences T1–T3 are significant (p < 0.05) between group 1 (treated with Venoplant®) and group 2 (control group).
Discussion
The present study suggests that Venoplant® significantly decreases postoperative edema in orthognathic surgery, thus precluding long-term corticosteroid use.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheginia S, Dhariwal DK (2012) Review of evidence for the use of steroids in orthognathic surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 50:97
Sahni D, Singh SG, Jit I et al (2008) Facial soft tissue thickness in Northwest Indian adults. Forensic Sci Int 179:137
Suazo GIC, Cantın LM, Zavando MDA et al (2008) Comparisons in soft-tissue thicknesses on the human face in fresh and embalmed corpses using needle puncture method. Int J Morphol 26:165
Kim DK, Ruprecht A, Wang G et al (2005) Accuracy of facial soft tissue thickness measurements in personal computer-based multiplanar reconstructed computed tomography images. Forensic Sci Int 155:28
George RM (1987) The lateral craniographic method of facial reconstruction. J Forensic Sci 32:1305
Phillips VM, Smuts NA (1996) Facial reconstruction: utilization of computerized tomography to measure facial tissue thickness in a mixed racial population. Forensic Sci Int 83:51
El-Mehallawi IH, Soliman EM (2011) Ultrasonic assessment of facial soft tissue thicknesses in adult Egyptians. Forensic SciInt 117:99
Lam EW, Hannam AG, Wood WW et al (1989) Imaging orofacial tissues by magnetic resonance. Oral Surg Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 68:2
FourieZ Damstra J, Gerrits PO et al (2010) Accuracy and reliability of facial soft tissue depth measurements using cone beam computer tomography. Forensic Sci Int 199:9
Williams WB, Abukawa H, Shuster V et al (2003) A comparison of postoperative edema after intraoral vs. endoscopic mandibular ramus osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61(8 suppl.): 61a
Shetty W, Mohan A (2013) A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial comparing the efficacy of systemic enzyme therapy for edema control in orthognathic surgery using ultrasound scan to measure facial swelling. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 71:1261–1267
Weber CR, Griffin JM (1994) Evaluation of dexamethasone for reducing postoperative oedema and inflammatory response after orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 52:35
Nusair YM (2007) Local application of ice bags did not affect postoperative facial swelling after oral surgery in rabbits. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45:48
Harrison JA, Nixon MA, Fright WR, Snape L (2004) Use of hand-held laser scanning in the assessment of facial swelling: a preliminary study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:8
Llewelyn J, Ryan M, Santosh C (1996) The use of magnetic resonance imaging to assess swelling after the removal of third molar teeth. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34:419
Conflict of interest
All authors disclose any financial and personal relationships with other people or organisations that could inappropriately influence their work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tozzi, U., Santillo, V., Tartaro, G.P. et al. A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial Comparing the Efficacy of Anti-edema Drugs for Edema Control in Orthognathic Surgery Using Digitizer 3-D to Measure Facial Swelling. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 14, 386–392 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-014-0685-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-014-0685-x