Abstract
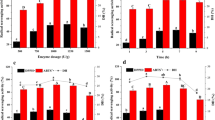
This study investigated the antioxidant potential and enzymatic inhibitory power of shrimp by-product protein hydrolysates (hyd) prepared using two purified serine alkaline proteases namely; alkaline protease from Anoxybacillus kamchatkensis strain M1V (SAPA) and alkaline protease from Aeribacillus pallidus strain VP3 (SPVP). The characterization of their molecular weights showed the presence of peptides less than 15 kDa. SAPA-hyd displayed the highest reducing power activity. Likewise, SAPA-hyd was found to be active against angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE), tyrosinase (Tyr), and amylase (Amy) enzymes with IC50 values of 10.01, 6.13, and 4.11 µg/mL, respectively. SPVP-hyd revealed the highest radical scavenging power, β-carotene protection, and ferrous chelating activity with EC50 values of 11.79, 3.69, and 0.61 µg/mL, respectively. After fraction nation, all fractions displayed a high inhibitory potential against ACE. Only fractions F2 and F3 from SAPA-hyd showed the highest anti-tyrosinase activity with IC50 values of 25.10 and 12.5 ng/mL, respectively. These results suggest that a simple, clean, economic, and controllable bioprocess for the utilization of shrimp by-product was investigated. This study gives an unprecedented report on the anti-Tyr activity of the protein hydrolysate from fish bio-waste. Additionally, two peptide hydrolysates with multifunctional biological activities were elaborated from Metapenaeus monoceros by two bacterial purified proteases.
Graphic Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
FAO I.: WFP (2015) The state of food insecurity in the world 2015. In: Proceedings of the meeting the 2015 international hunger targets: Taking stock of uneven progress. Rome, FAO.
Sila, A., Nasri, M., Bougatef, A.: Isolation and characterisation of carotenoproteins from deep-water pink shrimp processing waste. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 51, 953–959 (2012)
Mao, X., Guo, N., Sun, J., Xue, C.: Comprehensive utilization of shrimp waste based on biotechnological methods: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 143, 814–823 (2017)
Yuan, G., Li, W., Pan, Y., Wang, C., Chen, H.: Shrimp shell wastes: Optimization of peptide hydrolysis and peptide inhibition of α-amylase. Food Biosci. 25, 52–60 (2018)
Ambigaipalan, P., Shahidi, F.: Bioactive peptides from shrimp shell processing discards: antioxidant and biological activities. J. Funct. Foods 34, 7–17 (2017)
Hamdi, M., Hammami, A., Hajji, S., Jridi, M., Nasri, M., Nasri, R.: Chitin extraction from blue crab (Portunus segnis) and shrimp (Penaeus kerathurus) shells using digestive alkaline proteases from P.segnis viscera. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 101, 455–463 (2017)
Tu, M., Liu, H., Zhang, R., Chen, H., Fan, F., Shi, P., Xu, X., Lu, W., Du, M.: Bioactive hydrolysates from casein: generation, identification, and in silico toxicity and allergenicity prediction of peptides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 98, 3416–3426 (2018)
Tu, M., Cheng, S., Lu, W., Du, M.: Advancement and prospects of bioinformatics analysis for studying bioactive peptides from food-derived protein: Sequence, structure, and functions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 105, 7–17 (2018)
Tu, M., Liu, H., Zhang, R., Chen, H., Mao, F., Cheng, S., Lu, W., Du, M.: Analysis and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanism of a novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from casein hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66, 4139–4144 (2018)
Tu, M., Wang, C., Chen, C., Zhang, R., Liu, H., Lu, W., Jiang, L., Du, M.: Identification of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from casein and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanisms. Food Chem. 256, 98–104 (2018)
Kim, S.S., Ahn, C.B., Moon, S.W., Je, J.Y.: Purification and antioxidant activities of peptides from sea squirt (Halocynthia roretzi) protein hydrolysates using pepsin hydrolysis. Food Biosci. 25, 128–133 (2018)
Sarteshnizi, R.A., Sahari, M.A., Gavlighi, H.A., Regenstein, J.M., Nikoo, M.: Antioxidant activity of sind sardine hydrolysates with pistachio green hull (PGH) extracts. Food Biosci. 27, 37–45 (2019)
Je, J.Y., Qian, Z.J., Lee, S.H., Byun, H.G., Kim, S.K.: Purification and antioxidant properties of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) dark muscle peptide on free radical-mediated oxidative systems. J. Med. Food 11, 629–637 (2008)
Abdelhedi, O., Nasri, R., Mora, L., Jridi, M., Toldrá, F., Nasri, M.: In silico analysis and molecular docking study of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from smooth-hound viscera protein hydrolysates fractionated by ultrafiltration. Food Chem. 239, 453–463 (2018)
Bougatef, A., Nedjar Arroume, N., Ravallec Plé, R., Leroy, Y., Guillochon, D., Barkia, A., Nasri, M.: Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products protein hydrolysates obtained by treatment with microbial and visceral fish serine proteases. Food Chem. 111, 350–356 (2008)
Gammoh, S., Alu’datt, M.H., Alhamad, M.N., Rababah, T., Al Mahasneh, M., Qasaimeh, A., Johargy, A., Kubow, S., Hussein, N.M.: The effects of protein-phenolic interactions in wheat protein fractions on allergenicity, antioxidant activity and the inhibitory activity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE). Food Biosci. 24, 50–55 (2018)
Jiang, S., Zhao, Y., Shen, Q., Zhu, X., Dong, S., Liu, Z., Wu, H., Zeng, M.: Modification of ACE-inhibitory peptides from Acaudina molpadioidea using the plastein reaction and examination of its mechanism. Food Biosci. 26, 1–7 (2018)
Solanki, D., Hati, S.: Considering the potential of Lactobacillus rhamnosus for producing Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides in fermented camel milk (Indian breed). Food Biosci. 23, 16–22 (2018)
Mechri, S., Berrouina, M.B., Omrane Benmrad, M., Zaraî Jaouadi, N., Rekik, H., Moujehed, E., Chebbi, A., Sayadi, S., Chamkha, M., Bejar, S., Jaouadi, B.: Characterization of a novel protease from Aeribacillus pallidus strain VP3 with potential biotechnological interest. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 94, 221–232 (2017)
Mechri, S., Bouacem, K., Zaraî Jaouadi, N., Rekik, H., Berrouina, M.B., Omrane Benmrad, M., Hacene, H., Bejar, S., Bouanane-Darenfed, A., Jaouadi, B.: Identification of a novel protease from the thermophilic Anoxybacillus kamchatkensis M1V and its application as laundry detergent additive. Extremophiles 23, 687–706 (2019)
Bradford, M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976)
Folch, J., Lees, M., Sloane Stanley, G.: A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1957)
Dubois, J.: Influence of certain recent modifications in the sugar-cane culture on the evolution of populations of Yanga-guttulata-Sign (French). Tananarive : IRAM, (Document IRAM, n. 63). Agron. Trop. (Paris) 21 (6/7) , 786–821 , MAP . Jun/Jul 66. https://agritrop.cirad.fr/368512/. (1966).
Kembhavi, A.A., Buttle, D.J., Knight, C.G., Barrett, A.J.: The two cysteine endopeptidases of legume seeds: purification and characterization by use of specific fluorometric assays. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 303, 208–213 (1993)
Adler-Nissen, J.: Enzymic hydrolysis of food proteins. Elsevier Applied Science publishers, New York (1986)
Schägger, H.: Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Nat Protoc 1, 16–22 (2006)
Re, R., Pellegrini, N., Proteggente, A., Pannala, A., Yang, M., Rice Evans, C.: Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Bio. Med. 26, 1231–1237 (1999)
Pratt, D.E.: Natural antioxidants of soybeans and other oil-seeds. In: Simic, M.G., Karel, M. (eds.) Autoxidation in food and biological systems, pp. 283–293. Springer, Boston (1980)
Dinis, L.T., Oliveira, M.M., Almeida, J., Costa, R., Gomes Laranjo, J., Peixoto, F.: Antioxidant activities of chestnut nut of Castanea sativa Mill. (cultivar ‘Judia’) as function of origin ecosystem. Food Chem. 132, 1–8 (2012)
Oyaizu, M.: Antioxidative activities of browning products of glucosamine fractionated by organic solvent and thin-layer chromatography. Shok. Ko. Gakk. 35, 771–775 (1988)
Jeong, S.M., Xiao, C., Finley, L.W., Lahusen, T., Souza, A.L., Pierce, K., Li, Y.H., Wang, X., Laurent, G., German, N.J.: SIRT4 has tumor-suppressive activity and regulates the cellular metabolic response to DNA damage by inhibiting mitochondrial glutamine metabolism. Cancer Cell 23, 450–463 (2013)
Cushman, D., Cheung, H.: Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem. Pharmacol. 20, 1637–1648 (1971)
Rangkadilok, N., Sitthimonchai, S., Worasuttayangkurn, L., Mahidol, C., Ruchirawat, M., Satayavivad, J.: Evaluation of free radical scavenging and antityrosinase activities of standardized longan fruit extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 45, 328–336 (2007)
Sahnoun, M., Saibi, W., Brini, F., Bejar, S.: Apigenin isolated from A. americana encodes Human and Aspergillus oryzae S2 α-amylase inhibitions: Credible approach for antifungal and antidiabetic therapies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 55, 1–10 (2018)
Synowiecki, J., Al Khateeb, N.A.A.Q.: The recovery of protein hydrolysate during enzymatic isolation of chitin from shrimp Crangon crangon processing discards. Food Chem. 68, 147–152 (2000)
Klomklao, S., Kishimura, H., Benjakul, S.: Use of viscera extract from hybrid catfish (Clarias macrocephalus × Clarias gariepinus) for the production of protein hydrolysate from toothed ponyfish (Gazza minuta) muscle. Food Chem. 136, 1006–1012 (2013)
Abdelhedi, O., Jridi, M., Jemil, I., Mora, L., Toldrá, F., Aristoy, M.C., Boualga, A., Nasri, M., Nasri, R.: Combined biocatalytic conversion of smooth hound viscera: Protein hydrolysates elaboration and assessment of their antioxidant, anti-ACE and antibacterial activities. Food Res. Int. 86, 9–23 (2016)
Karoud, W., Sila, A., Krichen, F., Martinez Alvarez, O., Bougatef, A.: Characterization, surface properties and biological activities of protein hydrolysates obtained from hake (Merluccius merluccius) heads. Waste Biomass Valor. 10, 287–297 (2019)
Bougatef, H., Krichen, F., Kobbi, S., Martinez-Alvarez, O., Nedjar, N., Bougatef, A., Sila, A.: Physicochemical and biological properties of eel by-products protein hydrolysates: potential application to meat product preservation. Waste Biomass Valor. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0424-5
Kobbi, S., Bougatef, A., Balti, R., Mickael, C., Fertin, B., Chaabouni, S., Dhulster, P., Nedjar, N.: Purification and recovery of RuBisCO protein from alfalfa green juice: antioxidative properties of generated protein hydrolysate. Waste Biomass Valor. 8, 493–504 (2017)
Choksawangkarn, W., Phiphattananukoon, S., Jaresitthikunchai, J., Roytrakul, S.: Antioxidative peptides from fish sauce by-product: Isolation and characterization. Agric. Nat. Resour. 52, 460–466 (2018)
Yu, H.C., Hsu, J.L., Chang, C.I., Tan, F.J.: Antioxidant properties of porcine liver proteins hydrolyzed using Monascus purpureus. Food Sci. Biotech. 26, 1217–1225 (2017)
da Silva, V.G., de Castro, R.J.S.: Enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins from chicken viscera in the presence of an ionic liquid enhanced their antioxidant properties. Waste Biomass Valor. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00693-y
Sila, A., Bougatef, A.: Antioxidant peptides from marine by-products: Isolation, identification and application in food systems a Review. J. Funct. Foods. 21, 10–26 (2016)
Khaled, H.B., Ktari, N., Ghorbel-Bellaaj, O., Jridi, M., Lassoued, I., Nasri, M.: Composition, functional properties and in vitro antioxidant activity of protein hydrolysates prepared from sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) muscle. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 622–633 (2014)
Jemil, I., Mora, L., Nasri, R., Abdelhedi, O., Aristoy, M.C., Hajji, M., Nasri, M., Toldrá, F.: A peptidomic approach for the identification of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptides in sardinelle protein hydrolysates fermented by Bacillus subtilis A26 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens An6. Food Res. Int. 89, 347–358 (2016)
Ghorbel-Bellaaj, O., Jellouli, K., Maalej, H.: Shrimp processing by-products protein hydrolysates: evaluation of antioxidant activity and application in biomass and proteases production. Biocatal. Biotransform. 35, 287–297 (2017)
Lu, X., Zhang, L., Sun, Q., Song, G., Huang, J.: Extraction, identification and structure-activity relationship of antioxidant peptides from sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) protein hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 116, 707–716 (2018)
Lee, S.J., Kim, K.H., Kim, Y.S., Kim, E.K., Hwang, J.W., Lim, B.O., Moon, S.H., Jeon, B.T., Jeon, Y.J., Ahn, C.B., Park, P.J.: Biological activity from the gelatin hydrolysates of duck skin by-products. Process Biochem. 47, 1150–1154 (2012)
Ashooriha, M., Khoshneviszadeh, M., Khoshneviszadeh, M., Moradi, S.E., Rafiei, A., Kardan, M., Emami, S.: 1,2,3-Triazole-based kojic acid analogs as potent tyrosinase inhibitors: design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorganic Chem. 82, 414–422 (2019)
Arise, R.O., Yekeen, A., Ekun, O.: In vitro antioxidant and α-amylase inhibitory properties of watermelon seed protein hydrolysates. Environ. Exp. Biol. 14, 163–172 (2016)
Schurink, M., van Berkel, W.J., Wichers, H.J., Boeriu, C.G.: Novel peptides with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Peptides 28, 485–495 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mrs. M. Mezghani Abid and Mr. A. Hadj Brahim (LMBEE-CBS) and Mr. I. Hssairi, Mr. A. Zitoun, and Mr. F. Boukhili (UVRR-CBS) for their technical assistance. The authors would also like to express their gratitude to Mr. K. Walha, and Mrs. N. Masmoudi (Analysis Unit-CBS) for their technical assistance. Special thanks are also due to Dr. Z. Bouallagui (LBPE-CBS) and to Pr. W. Hariz from the English Department at the Sfax Faculty of Science, University of Sfax (Sfax, Tunisia) for constructive proofreading and language polishing services.
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Tunisia, under the Contract Program 2015–2019: Grant No. LMBEE_CBS/code: LR15CBS06 and the Tunisian-Algerian project JAOUADI/BADIS_TNDZ-MicrooZymes_2012-2018/code: TA/04/2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mechri, S., Sellem, I., Bouacem, K. et al. Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Metapenaeus monoceros By-Product Hydrolysates Elaborated by Purified Alkaline Proteases. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 6741–6755 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-00942-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-00942-5