Abstract
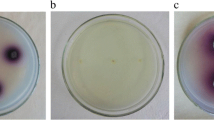
Recently, bacterial laccases has drawn researchers’ interest due to their ability to overcome high pH and salt concentration conditions compared to fungal laccases. Here we report a novel micro-aerobic cultivation strategy for enhancing CotA laccase expression and study its application for dye decolorization. Micro-aerobic cultivation of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) strain carrying pT7-FLAG-MAT-TAG-1-CotA had significantly enhanced CotA laccase activity up to 13903 U/L. The most unique findings of this investigation are that micro-aerobic cultivation strategy enhanced the reactive oxygen species production which consequently led to the over expression of CotA laccase gene. Malachite green, Crystal violet, Congo red and Bromophenol blue were efficiently decolorized by using purified CotA laccase without presence of any mediators at pH 6 and 9. These results provide a great platform for the dynamic production and application of bacterial laccase in industry.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brander, S., Mikkelsen, J.D., Kepp, K.P.: Characterization of an akali- and halide-resistant laccase expressed in E. coli: CotA from Bacillus clausii. PLoS ONE 9, e99402 (2014)
Sharma, P., Goel, R., Capalash, N.: Bacterial laccases. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 23, 823–832 (2007)
Dwivedi, U.N., Singh, P., Pandey, V.P., Kumar, A.: Structure–function relationship among bacterial, fungal and plant laccases: review. J. Mol. Catal. B 68, 117–128 (2011)
Lončar, N., Božić, N., Lopez-Santin, J., Vujčić, Z.: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens laccase—from soil bacteria to recombinant enzyme for wastewater decolorization. Bioresour. Technol. 147, 177–183 (2013)
Guan, Z.B., Shui, Y., Song, C.M., Zhang, N., Cai, Y.J., Liao, X.R.: Efficient secretory production of CotA-laccase and its application in the decolorization and detoxification of industrial textile wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22, 9515–9523 (2015)
Koschorreck, K., Richter, S.M., Ene, A.B., Roduner, E., Schmid, R.D., Urlacher, V.B.: Cloning and characterization of a new laccase from Bacillus licheniformis catalyzing dimerization of phenolic acids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 79, 217–224 (2008)
Dubé, E., Shareck, F., Hurtubise, Y., Daneault, C., Beauregard, M.: Homologous cloning, expression, and characterization of a laccase from Streptomyces coelicolor and enzymatic decolourisation of an indigo dye. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 79, 597–603 (2008)
Lu, L., Wang, T.N., Xu, T.F., Wang, J.Y., Wang, C.L., Zhao, M.: Cloning and expression of thermo-alkali-stable laccase of Bacillus licheniformis in Pichia pastoris and its characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 134, 81–86 (2013)
Mohorčič, M., Benčina, M., Friedrich, J., Jerala, R.: Expression of soluble versatile peroxidase of Bjerkandera adusta in Escherichia coli. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 851–858 (2009)
Ihssen, J., Reiss, R., Luchsinger, R., Thöny-Meyer, L., Richter, M.: Biochemical properties and yields of diverse bacterial laccase-like multicopper oxidases expressed in Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. (2015). doi:10.1038/srep10465
Santhanam, N., Vivanco, J.M., Decker, S.R., Reardon, K.F.: Expression of industrially relevant laccases: prokaryotic style. Trends Biotechnol. 29, 480–489 (2011)
Durão, P., Chen, Z., Fernandes, A.T., Hildebrandt, P., Murgida, D.H., Todorovic, S., Pereira, M.M., Melo, E.P., Martins, L.O.: Copper incorporation into recombinant CotA laccase from Bacillus subtilis: characterization of fully copper loaded enzymes. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 13, 183–193 (2008)
Salmon, K.A., Hung, S.P., Steffen, N.R., Krupp, R., Baldi, P., Hatfield, G.W., Gunsalus, R.P.: Global gene expression profiling in Escherichia coli K12: effects of oxygen availability and ArcA. J. Biol. Chem. 280(15), 15084–15096 (2005)
Constantinidou, C., Hobman, J.L., Griffiths, L., Patel, M.D., Penn, C.W., Cole, J.A., Overton, T.W.: A reassessment of the FNR regulon and transcriptomic analysis of the effects of nitrate, nitrite, NarXL, and NarQP as Escherichia coli K12 adapts from aerobic to anaerobic growth. J. Biol. Chem. 281(8), 4802–4815 (2006)
Partridge, J.D., Sanguinetti, G., Dibden, D.P., Roberts, R.E., Poole, R.K., Green, J.: Transition of Escherichia coli from aerobic to micro-aerobic conditions involves fast and slow reacting regulatory components. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 11230–11237 (2007)
Bradford, M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976)
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970)
Wilson, C.M.: Staining of proteins on gels: comparison of dyes and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 91, 236–247 (1983)
Livak, K.J., Schmittgen, T.D.: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods 25, 402–408 (2001)
Nygren, P.A., Stefan, S., Uhlén, M.: Engineering proteins to facilitate bioprocessing. Trends Biotechnol. 12, 184–188 (1994)
Bentley, W.E., Davis, R.H., Kompala, D.S.: Dynamics of induced cat expression in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 38, 749–760 (1991)
Duan, K.J., Lin, M.T., Hung, Y.C., Lin, C.T., Chen, C.W., Sheu, D.C.: Production of GST-SOD fusion protein by recombinant E coli XL1 Blue. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 75, 722–728 (2000)
Brissos, V., Pereira, L., Munteanu, F.D., Paulo, A.C., Lígia O., Martins, L.O.: Expression system of CotA-laccase for directed evolution and high-throughput screenings for the oxidation of high-redox potential dyes. Biotechnol. J. 4, 558–563 (2009)
Wang, C., Cui, D., Lei Lu, L., Zhang, N., Yang, H., Zhao, M., Dai, S.: Cloning and characterization of CotA laccase from Bacillus subtilis WD23 decoloring dyes. Ann. Microbiol. 66, 461–467 (2016)
Hu, J.H., Wang, F., Liu, C.Z.: Development of an efficient process intensification strategy for enhancing Pfu DNA olymerase production in recombinant Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 38, 651–659 (2015)
Lecina, M., Sarró, E., Casablancas, A., Godia, F., Cairo, J.J.: IPTG limitation avoids metabolic burden and acetic acid accumulation in induced fed-batch cultures of Escherichia coli M15 under glucose limiting conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 70, 78–83 (2013)
Imlay, J.A.: The molecular mechanisms and physiological consequences of oxidative stress: lessons from a model bacterium. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 11(7), 443–454 (2013)
Imlay, J.A.: Diagnosing oxidative stress in bacteria: not as easy as you might think. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 24,124–131(2015)
Lucana, D.O.O., Wedderhoff, I., Groves, M.R.: ROS-mediated signalling in bacteria: zinc-containing Cys-X-X-Cys redox centres and iron-based oxidative stress. J. Signal Transduct. (2012). doi:10.1155/2012/605905
Dalton, T.P., Shertzer, H.G., Alvaro Puga, A.: Regulation of gene expression by reactive oxygen. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 39, 67–101 (1999)
Kimura, T., Nishioka, H.: Intracellular generation of superoxide by copper sulphate in Escherichia coli. Mutat. Res. 389, 237–242 (1997)
Artsatbanov, V., Vostroknutova, G., Shleeva, M., Goncharenko, A., Zinin, A., Ostrovsky, D., Kapreliants, A.: Influence of oxidative and nitrosative stress on accumulation of diphosphate intermediates of the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in corynebacteria and mycobacteria. Biochemistry 77, 362–371 (2012)
Moldes, M.D., Sanromán, A.: Amelioration of the ability to decolorize dyes by laccase: relationship between redox mediators and laccase isoenzymes in Trametes versicolor. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 22, 1197–1204 (2006)
Chairin, T., Nitheranont, T., Watanabe, A., Asada, Y., Khanongnuch, C., Lumyong, S.: Biodegradation of bisphenol a and decolorization of synthetic dyes by laccase from white-rot fungus, Trametes polyzona. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 169, 539–545 (2013)
Xu, F.: Oxidation of phenols, anilines and benzenethiols by fungal laccases: correlation between activity and redox potentials as well as halide inhibition. Biochemistry 35, 7608–7614 (1996)
Kanagaraj, J., Senthilvelan, T., Panda, R.C.: Degradation of azo dyes by laccase: biological method to reduce pollution load in dye wastewater. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 17, 1443–1456 (2015)
Rodrigues, C.S.D., Madeira, L.M., Boaventura, R.A.R: Treatment of textile effluent by chemical (Fenton’s Reagent) and biological (sequencing batch reactor) oxidation. J. Hazard Mater. 172, 1551–1559 (2009)
Liu, H., Cheng, Y., Du, B., Tong, C., Liang, S., Han, S., Zheng, S., Lin, Y.: Overexpression of a novel thermostable and chloride-tolerant laccase from Thermus thermophilus SG0.5JP17-16 in Pichia pastoris and its application in synthetic dye decolorization. PLoS ONE (2015). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119833
Acknowledgements
The funding of this study was supported by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2015BAK45B01), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21476242), and the National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China (No. 2013CB733600). We would like to acknowledge the Chinese Government for the financial support of the Ph. D scholarship awarded to Nadia A. Samak.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samak, N.A., Hu, J., Wang, K. et al. Development of a Novel Micro-Aerobic Cultivation Strategy for High Potential CotA Laccase Production. Waste Biomass Valor 9, 369–377 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9824-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9824-6