Abstract
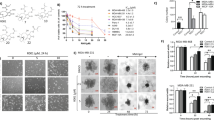
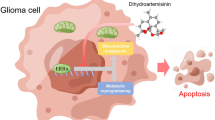
The rate of mitosis of cancer cells is significantly higher than normal primary cells with increased metabolic needs, which in turn enhances the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Higher ROS production is known to increase cancer cell dependence on ROS scavenging systems to counteract the increased ROS. Therapeutic options which selectively modulate the levels of intracellular ROS in cancers are likely candidates for drug discovery. Docetaxel (DTX) has demonstrated antitumor activity in preclinical and clinical studies. It is thought that DTX induces cell death through excessive ROS production and increased Ca2+ entry. The Ca2+ permeable TRPM2 channel is activated by ROS. Selenium (Se) has been previously used to stimulate apoptosis for the treatment of glioblastoma cells resistant to DTX. However, the potential mechanism(s) of the additive effect of DTX on TRPM2 channels in cancer cells remains unclear. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of combination therapy of DTX and Se on activation of TRPM2 in DBTRG glioblastoma cells. DBTRG cells were divided into four treatment groups: control, DTX (10 nM for 10 h), Se (1 μM for 10 h), and DTX+Se. Our study showed that apoptosis (Annexin V and propidium iodide), mitochondrial membrane depolarization (JC1), and ROS production levels were increased in DBTRG cells following treatment with Se and DTX respectively. Cell number and viability, and the levels of apoptosis, JC1, ROS, and [Ca2+]i, induced by DTX, were further increased following addition of Se. We also observed an additive increase in the activation of the NAD-dependent DNA repair enzyme poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) activity, which was accompanied by a decline in its essential substrate NAD+. As well, the Se- and DTX-induced increases in intracellular Ca2+ florescence intensity were decreased following treatment with the TRPM2 antagonist N-(p-amylcinnamoyl) anthranilic acid (ACA). Therefore, combination therapy with Se and DTX may represent an effective strategy for the treatment of glioblastoma cells and may be associated with TRPM2-mediated increases in oxidative stress and [Ca2+]i.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACA:
-
N-(p-amylcinnamoyl) anthranilic acid
- ADPR:
-
ADP-ribose
- Ca2+ :
-
Calcium ion
- cADPR:
-
Cyclic ADPR
- CPx:
-
Cumene hydroperoxide
- DBTRG-O5MG:
-
Denver Brain Tumor Research Group O5
- DHR 123:
-
Dihydrorhodamine 123
- DTX:
-
Docetaxel
- JC-1:
-
5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethyl-benzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide
- MeNAM:
-
N-methyl-nicotinamide
- NAD+:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
- NADH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced form
- NAM:
-
Nicotinamide
- PARP1:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- Se:
-
Selenium
- TRPA1:
-
Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1
- TRPM2:
-
Transient receptor potential melastatin 2
- TRPV1:
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1
References
Alptekin M, Eroglu S, Tutar E, Sencan S, Geyik MA, Ulasli M, Demiryurek AT, Camci C (2015) Gene expressions of TRP channels in glioblastoma multiforme and relation with survival. Tumour Biol 36(12):9209–9213
Bao L, Chen SJ, Conrad K, Keefer K, Abraham T, Lee JP, Wang JF, Zhang XQ, Hirschler-Laszkiewicz I, Wang HG, Dovat S, Gans B, Madesh M, Cheung JY, Miller BA (2016) Depletion of the human ion channel TRPM2 in neuroblastoma demonstrates its key role in cell survival through modulation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and bioenergetics. J Biol Chem 291(47):24449–24464
Berthier S, Arnaud J, Champelovier P, Col E, Garrel C, Cottet C, Boutonnat J, Laporte F, Faure P, Hazane-Puch F (2017) Anticancer properties of sodium selenite in human glioblastoma cell cluster spheroids. J Trace Elem Med Biol 44:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.04.012
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 53:452–458
Braidy N, Berg J, Clement J, Poljak A, Grant R et al. (2018) Role of NAD+ and related precursors as therapeutic targets for age-related degenerative diseases: rationale, biochemistry, pharmacokinetics, and outcomes. Antioxidant and Redox Signalling
Bustamante S, Jayasena T, Richani D, Gilchrist R, Wu L et al (2018) Quantifying the cellular NAD+ metabolome using a tandem liquid chromatography mass spectrometry approach. Metabolomics 14:15
Demirdas A, Naziroglu M, Ovey IS (2017) Duloxetine reduces oxidative stress, apoptosis, and Ca(2+) entry through modulation of TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels in the hippocampus and dorsal root ganglion of rats. Mol Neurobiol 54(6):4683–4695
Elf AK, Bernhardt P, Hofving T, Arvidsson Y, Forssell-Aronsson E, Wängberg B, Nilsson O, Johanson V (2017) NAMPT inhibitor GMX1778 enhances the efficacy of 177Lu-DOTATATE treatment of neuroendocrine tumors. J Nucl Med 58(2):288–292
Esposito E, Impellizzeri D, Mazzon E, Fakhfouri G, Rahimian R et al (2012) The NAMPT inhibitor FK866 reverts the damage in spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation 9:66
Gallego-Yerga L, Posadas I, de la Torre C, Ruiz-Almansa J, Sansone F, Ortiz Mellet C, Casnati A, García Fernández JM, Ceña V (2017) Docetaxel-loaded nanoparticles assembled from beta-cyclodextrin/calixarene giant surfactants: physicochemical properties and cytotoxic effect in prostate cancer and glioblastoma cells. Front Pharmacol 8:249
Gao H, Zhang S, Yang Z, Cao S, Jiang X, Pang Z (2014) In vitro and in vivo intracellular distribution and anti-glioblastoma effects of docetaxel-loaded nanoparticles functioned with IL-13 peptide. Int J Pharm 466(1–2):8–17
Ghoochani A, Hatipoglu Majernik G, Sehm T, Wach S, Buchfelder M, Taubert H, Eyupoglu IY, Savaskan N (2016) Cabazitaxel operates anti-metastatic and cytotoxic via apoptosis induction and stalls brain tumor angiogenesis. Oncotarget 7(25):38306–38318
Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE (2002) Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer 2(1):48–58
Hazane-Puch F, Arnaud J, Trocme C, Faure P, Laporte F et al (2016) Sodium selenite decreased HDAC activity, cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in three human glioblastoma cells. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem 16(4):490–500
Hua H, Zhang X, Mu H, Meng Q, Jiang Y, Wang Y, Lu X, Wang A, Liu S, Zhang Y, Wan Z, Sun K (2018) RVG29-modified docetaxel-loaded nanoparticles for brain-targeted glioma therapy. Int J Pharm 543(1–2):179–189
Huang K, Bian D, Jiang B, Zhai Q, Gao N, Wang R (2017) TRPA1 contributed to the neuropathic pain induced by docetaxel treatment. Cell Biochem Funct 35(3):141–143
Joshi DC, Bakowska JC (2011) Determination of mitochondrial membrane potential and reactive oxygen species in live rat cortical neurons. J Vis Exp(51)
Ju RJ, Mu LM, Li XT, Li CQ, Cheng ZJ et al. (2018) Development of functional docetaxel nanomicelles for treatment of brain glioma. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:sup1, 1180–1190
Lev-Ram V, Ellisman MH (1995) Axonal activation-induced calcium transients in myelinating Schwann cells, sources, and mechanisms. J Neurosci 15(4):2628–2637
Naziroglu M (2009) Role of selenium on calcium signaling and oxidative stress-induced molecular pathways in epilepsy. Neurochem Res 34(12):2181–2191
Naziroglu M (2017) Activation of TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels in dorsal root ganglion by NADPH oxidase and protein kinase C molecular pathways: a patch clamp study. J Mol Neurosci 61(3):425–435
Naziroglu M, Braidy N (2017) Thermo-sensitive TRP channels: novel targets for treating chemotherapy-induced peripheral pain. Front Physiol 8:1040
Naziroglu M, Luckhoff A (2008a) A calcium influx pathway regulated separately by oxidative stress and ADP-ribose in TRPM2 channels: single channel events. Neurochem Res 33(7):1256–1262
Naziroglu M, Luckhoff A (2008b) Effects of antioxidants on calcium influx through TRPM2 channels in transfected cells activated by hydrogen peroxide. J Neurol Sci 270(1–2):152–158
Naziroglu M, Karaoglu A, Aksoy AO (2004) Selenium and high dose vitamin E administration protects cisplatin-induced oxidative damage to renal, liver and lens tissues in rats. Toxicology 195(2–3):221–230
Naziroglu M, Tokat S, Demirci S (2012a) Role of melatonin on electromagnetic radiation-induced oxidative stress and Ca2+ signaling molecular pathways in breast cancer. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 32(6):290–297
Naziroglu M, Yildiz K, Tamturk B, Erturan I, Flores-Arce M (2012b) Selenium and psoriasis. Biol Trace Elem Res 150(1–3):3–9
Nur G, Naziroglu M, Deveci HA (2017) Synergic prooxidant, apoptotic and TRPV1 channel activator effects of alpha-lipoic acid and cisplatin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 37(6):569–577
Park SO, Yoo YB, Kim YH, Baek KJ, Yang JH, Choi PC, Lee JH, Lee KR, Park KS (2015) Effects of combination therapy of docetaxel with selenium on the human breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7. Ann Surg Treat Res 88(2):55–62
Saikali S, Avril T, Collet B, Hamlat A, Bansard JY, Drenou B, Guegan Y, Quillien V (2007) Expression of nine tumour antigens in a series of human glioblastoma multiforme: interest of EGFRvIII, IL-13Ralpha2, gp100 and TRP-2 for immunotherapy. J Neuro-Oncol 81(2):139–148
Sakalli Cetin E, Naziroglu M, Cig B, Ovey IS, Aslan Kosar P (2017) Selenium potentiates the anticancer effect of cisplatin against oxidative stress and calcium ion signaling-induced intracellular toxicity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: involvement of the TRPV1 channel. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 37(1):84–93
Shi K, Zhou J, Zhang Q, Gao H, Liu Y, Zong T, He Q (2015) Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-modified lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for docetaxel delivery in glioblastoma multiforme. J Biomed Nanotechnol 11(3):382–391
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68(1):7–30
Tabaczar S, Koceva-Chyla A, Matczak K, Gwozdzinski K (2010) Molecular mechanisms of antitumor activity of taxanes. I. Interaction of docetaxel with microtubules. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 64:568–581
Tanimura K, Uchino J, Tamiya N, Kaneko Y, Yamada T, Yoshimura K, Takayama K (2018) Treatment rationale and design of the RAMNITA study: a phase II study of the efficacy of docetaxel + ramucirumab for non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastasis. Medicine (Baltimore) 97(23):e11084
Uguz AC, Naziroglu M, Espino J, Bejarano I, Gonzalez D et al (2009) Selenium modulates oxidative stress-induced cell apoptosis in human myeloid HL-60 cells through regulation of calcium release and caspase-3 and -9 activities. J Membr Biol 232(1–3):15–23
Uslusoy F, Naziroglu M, Cig B (2017) Inhibition of the TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels through Hypericum perforatum in sciatic nerve injury-induced rats demonstrates their key role in apoptosis and mitochondrial oxidative stress of sciatic nerve and dorsal root ganglion. Front Physiol 8:335
Vercelli C, Barbero R, Cuniberti B, Odore R, Re G (2015) Expression and functionality of TRPV1 receptor in human MCF-7 and canine CF.41 cells. Vet Comp Oncol 13(2):133–142
Wang Q, Huang L, Yue J (2017) Oxidative stress activates the TRPM2-Ca(2+)-CaMKII-ROS signaling loop to induce cell death in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1864(6):957–967
Wrobel JK, Wolff G, Xiao R, Power RF, Toborek M (2016) Dietary selenium supplementation modulates growth of brain metastatic tumors and changes the expression of adhesion molecules in brain microvessels. Biol Trace Elem Res 172(2):395–407
Xu HL, Mao KL, Lu CT, Fan ZL, Yang JJ, Xu J, Chen PP, ZhuGe DL, Shen BX, Jin BH, Xiao J, Zhao YZ (2016) An injectable acellular matrix scaffold with absorbable permeable nanoparticles improves the therapeutic effects of docetaxel on glioblastoma. Biomaterials 107:44–60
Yakubov E, Buchfelder M, Eyupoglu IY, Savaskan NE (2014) Selenium action in neuro-oncology. Biol Trace Elem Res 161(3):246–254
Zhang XQ, Lu JT, Jiang WX, Lu YB, Wu M, Wei EQ, Zhang WP, Tang C (2015) NAMPT inhibitor and metabolite protect mouse brain from cryoinjury through distinct mechanisms. Neuroscience 291:230–240
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank technician Hulusi Gül (BSN Health, Analysis and Innovation Ltd. Inc. Teknokent, Isparta, Turkey) for their help in performing cell number and cell viability analyses.
Financial Support
The study was supported by BSN Health, Analysis and Innovation Ltd. Inc. Teknokent, Isparta, Turkey (Project No: 2018-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KE, MN, and NB formulated the present hypothesis and MN and NB were responsible for writing the report. MN performed the confocal analyses and the LC-MS analysis. ZSA was responsible for analysis of the data. KE, ZSA, and NB made critical revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ertilav, K., Nazıroğlu, M., Ataizi, Z.S. et al. Selenium Enhances the Apoptotic Efficacy of Docetaxel Through Activation of TRPM2 Channel in DBTRG Glioblastoma Cells. Neurotox Res 35, 797–808 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-0009-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-0009-5