Abstract
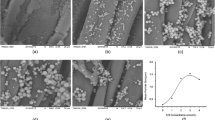
This paper investigates the change in size and morphology of the silica network with the change of water content by sol-gel method. Methyl triethoxysilane (MTES) and tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) were used as co-precursors. The results reveal that the morphology controllable silica network are prepared by changing water content, the size of silica network is in the range in 17–176 nm. There are two ways for the silica nanoparticles to grow in the sol media, condensing with the newly hydrolyzed precursor named monomer-addition model or condensing with the existing silica structure called controlled-aggregation model. As the molar ratio of water/siloxane increases from 1 to 12, the growth process change from the aggregation of oligomers to the condensation between oligomer and hydrolyzed precursor, and the final morphology of silica nanoparticles changes from a network structure to a monodisperse particle structure. When the water content reaches a very high value with the molar ratio of water/siloxane ≥12, the growth process of silica nanoparticles is dominated by the monomer-addition mechanism. The addition of MTES as co-precursor favors the formation of the network structure.

Graphical abstract
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are fully available without restriction.
References
Stöber W, Fink A (1968) Controlled growth of Monodisperse silica spheres in the Micron size range. J Colloid Interf Sci 26:62–69
Dourbash A, Motahari S, Omranpour HJJon-cs (2014) Effect of water content on properties of one-step catalyzed silica aerogels via ambient pressure drying 405:135–140
Ramezani M, Vaezi MR, Kazemzadeh A (2015) The influence of the hydrophobic agent, catalyst, solvent and water content on the wetting properties of the silica films prepared by one-step sol–gel method. Appl Surf Sci 326:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.11.013
Li Z, Cheng X, He S, Huang D, Bi H, Yang H (2014) Preparation of ambient pressure dried MTMS/TEOS co-precursor silica aerogel by adjusting NH4OH concentration. Mater Lett 129:12–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.05.024
Seraji MM, Sameri G, Davarpanah J, Bahramian AR (2017) The effect of high temperature sol-gel polymerization parameters on the microstructure and properties of hydrophobic phenol-formaldehyde/silica hybrid aerogels. J Colloid Interface Sci 493:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.014
Cai S, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Yan H, Lv H, Jiang B (2014) Sol-gel preparation of hydrophobic silica antireflective coatings with low refractive index by base/acid two-step catalysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(14):11470–11475. https://doi.org/10.1021/am501972y
Zhang Y, Zhao C, Wang P, Ye L, Luo J, Jiang B (2014) A convenient sol-gel approach to the preparation of nano-porous silica coatings with very low refractive indices. Chem Commun 50(89):13813–13816. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc05397d
Dourbash A, Motahari S, Omranpour H (2014) Effect of water content on properties of one-step catalyzed silica aerogels via ambient pressure drying. J Non-Cryst Solids 405:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2014.09.013
Xia B, Yan L, Li Y, Zhang S, He M, Li H, Yan H, Jiang B (2018) Preparation of silica coatings with continuously adjustable refractive indices and wettability properties via sol–gel method. RSC Adv 8(11):6091–6098. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra12817g
Ilkhechi NN, Ghobadi N, Khazaie F, Kaleji BK (2016) The effect of Sn/Si dopant on optical and structural properties of nanostructured zinc oxide thin films. Silicon 10(2):503–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9480-2
Ilkhechi NN, Dousi F, Kaleji BK, Salahi E (2014) Optical and structural properties of TiO $$_{\mathbf{2}}$$ 2 nanocomposite doped by Si and cu at high temperature. Opt Quant Electron 47(7):1751–1763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-014-0033-x
Ilkhechi NN, Ahmadi A, Kaleji BK (2015) Optical and structural properties of nanocrystalline anatase powders doped by Zr, Si and cu at high temperature. Opt Quant Electron 47(8):2423–2434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-015-0120-7
LaMer VK, Dinegar RH (1950) Theory, production and mechanism of formation of Monodispersed hydrosols. Acc Chem Soc 72:4847–4854. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01167a001‚
Zhao Y, Li M, Lu Q, Shi ZJL (2008) Superhydrophobic polyimide films with a hierarchical topography: combined replica molding and layer-by-layer assembly. 24 (21):12651-12657
Pereira C, Alves C, Monteiro A, Magén C, Pereira A, Ibarra A, Ibarra M, Tavares P, Araújo J, Blanco GJAam, interfaces (2011) Designing novel hybrid materials by one-pot co-condensation: from hydrophobic mesoporous silica nanoparticles to superamphiphobic cotton textiles. 3 (7):2289–2299
Celichowski G, Piwonski I, Cichomski M, Koralewski K, Plaza S, Olejniczak W, Grobelny JJTL (2003) The influence of methyl group content on tribological properties of organo-silica thin films. 14 (3):181–185
Ilkhechi NN, Kaleji BK (2015) Temperature stability and Photocatalytic activity of Nanocrystalline Cristobalite powders with cu dopant. Silicon 9(6):943–948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-015-9363-y
Ilkhechi NN, Kaleji BK, Mozammel M, Ghobadi N (2016) Effect of cu and Zr co-doped SiO2 nanoparticles on the stability of phases (quartz-Tridymite-Cristobalite) and degradation of methyl Orange at high temperature. Silicon 9(2):293–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9416-x
Han Y, Lu Z, Teng Z, Liang J, Guo Z, Wang D, Han M-Y, Yang aW (2017) Unravelling the growth mechanism of silica particles in Stöber method: in-situ seeded growth model. Langmuir 33 (23):5879–5890
Roder A, Kob W, Binder K (2001) Structure and dynamics of amorphous silica surfaces. J Chem Phys 114(17):7602–7614. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1360257
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (2013) Sol-gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. Elsevier Science
Matsoukas T, Gulari E (1988) Dynamics of growth of silica particles from Ammonia-catalyzed hydrolysis of tetra-ethyl-orthosilicate. J Colloid Interf Sci 124:252–261
Matsoukas T, Gulari E (1989) Monomer-addition growth with a slow initiation step: a growth model for silica particles from Alkoxides. J Colloid Interf Sci 132:13–21
Matsoukas T, Gulari E (1991) Self-sharpening Disrtibutions revisited-Polydispersity in growth by monomer addition. J Colloid Interf Sci 45:557–562
Bogush GH, Zukoski CF (1991) Uniform silica particle precipitation: an aggregative growth model. J Colloid Interf Sci 142:19–34
Bogush GH, Zukoski CF (1991) Studies of the kinetics of the precipitation of uniform silica particles through the hydrolysis and condensation of silicon Alkoxides. J Colloid Interf Sci 142:1–18
Carcouet CC, van de Put MW, Mezari B, Magusin PC, Laven J, Bomans PH, Friedrich H, Esteves AC, Sommerdijk NA, van Benthem RA, de With G (2014) Nucleation and growth of monodisperse silica nanoparticles. Nano Lett 14(3):1433–1438. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl404550d
Wang XD, Shen ZX, Sang T, Cheng XB, Li MF, Chen LY, Wang ZS (2010) Preparation of spherical silica particles by Stober process with high concentration of tetra-ethyl-orthosilicate. J Colloid Interface Sci 341(1):23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.09.018
Yokoi T, Wakabayashi J, Otsuka Y, Fan W, Iwama M, Watanabe R, Aramaki K, Shimojima A, Tatsumi T, Okubo T (2009) Mechanism of formation of uniform-sized silica Nanospheres catalyzed by basic amino acids. Chem Mater 21(15):3719–3729. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm900993b
Pontoni D, Narayanan T, Rennie AR (2002) Time-resolved SAXS study of nucleation and growth of silica colloids. Langmuir 18(1):56–59
Funding
The funding support of the research is from the Petro China Scientific Research and Technology Development Project (2018A-0907)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xijia Zhao conceived and designed the study, performed the experiments, and wrote the paper. Yihan Wang and Bo Jiang reviewed and edited the manuscript. Jianhui Luo, Pingmei Wang, and Peiwen Xiao provided funding and technical support. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest/Competing Interests
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlight
1. Monomer-addition model and controlled-aggregation model are integrated to explain the growth mechanism of silica nanoparticles.
2. Changes in water content affect the final morphology and growth process of silica nanoparticles.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Luo, J. et al. The Influence of Water Content on the Growth of the Hybrid-Silica Particles by Sol-Gel Method. Silicon 13, 3413–3421 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00756-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00756-z