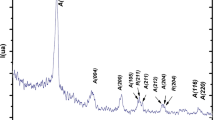
Abstract
Infra-red spectroscopy as an effective tool used to establish platelet like configuration in nanocrystalline silicon thin films (nc-Si:H). These films were deposited using 60 MHz assisted very high frequency plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition process with varying pressure from 4 to 40 Pa. The deposited films were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), Atomic force microscopy (AFM), Raman spectroscopy (RS), Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy (FTIR), Dark conductivity, UV-Vis Spectra and photosensitivity. Infra-red studies of these films reveals that the hydrogen bonding is a platelet like configuration (Si-H groups at 2033 cm− 1) located at grain boundaries resulting in crystalline grains wrapped with hydrogen rich amorphous tissues that provides good passivation resulting in less dangling bonds on grain boundary surface. Structural transformation from amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) to nanocrystalline (nc-Si:H ) phase has been identified at pressure of 24 Pa. The increase in deposition pressure provides clear evidence of improved crystallinity (∼ 37%) which were depicted by increased grain size (∼ 12 nm), reduced hydrogen bonded content (∼ 5.0%), widening of optical gap (∼ 1.9 eV) with enhanced polymerization in the network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rech B, Wagner H (1999) Potential of amorphous silicon for solar cells. Appl Phys A 69(2):155–167
Juneja S, Sudhakar S, Lodhi K, Sharma M, Kumar S (2014) Kinetics of recovery of light induced defects on thermal annealing towards stability of microcrystalline silicon films. Adv Sci Lett 20(7-8):1499–1503
Saleh R, Nickel NH (2003) Raman spectroscopy of B-doped microcrystalline silicon films. Thin Solid Films 427(1):266–269
Martins R, Ferreira I, Fortunato E (1995) Wide band gap microcrystalline silicon thin films. In: Solid state phenomena, vol 44. Trans Tech Publications, pp 299–346
Yan WS, Wei DY, Guo YN, Xu S, Ong TM, Sern CC (2012) Low-temperature preparation of phosphorus doped μc-Si: H thin films by low-frequency inductively coupled plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films 520 (6):1724–1728
Juneja S, Sudhakar S, Gope J, Lodhi K, Sharma M, Kumar S (2015) Highly conductive boron doped micro/nanocrystalline silicon thin films deposited by VHF-PECVD for solar cell applications. J Alloys Compd 643:94–99
Jadkar SR, Sali JV, Takwale MG, Musale DV, Kshirsagar ST (2001) The role of hydrogen dilution of silane and phosphorus doping on hydrogenated microcrystalline silicon (μc-Si:H) films prepared by hot-wire chemical vapor deposition (HW-CVD) technique. Thin Solid Films 395(1):206–212
Ali AM, Kobayashi H, Inokuma T, Al-Hajry A (2013) Morphological, luminescence and structural properties of nanocrystalline silicon thin films. Mater Res Bull 48(3):1027–1033
Juneja S, Sudhakar S, Srivastava AK, Kumar S (2016) Morphology and micro-structural studies of distinct silicon thin films deposited using very high frequency plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition process. Thin Solid Films 619:273–280
Smirnov V, Das C, Melle T, Lambertz A, Hülsbeck M, Carius R, Finger F (2009) Improved homogeneity of microcrystalline absorber layer in thin-film silicon tandem solar cells. Mater Sci Eng B 159:44–47
Jackson WB, Tsai CC (1992) Hydrogen transport in amorphous silicon. Phys Rev B 45(12):6564
Morral AFI, Bertomeu J, Cabarrocas PRI (2000) The role of hydrogen in the formation of microcrystalline silicon. Mater Sci Eng B 69:559–563
Guha S (2004) Thin film silicon solar cells grown near the edge of amorphous to microcrystalline transition. Sol Energy 77(6):887–892
Shah A, Vallat-Sauvain E, Torres P, Meier J, Kroll U, Hof CH, Droz C, Goerlitzer M, Wyrsch N, Vanecek M (2000) Intrinsic microcrystalline silicon (μc-Si: H) deposited by VHF-GD (very high frequency-glow discharge): a new material for photovoltaics and optoelectronics. Mater Sci Eng B 69:219–226
He Y, Yin C, Cheng G, Wang L, Liu X, Hu GY (1994) The structure and properties of nanosize crystalline silicon films. J Appl Phys 75(2):797–803
Oliveira EC, Cruz SA, Aguiar PHL (2012) Effect of PECVD deposition parameters on the DLC/PLC composition of aC: H thin films. J Braz Chem Soc 23(9):1657–1662
Rath JK, Verkerk AD, Liu Y, Brinza M, Goedheer WJ, Schropp REI (2009) Gas phase considerations for the growth of device quality nanocrystalline silicon at high rate. Mater Sci Eng B 159:38–43
Heintze M, Westlake W, Santos PV (1993) Surface controlled plasma deposition and etching of silicon near the chemical equilibrium. J Non-Cryst Solids 164:985–988
Cabarrocas PRI, Layadi N, Heitz T, Drevillon B, Solomon I (1995) Substrate selectivity in the formation of microcrystalline silicon: mechanisms and technological consequences. Appl Phys Lett 66(26):3609–3611
Shah AV, Meier J, Vallat-Sauvain E, Wyrsch N, Kroll U, Droz C, Graf U (2003) Material and solar cell research in microcrystalline silicon. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 78(1):469–491
Kondo M, Matsuda A (2004) Novel aspects in thin film silicon solar cells–amorphous, microcrystalline and nanocrystalline silicon. Thin Solid Films 457(1):97–102
Bhattacharya K, Das D (2007) Nanocrystalline silicon films prepared from silane plasma in RF-PECVD, using helium dilution without hydrogen: structural and optical characterization. Nanotechnology 18(41):415704
Tauc J (2012) Amorphous and liquid semiconductors. Springer, Berlin
Jadhavar A, Pawbake AM, Waykar R, Jadkar V, Kulkarni R, Bhorde A, Rondiya S, et al. (2017) Growth of hydrogenated nano-crystalline silicon (nc-Si: H) films by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PE-CVD). Energy Procedia 110:45–52
Kumar S, Dixit PN, Rauthan CMS, Parashar A, Gope J (2008) Effect of power on the growth of nanocrystalline silicon films. J Phys Condens Matter 20(33):335215
Mullerova J, Jurecka S, Sutta P (2006) Optical characterization of polysilicon thin films for solar applications. Sol Energy 80(6):667–674
Wang Y, Lin J, Huan CHA (2003) Structural and optical properties of a-Si: H/nc-Si: H thin films grown from Ar–H2–SiH4 mixture by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Mater Sci Eng B 104(1):80–87
Vasiliev I, Öğüt S, Chelikowsky JR (2001) Ab initio absorption spectra and optical gaps in nanocrystalline silicon. Phys Rev Lett 86(9):1813
Sun C, Chen TP, Tay BK, Li S, Zhang YB, Huang H, Pan LK, Lau SP, Sun XW (2001) An extended quantum confinement’ theory: surface-coordination imperfection modifies the entire band structure of a nanosolid. J Phys D Appl Phys 34(24):3470
Fischer M, Tan H, Melskens J, Vasudevan R, Zeman M, Smets AHM (2015) High pressure processing of hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells: relation between nanostructure and high open-circuit voltage. Appl Phys Lett 106(4):043905
Kroll U, Meier J, Mikhailov ASS, Weber J (1996) Hydrogen in amorphous and microcrystalline silicon films prepared by hydrogen dilution. J Appl Phys 80(9):4971–4975
Finger F, Carius R, Dylla T, Klein S, Okur S, Gunes M (2003) Stability of microcrystalline silicon for thin film solar cell applications. IEE Proceedings-Circuits, Devices and Systems 150:300–308
Matsui T, Matsuda A, Kondo M (2006) High-rate microcrystalline silicon deposition for p–i–n junction solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90(18):3199–3204
Green ML, Gusev EP, Degraeve R, Garfunkel EL (2001) Ultrathin (4 nm) SiO2 and Si–O–N gate dielectric layers for silicon microelectronics: understanding the processing, structure, and physical and electrical limits. J Appl Phys 90(5):2057– 2121
Shah AV, Meier J, Vallat-Sauvain E, Wyrsch N, Kroll U, Droz C, Graf U (2003) Material and solar cell research in microcrystalline silicon. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 78(1):469–491
Plaza-Castillo J, García-barrientos A, Moreno-Moreno M, Arellano-Jiménez MJ, Vizcaíno KY, Bernal JL (2016) Analysis of H2 and SiH4 in the deposition of pm-Si: H thin films by pecvd process for solar cell applications. Microsc Microanal 22 (S3):1874–1875
Juneja S, Verma P, Savelyev DA, Khonina SN, Sudhakar S, Kumar S (2016) Effect of power on growth of nanocrystalline silicon films deposited by VHF PECVD technique for solar cell applications. AIP Conf Proc 1724:020016
Langford AA, Fleet ML, Nelson BP, Lanford WA, Maley N (1992) Infrared absorption strength and hydrogen content of hydrogenated amorphous silicon. Phys Rev B 45(23):13367
Smets AHM, van de Sanden MCM (2007) Relation of the Si- H stretching frequency to the nanostructural Si-H bulk environment. Phys Rev B 76(7):073202
Vignoli S, Morral AFI, Butté R, Meaudre R, Meaudre M (2002) Hydrogen related bonding structure in hydrogenated polymorphous and microcrystalline silicon. J Non-Cryst Solids 299:220–225
Gleason KK, Petrich MA, Reimer JA (1987) Hydrogen microstructure in amorphous hydrogenated silicon. Phys Rev B 36(6):3259
Zhang SB, Jackson WB (1991) Formation of extended hydrogen complexes in silicon. Phys Rev B 43 (14):12142
Johnson NM, Doland C, Ponce F, Walker J, Anderson G (1991) Hydrogen in crystalline semiconductors: a review of experimental results. Phys B Condens Matter 170(1):3–20
Jackson WB, Tsai CC (1992) Hydrogen transport in amorphous silicon. Phys Rev B 45(12):6564
Marra DC, Edelberg EA, Naone RL, Aydil ES (1998) Silicon hydride composition of plasma-deposited hydrogenated amorphous and nanocrystalline silicon films and surfaces. J Vac Sci Technol A 16(6):3199–3210
Keudell AV, Abelson JR (1998) The interaction of atomic hydrogen with very thin amorphous hydrogenated silicon films analyzed using in situ real time infrared spectroscopy: reaction rates and the formation of hydrogen platelets. J of Appl Phys 84(1):489–495
Agarwal S, Hoex B, van de Sanden MCM, Maroudas D, Aydil ES (2004) Hydrogen in Si-Si bond center and platelet-like defect configurations in amorphous hydrogenated silicon. J Vac Sci Technol B 22(6):2719–2726
Niwano M, Kageyama J, Kurita K, Kinashi K, Takahashi I, Miyamoto N (1994) Infrared spectroscopy study of initial stages of oxidation of hydrogen-terminated Si surfaces stored in air. J Appl Phys 76 (4):2157–2163
Juneja S, Sudhakar S, Khonina SN, Skidanov RV, Porfirevb AP, Moissev OY, Kazanskiy NL, Kumar S (2016) Nanocrystalline silicon thin films and grating structures for solar cells. In: Optical technologies for telecommunications 2015, vol 9807. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 98070F
Kondo M, Matsuda A (2002) An approach to device grade amorphous and microcrystalline silicon thin films fabricated at higher deposition rates. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 6(5):445–453
Xu L, Li ZP, Wen C, Shen WZ (2011) Bonded hydrogen in nanocrystalline silicon photovoltaic materials: impact on structure and defect density. J Appl Phys 110(6):064315
Vignoli S, Butte R, Meaudre R, Meaudre M, Brenier R (2003) Links between hydrogen bonding, residual stress. structural properties and metastability in hydrogenated nanostructured silicon thin films. J Phys Condens Matter 15(43):7185
Van Veen MK, Van der Werf CHM, Rath JK, Schropp REI (2003) Incorporation of amorphous and microcrystalline silicon in n–i–p solar cells. Thin Solid Films 430(1):216–219
Street RA (1991) Hydrogen chemical potential and structure of a-Si: H. Phys Rev B 43(3):2454
Tsu DV, Chao BS, Ovshinsky SR, Jones SJ, Yang J, Guha S, Tsu R (2001) Heterogeneity in hydrogenated silicon: evidence for intermediately ordered chainlike objects. Phys Rev B 63(12):125338
Gope J, Kumar S, Singh S, Rauthan CMS, Srivastava PC (2012) Growth of mixed-phase amorphous and ultra nanocrystalline silicon thin films in the low pressure regime by a VHF PECVD process. Silicon 4(2(2012)):127–135
Richter H, Wang ZP, Ley L (1981) The one phonon raman spectrum in microcrystalline silicon. Solid State Commun 39(5):625–629
Juneja S, Sudhakar S, Gope J, Kumar S (2015) Mixed phase silicon thin films grown at high rate using 60 MHz assisted VHF-PECVD technique. Mater Sci Semicond Process 40:11–19
Trung TQ, Jiri S, Stuchlikova H, Dinh NN, Khuong HK, Quynh PTN, Nga NTH (2009) The effects of hydrogen dilution on structure of Si: H thin films deposited by PECVD. J Phys Conf Series 187(1):012035
Campbell IH, Fauchet PM (1986) The effects of microcrystal size and shape on the one phonon raman spectra of crystalline semiconductors. Solid State Commun 58(10):739–741
Fauchet PM, Campbell IH (1988) Raman spectroscopy of low-dimensional semiconductors. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 14(S1):s79–s101
Zi J, Buscher H, Falter C, Ludwing W, Zhang K, Xie X (1996) Raman shifts in Si nanocrystals. Appl Phys Lett 69(2):200– 202
Agarwal S, Hoex B, van de Sanden MCM, Maroudas D, Aydil ES (2004) Hydrogen in Si–Si bond center and platelet-like defect configurations in amorphous hydrogenated silicon. J Vac Sci Technol, B: Microelectron Nanometer Struct–Process, Meas, Phenom 22(6):2719–2726
Samanta S, Das D (2018) Microstructural association of diverse chemical constituents in nc-SiO x: H network synthesized by spontaneous low temperature plasma processing. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures
Chaudhary D, Sharma M, Sudhakar S, Kumar S (2018) Effect of pressure on bonding environment and carrier transport of a-Si: H thin films deposited using 27.12 MHz Assisted PECVD process. Silicon 10(1):91–97
Ray S, Mukhopadhyay S, Jana T (2006) Studies on microstructure of silicon thin films and its effect on solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90(5):631–639
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Director, CSIR-NPL, New Delhi for his kind support and encouragement. We are thankful to silicon thin film group members for their help and support. One of the authors Sucheta Juneja would like to acknowledge science and engineering research board (SERB), govt. of India for providing National Post– Doc Fellowship (NPDF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juneja, S., Sharma, M. & Kumar, S. Study of Infra-red Spectroscopy on Bonding Environment and Structural Properties of Nanocrystalline Silicon Thin Films Grown by VHF-PECVD Process. Silicon 11, 1925–1937 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-0008-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-0008-9