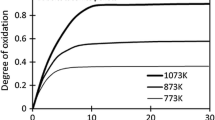
Abstract
The oxidation behavior of artificial magnetite pellets was investigated through measurements of the oxidation degree and mineralogical analysis. The results show that artificial magnetite pellets are much easier to oxidize than natural magnetite. The oxidation is controlled through two different reaction mechanisms. The oxidation of artificial magnetite is dominated by internal diffusion, with an activation energy of 8.40 kJ/mol, at temperatures less than 800°C, whereas it is controlled by chemical reaction, with a reaction activation energy of 67.79 kJ/mol, at temperatures greater than 800°C. In addition, factors such as the oxygen volume fraction and the pellet diameter strongly influence the oxidation of artificial magnetite: a larger oxygen volume fraction and a smaller pellet diameter result in a much faster oxidation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Cheng, Q.G. Xue, G. Wang, Y.Y. Zhang, and J.S. Wang, Phosphorus migration during direct reduction of coal composite high-phosphorus iron ore pellets, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 47(2016), No. 1, p. 154.
X.L. Zhou, D.Q. Zhu, J. Pan, Y.H. Luo, and X.Q. Liu, Upgrading of high-aluminum hematite-limonite ore by high temperature reduction-wet magnetic separation process, Metals, 6(2016), No. 3, p. 57.
D.Q. Zhu, Q. Zhao, G.Z. Qiu, J. Pan, Z.Q. Wang, and C.J. Pan, Magnetizing roasting-magnetic separation of limonite ores from Anhui province in east China, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 32(2010), No. 6, p. 713.
H. Yang, Y. Rong, C. Han, R. Tang, X.X. Xue, Y. Li, and Y.N. Li, Magnetizing roast and magnetic separation of iron in rare-earth tailings, J. Cent. South Univ. Sci. Technol., 23(2016), No. 8, p. 1899.
L.Q. Luo, M. Chen, C. Yang, J. Xu, and B. Liu, Characteristics of magnetic roasting and analysis of phase transformation process of oolitic iron ore, J. Cent. South Univ. Sci. Technol., 46(2015), No. 1, p. 6.
H.Q. Zhang, Concentration on limonitic iron ore by multi-grade magnetic roasting–low intensity magnetic separation, Adv. Mater. Res., 933(2014), p. 125.
R. Wang, Y.X. Han, Y.J. Li, and Y.S. Zhang, Roasting on magnetic properties of oolitic hematite roasted by suspension roasting furnace, J. Northeast Univ. Nat. Sci., 36(2015), No. 7, p. 1024.
S.S. Guo, Research on Magnetic Property and Magnetic Separation Behavior of Artificial Magnetite and Natural Magnetite [Dissertation], Guangxi University, Nanning, 2011, p. 10.
C.Z. Wu, Research on Flotation Behavior and Mechanism of Artificial Magnetite and Natural Magnetite [Dissertation], Guangxi University, Nanning, 2012, p. 55.
H.Q. Zhang and F.L. Wang, Analysis of surface wettability of synthetic magnetite, J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed., 29(2014), No. 4, p. 679.
H.Q. Zhang and F.L. Wang, Regulation of mineral composition and phase transformation in hematite and limonite magnetic roasting process, J. Iron Steel Res., 26(2014), No. 7, p. 10.
L.Q. Luo, Y.F. Yu, and Y.J. Shang, Physical and chemistry characteristics on flash magnetic roasting of complicated iron minerals, China Min. Mag., 18(2009), No. 11, p. 84.
H.Q. Zhang and L.Q. Luo, Theories and Process of Pelletizing and Sintering, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2015, p. 15.
H.Q. Zhang, Technology and application of multi-grades dynamic state magnetizing roasting, Met. Mine, 9(2012), p. 123.
Z.C. Huang, L.L. Lv, L.Z. Zhu, and T. Jiang, Effect of neonatal Fe2O3 on preheated magnetite concentrate pellets strength, J. Cent. South Univ. Sci. Technol., 42(2011), No. 5, p. 1179.
J.P. Sanders and P.K. Gallagher, Thermomagnetometric evidence of γ-Fe2O3 as an intermediate in the oxidation of magnetite, Thermochim. Acta, 406(2003), No. 1-2, p. 241.
D.Q. Zhu, Y.H. Luo, J. Pan, and W. T. Zhou, Study on high temperature oxidation kinetics of magnetite, Met. Mine, 2011, No. 4, p. 89.
R.Q. Liang, S. Yang, F.S. Yan, and J.C. He, Kinetics of oxidation reaction for magnetite pellets, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 20(2013), No. 9, p. 16.
Y.M. Chen and J. Li, Crystal rule of Fe2O3 in oxidized pellet, J. Cent. South Univ. Sci. Technol., 38(2007), No. 1, p. 72.
G.Z. Qiu, D.Q. Zhu, J. Pan, C.A. Wang, Y.F. Guo, T. Jiang, C.F. Hu, J. Clout, and F.H. Shu, Improving the oxidizing kinetics of pelletization of magnetite concentrate by high press roll grinding, ISIJ Int., 44(2004), No. 1, p. 69.
Y.X. Hua, Introduction to Kinetics of Process Metallurgy, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2004, p. 186.
H.Q. Zhang, M.M. Lu, and J.T. Fu, Oxidation and roasting characteristics of artificial magnetite pellets, J. Cent. South Univ. Sci. Technol., 23(2016), No. 11, p. 2999.
T.K.S. Kumar, N.N. Viswanathan, H.M. Ahmed, C. Andersson, and B. Björkman, Estimation of sintering kinetics of oxidized magnetite pellet using optical dilatometer, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 46(2014), No. 2, p. 635.
L.U. Buiyan, J. Mouzon, S.P.E. Forsmo, and J. Hedlund, Quantitative image analysis of bubble cavities in iron ore green pellets, Powder Technol., 214(2011), No. 3, p. 306.
M. Tang, H.J. Cho, and P.C. Pistorius, Early gaseous oxygen enrichment to enhance magnetite pellet oxidation, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 45(2014), No. 4, p. 1304.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51474161).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Hq., Fu, Jt. Oxidation behavior of artificial magnetite pellets. Int J Miner Metall Mater 24, 603–610 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1442-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1442-1