Abstract
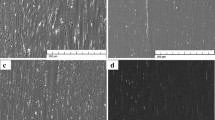
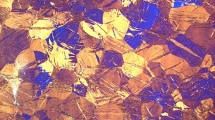
A biodegradable Zn alloy, Zn–1.6Mg, with the potential medical applications as a promising coating material for steel components was studied in this work. The alloy was prepared by three different procedures: gravity casting, hot extrusion, and a combination of rapid solidification and hot extrusion. The samples prepared were characterized by light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray diffraction analysis. Vickers hardness, tensile, and compressive tests were performed to determine the samples’ mechanical properties. Structural examination reveals that the average grain sizes of samples prepared by gravity casting, hot extrusion, and rapid solidification followed by hot extrusion are 35.0, 9.7, and 2.1 μm, respectively. The micrograined sample with the finest grain size exhibits the highest hardness (Hv = 122 MPa), compressive yield strength (382 MPa), tensile yield strength (332 MPa), ultimate tensile strength (370 MPa), and elongation (9%). This sample also demonstrates the lowest work hardening in tension and temporary softening in compression among the prepared samples. The mechanical behavior of the samples is discussed in relation to the structural characteristics, Hall–Petch relationship, and deformation mechanisms in fine-grained hexagonal-close-packed metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.A. Jones, Principles and Prevention of Corrosion, Prentice Hall, Lebanon, Indiana, USA, 1996, p. 572.
C.Z. Yao, Z.C. Wang, S.L. Tay, and W. Gao, Effects of Mg on morphologies and properties of hot dipped Zn–Mg coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 260(2014), p. 39.
C.Z. Yao, W.W. Chen, and W. Gao, Codeposited Zn–Mg coating with improved mechanical and anticorrosion properties, Surf. Coat. Technol., 219(2013), p. 126.
T. Prosek, A. Nazarov, U. Bexell, D. Thierry, and J. Serak, Corrosion mechanism of model zinc–magnesium alloys in atmospheric conditions, Corros. Sci., 50(2008), No. 8, p. 2216.
T. Prosek, D. Persson, J. Stoulil, and D. Thierry, Composition of corrosion products formed on Zn–Mg, Zn–Al and Zn–Al–Mg coatings in model atmospheric conditions, Corros. Sci., 86(2014), p. 231.
M. Dutta, A.K. Halder, and S.B. Singh, Morphology and properties of hot dip Zn–Mg and Zn–MgAl alloy coatings on steel sheet, Surf. Coat. Technol., 205(2010), No. 7, p. 2578.
M. Vlot, R. Bleeker, T. Maalman, and E. van Perlstein, MagiZincTM: a new generation of hot-dip galvanised products, [in] Proceedings of the Galvanized Steel Sheet Forum, Dusseldorf, Germany, 2006.
T. Koll, K. Ullrich, J. Faderl, J. Hagler, and A. Spalek, Properties and potential applications of ZnMg-alloy-coatings on steel sheet by PVD, [in] Proceedings of the Galvatech ′04, International Conference on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet, 6th, Chicago, USA, 2004, p. 803.
C. Schwerdt, M. Riemer, S. Koehler, B. Schuhmacher, M. Steinhorst, and A. Zwick, A study of the application related properties of novel Zn–Mg coated steel sheet produced in a continuous pilot line, [in] Proceedings of the Galvatech ′04, International Conference on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet, 6th, Chicago, USA, 2004, p. 783.
B. Schuhmacher, C. Schwerdt, U. Seyfert, and O. Zimmer, Producing a flat steel product, which comprises base layer composed of steel material and multilayer anti-corrosion coating, comprises applying zinc layer to base layer by electrolytic coating, and applying aluminum layer to zinc layer, Surf. Coat. Technol., 163(2003), p. 703.
A.E. Ares and C.E. Schvezov, The effect of structure on tensile properties of directionally solidified Zn-based alloys, J. Cryst. Growth, 318(2011), No. 1, p. 59.
A.E. Ares and L.M. Gassa, Corrosion susceptibility of Zn–Al alloys with different grains and dendritic microstructures in Nacl solutions, Corros. Sci., 59(2012), No. 2-3, p. 290.
A.E. Ares, L.M. Gassa, C.E. Schvezov, and M.R. Rosenberger, Corrosion and wear resistance of hypoeutectic Zn–Al alloys as a function of structural features, Mater. Chem. Phys., 136(2012), No. 2-3, p. 394.
C.Z. Yao, Z.C. Wang, S.L. Tay, T.P. Zhu, and W. Gao, Effects of Mg on microstructure and corrosion properties of Zn–Mg alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 602(2014), p. 101.
D. Vojtěch, J. Kubásek, J. Šerák, and P. Novák, Mechanical and corrosion properties of newly developed biodegradable Zn-based alloys for bone fixation, Acta Biomater., 7(2011), No. 9, p. 3515.
P.K. Bowen, J. Drelich, and J. Goldman, A new in vitro-in vivo correlation for bioabsorbable magnesium stents from mechanical behavior, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 33(2013), No. 8, p. 5064.
W.F. Gale and T.C. Totemeier, Smithells Metals Reference Book, 8th Ed., Elsevier, Oxford, 2004.
J. Kubásek, I. Pospíšilová, D. Vojtěch, E. Jablonská, and T. Ruml, Structural, mechanical and cytotoxicity characterization of as-cast biodegradable Zn–xMg (x=0.8–8.3%) alloys, Mater. Tehnol., 48(2014), No. 5, p. 623.
H. Gleiter, Nanocrystalline materials, Prog. Mater. Sci., 33(1989), No. 4, p. 223.
C. Suryanarayana and C.C. Koch, Nanocrystalline materials: current research and future directions, Hyperfine Interact., 130(2000), p. 5.
M.V. Akdepniz and J.V. Wood, Microstructures and phase selection in rapidly solidified Zn–Mg alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 31(1996), No. 2, p. 54.
L.B. Tong, M.Y. Zheng, S.W. Xu, X.S. Hu, K. Wu, S. Kamado, G.J. Wang, and X.Y. Lv, Room-temperature compressive deformation behavior of Mg–Zn–Ca alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528(2010), No. 2, p. 672.
G. Caglioti, A. Paoletti, and F.P. Ricci, Choice of collimators for a crystal spectrometer for neutron diffraction, Nucl. Instrum., 3(1958), No. 4, p. 223.
H. Mueller and F. Haessner, Influence of grain size and texture on the flow stress of zinc, Scripta Metall., 15(1981), No. 5, p. 487.
H. Naziri and R. Pearce, The effect of grain size on workhardening and superplasticity in Zn/0.4%Al alloy, Scripta Metall., 3(1969), No. 11, p. 811.
B. Srinivasarao, A.P. Zhilyaev, T.G. Langdon, and M.T. Pérez-Prado, On the relation between the microstructure and the mechanical behavior of pure Zn processed by high pressure torsion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 562(2013), p. 196.
A.H. Chokshi, A. Rosen, J. Karch, and H. Gleiter, On the validity of the hall-petch relationship in nanocrystalline materials, Scripta Metall., 23(1989), No. 10, p. 1679.
C.E. Carlton and P.J. Ferreira, What is behind the inverse Hall–Petch effect in nanocrystalline materials? Acta Mater., 55(2007), No. 11, p. 3749.
X. Zhang, H. Wang, R.O. Scattergood, J. Narayan, C.C. Koch, A.V. Sergueeva, and A.K. Mukherjee, Studies of deformation mechanisms in ultra-fine-grained and nanostructured Zn, Acta Mater., 50(2002), No. 19, p. 4823.
B.L. Zheng, O. Ertorer, Y. Li, Y.Z. Zhou, S.N. Mathaudhu, C.Y.A. Tsao, and E.J. Lavernia, High strength, nano-structured Mg–Al–Zn alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528(2011), No. 4-5, p. 2180.
H.M. Ledbetter, Elastic properties of zinc: a compilation and a review, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 6(1977), No. 4, p. 1181.
ASM Handbook, Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, 1990, p. 1328.
J.G. Antonopoulos, Th. Karakostas, Ph. Komninou, and P. Delavignette, Dislocation movements and deformation twinning in zinc, Acta Metall., 36(1988), No. 9, p. 2493.
Y.M. Wang, M.W. Chen, F.H. Zhou, and E. Ma, High tensile ductility in a nanostructured metal, Nature, 419(2002), No. 6910, p. 912.
L. Zhang, A.M. Elwazri, T. Zimmerly, and M. Brochu, Fabrication of bulk nanostructured silver material from nanopowders using shockwave consolidation technique, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 487(2008), No. 1-2, p. 219.
L. Zhang, A.M. Elwazri, T. Zimmerly, and M. Brochu, Shear punch testing and fracture toughness of bulk nanostructured silver, Mater. Des., 30(2009), No. 5, p. 1445.
M.H. Yoo, Slip, twinning, and fracture in hexagonal close-packed metals, Metall. Trans. A, 12(1981), No. 3, p. 409.
N. Munroe, X.L. Tan, and H.C. Gu, Orientation dependence of slip and twinning in HCP metals, Scripta Mater., 36(1997), No. 12, p. 1383.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubásek, J., Vojtěch, D., Pospíšilová, I. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the micrograined hypoeutectic Zn–Mg alloy. Int J Miner Metall Mater 23, 1167–1176 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-016-1336-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-016-1336-7