Abstract
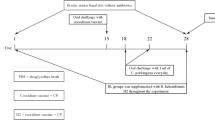
The aim of this study is to explore whether or not the combined application of BS15 and H2 is capable to have a more effective control effect on SNE in broilers. A total of 240 1-day-old female chickens were randomly divided into 5 groups: (a) basal diet in negative control group (NC group); (b) basal diet + SNE infection (coccidiosis vaccine + CP) (PC group); (c) basal diet + SNE infection + H2 pre-treatment (BT group); (d) basal diet + SNE infection + BS15 pre-treatment (LT group); and (e) basal diet + SNE infection + H2 pre-treatment + BS15 pre-treatment (MT group). The results showed the MT group had the most positive effect on inhibiting the negative effect of growth performance at 42 days of age. In the detection of the NC, PC, and MT group indicators at 28 days of age, we found that MT group significantly promoted ileum tissue development of broilers, and the ileum of broilers in the MT group formed a flora structure different from NC and PC, although it was found that the MT group had no effect on the butyrate level in the cecum, but it could affect the serum immune level, such as significantly reducing the level of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-8 and increasing the content of immunoglobulin IgM and IgG. In conclusion, the composite preparation of Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 and Bacillus licheniformis H2 could effectively improve the growth performance against SNE broilers, which is possibly caused by the improvement of the immune levels, the reduction of inflammation levels, and the promotion of the intestinal development.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All the raw sequencing data used in this work were uploaded to the BioSample database (accession number: SAMN18203622).
References
Songer JG (1996) Clostridial enteric diseases of domestic animals. Clin Microbiol Rev 9(2):216–234. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.9.2.216-234.1996
Lovland A, Kaldhusdal M (2001) Severely impaired production performance in broiler flocks with high incidence of Clostridium perfringens associated hepatitis. Avian Pathol 30(1):73–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/03079450020023230
Dahiya JP, Wilkie DC, Van Kessel AG, Drew MD (2006) Potential strategies for controlling necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens in post-antibiotic era. Anim Feed Sci Technol 129:60–88
Kaldhusdal M, Hofshagen H, Løvland A, Langstrand H, Redhead K, (1999) Necrotic enteritis challenge models with broiler chickens raised on litter: evaluation of preconditions, Clostridium perfringens strains and outcome variables. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 24:337–343. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695X.1999.tb01303.x
Wade B, Keyburn A (2015) The true cost of necrotic enteritis’. World Poult 31:16–17
Alagawany M, Abd El-Hack ME, Farag MR, Sachan S, Karthik K, Dhama K (2018) The use of probiotics as eco-friendly alternatives for antibiotics in poultry nutrition. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(11):10611–10618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1687-x
Homyouni-Rad A, Soroush AR, Khalili L, Norouzi-Panahi L, Ejtahed HS (2017) Diabetes Management by Probiotics: Current Knowledge and Future Pespective. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 13(3-4):1-13. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573399812666161014112515
Liu Y, Tran DQ, Fatheree NY, Marc Rhoads J (2014) Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 differentially modulates effector memory T cells and Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in a mouse model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 15 307(2):G177–86. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00038.2014
Wu Y, Wang B, Zeng Z, Liu R, Tang L, Gong L, Li W (2019) Effects of probiotics Lactobacillus plantarum 16 and Paenibacillus polymyxa 10 on intestinal barrier function, antioxidative capacity, apoptosis, immune response, and biochemical parameters in broilers. Poult Sci 98:5028–5039. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pez226
Wang H, Ni X, Qing X, Liu L, Xin J, Luo M, Khalique A, Dan Y, Pan K, Jing B, Zeng D (2018) Probiotic Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 improves blood parameters related to immunity in broilers experimentally infected with subclinical necrotic enteritis. Front Microbiol 9:49. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00049
Khalique A, Zeng D, Wang H, Qing X, Zhou Y, Xin J, Zeng Y, Pan K, Shu G, Jing B, Shoaib M, Naqash NX (2019) Transcriptome analysis revealed ameliorative effect of probiotic Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 against subclinical necrotic enteritis induced hepatic inflammation in broilers. Microb Pathog 132:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.05.011
Qing X, Zeng D, Wang H, Ni X, Lai J, Liu L, Khalique A, Pan K, Jing B (2018) Analysis of hepatic transcriptome demonstrates altered lipid metabolism following Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 prevention in chickens with subclinical necrotic enteritis. Lipids Health Dis 17:93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0741-5
Qing X, Zeng D, Wang H, Ni X, Liu L, Lai J, Khalique A, Pan K, Jing B (2017) Preventing subclinical necrotic enteritis through Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 by ameliorating lipid metabolism and intestinal microflora in broiler chickens. AMB Express 7:139. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-017-0439-5
Li J (2010) Genetic diversity of Clostridium perfringens and effects of Bacillus licheniformis on the ileum flora of chicken necrotic enterocolitis. Dissertation, Sichuan Agricultural University
Xu S, Lin Y, Zeng D, Zhou M, Zeng Y, Wang H, Zhou Y, Zhu H, Pan K, Jing B, Ni X (2018) Bacillus licheniformis normalize the ileum microbiota of chickens infected with necrotic enteritis. Sci Rep 8:1744. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20059-z
Zhao Y, Zeng D, Wang H, Qing X, Sun N, Xin J, Luo M, Khalique A, Pan K, Shu G, Jing B, Ni X (2019) Dietary probiotic Bacillus licheniformis H2 enhanced growth performance, morphology of small intestine and liver, and antioxidant capacity of broiler chickens against Clostridium perfringens -induced subclinical necrotic enteritis. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 12:883–895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-09597-8
Zhao Y, Zeng D, Wang H, Sun N, Xin J, Yang H, Lei L, Khalique A, Rajput DS, Pan K, Shu G, Jing B, Ni X (2020) Analysis of miRNA expression in the ileum of broiler chickens during Bacillus licheniformis H2 supplementation against subclinical necrotic enteritis. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 13(2):356–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09709-9
White R, Atherly T, Guard B, Rossi G, Wang C, Mosher C, Webb C, Hill S, Ackermann M, Sciabarra P, Allenspach K, Suchodolski J, Jergens AE (2017) Randomized, controlled trial evaluating the effect of multi-strain probiotic on the mucosal microbiota in canine idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 8:451–466. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2017.1334754
Sabico S, Al-Mashharawi A, Al-Daghri NM, Wani K, Amer OE, Hussain DS, Ahmed Ansari MG, Masoud MS, Alokail MS, McTernan PG (2019) Effects of a 6-month multi-strain probiotics supplementation in endotoxemic, inflammatory and cardiometabolic status of T2DM patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Nutr 38:1561–1569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.009
Ibrahim A, Ali RAR, Manaf MRA, Ahmad N, Tajurruddin FW, Qin WZ, Desa SHM, Ibrahim NM (2020) Multi-strain probiotics (Hexbio) containing MCP BCMC strains improved constipation and gut motility in Parkinson’s disease: a randomised controlled trial. PLoS ONE 15:e0244680. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0244680
Yang J, Huang K, Wang J, Wu D, Liu Z, Yu P, Wei Z, Chen F (2020) Combined use of Bacillus subtilis yb-114,246 and Bacillus licheniformis yb-214,245 improves body growth performance of Chinese Huainan Partridge Shank chickens by enhancing intestinal digestive profiles. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 13(2):327–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09691-2
Chang HY, Chen JH, Chang JH, Lin HC, Lin CY, Peng CC (2017) Multiple strains probiotics appear to be the most effective probiotics in the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis and mortality: an updated meta-analysis. PLoS One 12(2):e0171579. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171579
McFarland LV (2020) Efficacy of single-strain probiotics versus multi-strain mixtures: systematic review of strain and disease specificity. Dig Dis Sci undefined: undefined. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06244-z
Korada SK, Yarla NS, Mishra V, Daim MA, Sharma B, Gm A, R R, M P, Peluso I, Kamal MA, (2018) Single probiotic versus multiple probiotics - a debate on current scenario for alleviating health benefits. Curr Pharm Des 24:4150–4153. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612824666181012124136
Aalaei M, Khatibjoo A, Zaghari M, Taherpour K, Akbari Gharaei M, Soltani M (2018) Comparison of single-strain and multi-strain probiotics effects on broiler breeder performance, egg production, egg quality and hatchability. Br Poult Sci 59:531–538. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071668.2018.1496400
Guo Q, Goldenberg JZ, Humphrey C, El Dib R, Johnston BC (2019) Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD004827. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004827.pub5
Nelson JR, Bray JL, Delabbio J, Archer, GS (2020) Comparison of an intermittent, short-dawn/dusk photoperiod with an increasing, long-dawn/dusk photoperiod on broiler growth, stress, and welfare. Poult Sci 99(8):3908–3913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2020.05.015
Hartman K, van der Heijden MGA, Wittwer RA, Banerjee S, Walser JC, Schlaeppi K (2020) Correction to: cropping practices manipulate abundance patterns of root and soil microbiome members paving the way to smart farming. Microbiome 8(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-020-00855-4
Minchin PR (1987) An evaluation of the relative robustness of techniques for ecological ordination. Vegetatio 69(1/3):89–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00038690
Oksanen JF, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Wagner H (2015) Vegan: community ecology package
Caceres D, Legendre M (2010) Improving indicator species analysis by combining groups of sites. Oikos 119:1674–1684. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2010.18334.x
Mora A, Donaldson IM (2006) The igraph software package for complex network research. Int J Complex Syst 1695
Lin Y, Xu S, Zeng D, Ni X, Zhou M, Zeng Y, Wang H, Zhou Y, Zhu H, Pan K, Li G (2017) Disruption in the cecal microbiota of chickens challenged with Clostridium perfringens and other factors was alleviated by Bacillus licheniformis supplementation. PLoS One 3 12(8):e0182426. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182426
Timbermont L, Haesebrouck F, Ducatelle R, Van Immerseel F (2011) Necrotic enteritis in broilers: an updated review on the pathogenesis. Avian Pathol 40:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/03079457.2011.590967
Cai L, Indrakumar S, Kiarie E, Kim IH (2015) Effects of a multi-strain Bacillus species-based direct-fed microbial on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, blood profile, and gut health in nursery pigs fed corn-soybean meal-based diets. J Anim Sci 93:4336–4342. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2015-9056
Chang J, Wang T, Wang P, Yin Q, Liu C, Zhu Q, Lu F, Gao T (2020) Compound probiotics alleviating aflatoxin B and zearalenone toxic effects on broiler production performance and gut microbiota. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 194:110420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110420
Ramlucken U, Ramchuran SO, Moonsamy G, Lalloo R, Thantsha MS, Jansen van Rensburg C (2020) A novel Bacillus based multi-strain probiotic improves growth performance and intestinal properties of Clostridium perfringens challenged broilers. Poult Sci 99:331–341. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pez496
Zahoor I, Ghayas A, Basheer A (2018) Genetics and genomics of susceptibility and immune response to necrotic enteritis in chicken: a review. Mol Biol Rep 45:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-017-4138-8
Gholamiandehkordi AR, Timbermont L, Lanckriet A, Van Den Broeck W, Pedersen K, Dewulf J, Pasmans F, Haesebrouck F, Ducatelle R, Van Immerseel F (2007) Quantification of gut lesions in a subclinical necrotic enteritis model. Avian Pathol 36:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1080/03079450701589118
Van Immerseel F, Rood JI, Moore RJ, Titball RW (2008) Rethinking our understanding of the pathogenesis of necrotic enteritis in chickens. Trends Microbiol 17:32–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2008.09.005
Kai Y (2021) Intestinal villus structure contributes to even shedding of epithelial cells. Biophys J 120(4):699–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2021.01.003
Yamauchi K, Isshiki Y (1991) Scanning electron microscopic observations on the intestinal villi in growing white leghorn and broiler chickens from 1 to 30 days of age. Br Poult Sci 32:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071669108417328y
Walton KD, Freddo AM, Wang S, Gumucio DL (2016) Generation of intestinal surface: an absorbing tale. Development 143:2261–2272. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.135400
Shini S, Aland RC, Bryden WL (2021) Avian intestinal ultrastructure changes provide insight into the pathogenesis of enteric diseases and probiotic mode of action. Sci Rep 11:167. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80714-2
Awad WA, Ghareeb K, Abdel-Raheem S, Böhm J (2009) Effects of dietary inclusion of probiotic and synbiotic on growth performance, organ weights, and intestinal histomorphology of broiler chickens. Poultry Sci 88(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2008-00244
Wang H, Ni X, Qing X, Zeng D, Luo M, Liu L, Li G, Pan K, Jing B (2017) Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 promotes growth performance and lowers fat deposition by improving lipid metabolism, intestinal development, and gut microflora in broilers. Front Microbiol 8:1073. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01073
Fang H, Fu L, Li X, Lu C, Su Y, Xiong K, Zhang L (2021) Long-term efficacy and safety of monotherapy with a single fresh fecal microbiota transplant for recurrent active ulcerative colitis: a prospective randomized pilot study. Microb Cell Fact 19 20(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01513-6
Piersigilli F, Grambezen BV, Hocq C, Danhaive O (2020) Nutrients and microbiota in lung diseases of prematurity: the Placenta-Gut-Lung Triangle. Nutrients 12:undefined. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020469
Wells JM, Brummer RJ, Derrien M, Macdonald TT, Troost F, Cani PD, Theodorou V, Dekker J, Méheust A (2017) Homeostasis of the gut barrier and potential biomarkers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 312:G171–G193. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00048.2015
Garcia A, Olmo B, Lopez-Gonzalvez A et al (2008) Capillary electrophoresis for short chain organic acids in faeces Reference values in a Mediterranean elderly population. J Pharm Bionmed Anal 46(2):356–361
Takakuwa A, Nakamura K, Kikuchi M, Sugimoto R, Ayabe v (2009) Butyric acid and leucine induce α-defensin secretion from small intestinal paneth cells. Nutrients 11:undefined. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112817
Xue GD, Wu SB, Choct M, Swick RA (2017) Effects of yeast cell wall on growth performance, immune responses and intestinal short chain fatty acid concentrations of broilers in an experimental necrotic enteritis model. Anim Nutr 3:399–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2017.08.002
Levy AW, Kessler JW, Fuller L, Williams S, Mathis GF, Lumpkins B, Valdez F (2015) Effect of feeding an encapsulated source of butyric acid (ButiPEARL) on the performance of male Cobb broilers reared to 42 d of age. Poult Sci 94:1864–1870. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pev130
Ramirez K, Huerta R, Oswald E, Garcia-Tovar C, Hernandez JM, Navarro-Garcia F (2005) Role of EspA and intimin in expression of proinflammatory cytokines from enterocytes and lymphocytes by rabbit enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-infected rabbits. Infect Immun 73:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.73.1.103-113.2005
Li A, Wang Y, Li Z, Qamar H, Li J (2019) Probiotics isolated from yaks improves the growth performance, antioxidant activity, and cytokines related to immunity and inflammation in mice. Microb Cell Fact 18:112. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1161-6
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Cheroutre H, Eckmann L, Karin M (2009) IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 15:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.01.001
He C, Shi Y, Wu R, Sun M, Fang L, Wu W, Liu C, Tang M, Li Z, Wang P, Cong Y, Liu Z (2016) miR-301a promotes intestinal mucosal inflammation through induction of IL-17A and TNF-α in IBD. Gut 65:1938–1950. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309389
Hammond ME, Lapointe GR, Feucht PH, Hilt S, Gallegos CA, Gordon CA, Giedlin MA, Mullenbach G, Tekamp-Olson P (1995) IL-8 induces neutrophil chemotaxis predominantly via type I IL 8 receptors. J Immunol 155:1428–1433. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.182.2.623
Fan X, Chua A, Fan X, Keeling PW (1995) Increased gastric production of interleukin-8 and tumour necrosis factor in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. J Clin Pathol 48:133–136. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.48.2.133
Liu Y, Zhu L, Fatheree NY, Liu X, Pacheco SE, Tatevian N (2009) Rhoads JM (2009) Changes in intestinal Toll-like receptors and cytokines precede histological injury in a rat model of necrotic enterocolitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297:G442–G450. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00182.2009
Lee KW, Kim DK, Lillehoj HS, Jang SI, Lee SH (2015) Immune modulation by Bacillus subtilis-based direct-fed microbials in commercial broiler chickens. Anim Feed Sci Tech 200:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2014.12.006
Cao W, Liu X, Bai T, Fan H, Hong K, Song H, Han Y, Lin L, Ruan L, Li T (2020) High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin as a therapeutic option for deteriorating patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Open Forum Infect Dis 7(3)ofaa102. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofaa102
Singh N, Sonika U, Moka P, Sharma B, Sachdev V, Mishra SK, Upadhyay AD, Saraya A (2019) Association of endotoxaemia & gut permeability with complications of acute pancreatitis: secondary analysis of data. Indian J Med Res 149:763–770. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijmr.IJMR.763.17
Keyburn AL, Boyce JD, Vaz P, Bannam TL, Ford ME, Parker D, Di Rubbo A, Rood JI, Moore RJ (2008) NetB, a new toxin that is associated with avian necrotic enteritis caused by Clostridium perfringens. PLoS Pathog 4:e26. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.0040026
Smyth JA, Martin TG (2010) Disease producing capability of NetB positive isolates of C. Perfringens recovered from normal chickens and a cow, and NetB positive and negative isolates from chickens with necrotic enteritis. Vet Microbiol 146:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.04.022
Al-Bahrani AZ, Darwish A, Hamza N, Benson J, Eddleston JM, Snider RH, Nylén ES, Becker KL (2010) Gut barrier dysfunction in critically ill surgical patients with abdominal compartment syndrome. Pancreas 39:1064–1069. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181da8d51
Maes M, Sirivichayakul S, Kanchanatawan B, Vodjani A (2019) Breakdown of the paracellular tight and adherens junctions in the gut and blood brain barrier and damage to the vascular barrier in patients with deficit schizophrenia. Neurotox Res 36: 306–322. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.27744.12801
Vidarsson G, Dekkers G, Rispens T (2014) IgG subclasses and allotypes: from structure to effector functions. Front Immunol 5:520. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00520
Pierce JL, Cromwell GL, Lindemann MD, Russell LE, Weaver EM (2005) Effects of spray-dried animal plasma and immunoglobulins on performance of early weaned pigs. J Anim Sci 83:2876–2885. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2005.00611.x
Gharib-Naseri K, de Paula Dorigam JC, Doranalli K, Kheravii S, Swick RA, Choct M, Wu SB (2020) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Modulations of genes related to gut integrity, apoptosis, and immunity underlie the beneficial effects of CECT 5940 in broilers fed diets with different protein levels in a necrotic enteritis challenge model. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 11:104
Funding
The present study was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2021YFH0097, 2019YFH0060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the design of the experiments. YX, SW, and YZ performed the experiments. NS, YX, and HW analyzed and interpreted the results. NS, YX, HW, JB, and XN drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All animal experiment procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Animal Welfare Act, and all procedures and protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Sichuan Agricultural University (approval number: SYXKchuan2019-187).
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, N., Xue, Y., Wei, S. et al. Compound Probiotics Improve Body Growth Performance by Enhancing Intestinal Development of Broilers with Subclinical Necrotic Enteritis. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 15, 558–572 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09867-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09867-4