Abstract
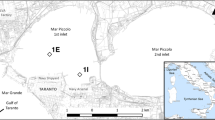
We characterized the biogeochemical organic carbon cycles in the surface sediment layer (< 25 cm) in the coastal waters of Namhae off the South Sea of Korea. The total and diffusive sediment oxygen uptake rates were measured using an in situ benthic lander equipped with a benthic chamber and a microprofiler. The bottom water above the sediment-water interface was incubated to estimate the benthic flux of the dissolved inorganic nutrients and the total alkalinity using an in situ benthic chamber. In addition, the particulate materials vertically deposited onto the surface sediment and the sedimentation rates were quantified to calculate the sedimentary organic carbon budget. The total oxygen uptake rate was in the range 34.9 to 54.1 mmol O2 m-2d-1, which is about three times the diffusive oxygen uptake rate. An abnormal oxygen peak observed in the anoxic sediment layer suggests a higher bioirrigation activity in the sediment layer. The oxidation rate of organic carbon at the sediment surface showed a very narrow range (36 ± 7 to 37 ± 7 mmol C m-2d-1), and the burial flux into the sediment layer was in the range 3 to 13 mmol C m-2d-1, which accounted for 9% to 36% of the remineralization rate of the organic carbon. The N and P requirement fluxes for pelagic production could be supported by 29% and 42% of the benthic flux, respectively, which strongly suggests a benthic-pelagic coupling in the coastal area of the South Sea of Korea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almroth E, Tengberg A, Andersson J, Pakhomova S, Hall POJ (2009) Effects of resuspension on benthic fluxes of oxygen, nutrients, dissolve inorganic carbon, iron and manganese in the Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Cont Shelf Res 29:807–818
Berelson W, McManus J, Coale K, Johnson K, Burdige D, Kilgore T, Colodner D, Chavez F, Kudela R, Boucher J (2003) A time series of benthic flux measurements from Monterey Bay, CA. Cont Shelf Res 23:457–481
Berelson WM, McManus J, Severmann S, Reimers CE (2013) Benthic flux of oxygen and nutrients across Oregon/California shelf sediments. Cont Shelf Res 55:66–75
Broecker WS, Peng T-H (1974) Gas exchange rates between air and sea. Tellus 26:21–35
Canfield DE, Thamdrup B, Kristensen E (2006) Aquatic geomicrobiology. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego CA, USA, 640 p
Cho, Y-S, Kim Y-B, Lee W-C, Hong S-J, Lee S-M (2013) The trophic state assessment using biochemical composition in the surface sediment, the southern coast of Korea. J Korean Soc Mar Environ Safety 19:101–110 (in Korean)
Dickson AG, Sabine CL, Christian JR (2007) Guide to best practices for ocean CO2 measurements. PICES Special Publication 3, 191 p
Forja JM, Ortega T, DelValls TA, Gómez-Parra A (2004) Benthic fluxes of inorganic carbon in shallow coastal ecosystems of the Iberian Peninsula. Mar Chem 85:141–156
Ferrón S, Alonso-Pérez F, Ortega T, Forja JM (2009) Benthic respiration on the northeastern shelf of the Gulf of Cádiz (SW Iberian Peninsular). Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 392:69–80
Gattuso JP, Frankignoulle M, Wollast R (1998) Carbon and carbonate metabolism in coastal aquatic ecosystem. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 29:405–434
Glud RN (2008) Oxygen dynamics of marine sediments. Mar Biol Res 4:243–289
Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M (1999) Methods of seawater analysis. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 600 p
Hammond DE, Fuller C, Harmon D, Hartman B, Korosec M, Miller L, Rea R, Berelson W, Hager S (1985) Benthic fluxes in San Francisco Bay. Hydrobiologia 129:69–90
Holtappels M, Kuypers MMM, Schlüter M, Brüchert V (2011) Measurement and interpretation of solute concentration gradients in the benthic boundary layer. Limnol Oceanogr-Meth 9:1–13
Han MW, Lee IH, Kim K-H, Noh I (1997) The partitioning of organic carbon cycle in coastal sediments of Kwangyang Bay. J Oceanol Soc Korea 32:103–111
Hong GH, Kim KT, Pae SJ, Kim SH, Lee SH (1991) Annual cycles of nutrients and dissolved oxygen in a nutrient-rich temperate coastal bay, Chinhae Bay, Korea. J Oceanol Soc Korea 26:204–222
Hulth S, Tengberg A, Landén A, Hall POJ (1997) Mineralization and burial of organic carbon in sediments of the southern Weddell Sea (Antarctica). Deep-Sea Res I 44:955–981
Jørgensen BB, Revsbech NP (1985) Diffusive boundary layers and the oxygen uptake of sediment and detritus. Limnol Oceanogr 30:111–122
Kim KH, Burnett W (1983) Gamma-ray spectrometric determination of uranium-series nuclides in marine phosphorites. Anal Chem 55:1796–1800
Kim J-B, Lee SY, Yu J, Choi YH, Jung C-S, Lee P-Y (2006) The characteristics of oxygen deficient water mass in Gamak Bay. J Korean Soc Mar Environ Eng 9:216–224 (in Korean)
Kristensen E (2000) Organic matter diagenesis at the oxic/anoxic interface in coastal marine sediment, with emphasis on the role of burrowing animals. Hydrobiologia 426:1–24
Lee JS, Kim KH, Kim SS, Jung RH, Kim KY, Park JS, Lee PY, Lee YS, Choi WJ, Park YC, Kim PJ, Lee WC, Kwon JN, Uhm KH, Choi JI, Jeon KA, Han JH (2004) The assessment of trophic state and the importance of benthic boundary layer in the southern coast of Korea. J Korean Soc Oceanogr (The Sea) 9(4):179–195 (in Korean)
Lee JS, Kim S, Kim S-S, An S, Kim Y-T, Choi O-I (2009) Sediment oxygen consumption in semi-closed bays during summer. Ocean Sci J 44(3):161–171
Lee JS, Bahk KS, Khang BJ, Kim YT, Bae JH, Kim SS, Park JJ, Choi OI (2010) The development of a benthic chamber (BelcI) for benthic boundary layer studies. J Korean Soc Oceanogr 15:41–50 (in Korean)
Lee JS, Kim YT, Shin K-H, Hyun J-H, Kim S-Y (2011) Benthic nutrient fluxes at longline sea squirt and oyster aquaculture farms and their role in coastal ecosystems. Aquacult Int 19:931–944
Lee JS, Kim KH, Shim J, Han JH, Choi YH, Khang B (2012a) Massive sedimentation of fine sediment with organic matter and enhanced benthic-pelagic coupling by an artificial dyke in semi-closed Chonsu Bay, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 64:153–163
Lee JS, Kim S-H, Kim Y-T, Hong SJ, Han JH, Hyun JH, Shin K-H (2012b) Influence of sea squirt (Halocynthia roretzi) aquaculture on benthic-pelagic coupling in coastal waters: A study of the South Sea in Korea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 99:10–20
Lee JS, Kim E-S, Kahng S-H, Yoon S-H, Cho J-H, Bahk K-S, Kang D-J (2012c) Development and application of a novel miniature in situ microprofiler (NAFRI BelpI). Ocean Sci J 47(3):489–495
Lee M-O, Kim J-K (2008) Characteristics of algal blooms in the southern coastal waters of Korea. Mar Environ Res 65:128–147
Lee YS, Lee SY (2006) Factors affecting outbreaks of Cochlodinium polykrikoides blooms in coastal areas of Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 52:626–634
Li Y-H, Gregory S (1974) Diffusion of ions in sea water and in deep sea sediment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38:703–714
Mucci A, Sundby B, Gehlen M, Arakaki T, Zhong S, Silverberg N (2000) The fate of carbon in continental shelf sediments of eastern Canada: a case study. Deep-Sea Res II 47:733–760
National Fisheries Research and Development Institute (2010) In: Environmental Research of Aquaculture Farm (2009). pp. 94 (in Korean)
Ortega T, Ponce R, Forja J, Gómez-Parra A (2005) Fluxes of dissolved inorganic carbon in three estuarine systems of the Cantabrian Sea (North of Spain). J Marine Syst 53:125–142
Pratihary AK, Naqvi SWA, Naik H, Thorat BR, Narvenkar G, Manjunatha BR, Rao VP (2009) Benthic fluxes in a trophical estuary and their role in ecosystem. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 85:387–398
Rowe GT, Clifford CH, Smith KL, Hamilton PL (1975) Benthic nutrient regeneration and its coupling to primary productivity in coastal waters. Nature 255:215–217
Sommer S, Türk M, Kriwanek S, Pfannkuche O (2008) Gas exchange system for extended in situ benthic chamber flux measurements under controlled oxygen conditions: First application — Sea bed methane emission measurements at Captain Arutyunov mud volcano. Limnol Oceanogr-Meth 6:23–33
Ståhl H, Tengberg A, Brunnegård J, Bjørnbom E, Forbes T, Josefson A, Kaberi H, Farle Hassellöv I-M, Olsgard F, Roos P, Hall POJ (2004) Factors influencing organic carbon recycling and burial in Skagerrak sediments. J Mar Res 62:867–907
Tengberg A, Bovee FD, Hall P, Berelson W, Chadwick D, Ciceri G, Grassous P, Devel A, Emerson S, Gage J, Glud R, Graziottini F, Gundersen J, Hammond D, Helder W, Hinga K, Holby O, Jahnke R, Khripounoff A, Lieberman S, Nuppenau V, Pfannkuche O, Reimers C, Rowe G, Sahami A, Sayles F, Schurter M, Smallman D, Wehrli B, Wilde PD (1995) Benthic chamber and profiling landers in oceanography — A review of design, technical solutions and functioning. Prog Oceanogr 35:253–294
Wenzhöfer F, Glud RN (2002) Benthic carbon mineralization in the Atlantic: A synthesis based on in situ data from the last decade. Deep-Sea Res I 49:1255–1279
Witte U, Wenzhöfer F, Sommer S, Boetius A, Heinz P, Aberle N, Sand M, Cremer A, Abraham W-R, Jørgensen BB, Pfannkuche O (2003) In situ experimental evidence of the fate of a phytodetritus pulse at the abyssal sea floor. Nature 424:763–765
Wollast R (1991) The coastal organic carbon cycle: Fluxes, sources, and sinks. In: Mantoura RFC, Martin J-M, Wollast R (eds) Ocean Margin Processes in Global Change. John Wiley & Sons, pp 356–381
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.S., Han, J.H., An, SU. et al. Sedimentary organic carbon budget of coastal sediments and the importance of benthic-pelagic coupling off Namhae Island in the South Sea of Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 49, 433–447 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-014-0041-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-014-0041-6