Abstract
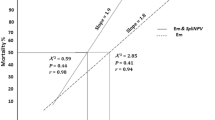
The combined and alone effects of azadirachtin (AZA) and Spodoptera frugiperda multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus (SfMNPV) on the mortality and food consumption of third instar S. frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) were evaluated under laboratory conditions using maize leaf bioassays. The LC50 values for SfMNPV and AZA were determined to be 1.30x106 viral occlusion bodies (OBs)/ml and 6.54 mg l -1 at 192 h and 144 h after treatment, respectively. These LC50 values were estimated for 4 days of continuous exposure. Although the interaction of SfMNPV with AZA increased the percentage of mortality observed in most of the cases, only one mixture (1x106 OBs/ml + 5 mg l -1) resulted in a synergistic effect on mortality of S. frugiperda. Application of SfMNPV (1x106 OBs/ml), AZA (0.5, 0.1 or 0.25 mg l -1) or SfMNPV–AZA mixtures resulted in a significant reduction in the maize-leaf piece consumption of larvae treated in the third instar across the experiment, by onefold, 2–5-fold, and 2–3-fold, respectively, compared with the control. However, the interaction of two SfMNPV–AZA mixtures (1x106 OBs/ml + 5 mg l -1 and 1x106 OBs/ml + 10 mg l -1) did not reduce the food consumption compared with AZA alone. It was concluded that SfMNPV–AZA mixtures require validation to determine whether this mixture may offer a valuable means of improving the efficacy of the SfMNPV.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adel, M. M., & Sehnal, F. (2000). Azadirachtin potentiates the action of ecdysteroid agonist RH-2485 in Spodoptera littoralis. Journal of Insect Physiology, 46, 267–274.
Andrews, K. L. (1980). The whorlworm, Spodoptera frugiperda in Central America and neighboring areas. Florida Entomologist, 63, 456–467.
Bhandari, K., Sood, P., Mehta, P. K., Choudhary, A., & Prabhakar, C. S. (2009). Effect of botanical extracts on the biological activity of granulosis virus against Pieris brassicae. Phytoparasitica, 37, 317–322.
Blaney, W. M., & Simmons, M. S. J. (2002). Feeding behavior. In H. Schmutterer (Ed.), The neem tree Azadirachta indica A. Juss. and other meliaceous plants (pp. 171–176). Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH Publishers.
Capinera, J. L., & Froeba, J. G. (2007). Behavioral response of Schistocerca americana (Orthoptera: Acrididae) to azadirex (neem)-treated host plants. Journal of Economic Entomology, 100, 117–122.
Cook, S. P., Webb, R. E., & Thorpe, K. W. (1996). Potential enhancement of the gypsy moth (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) nuclear polyhedrosis virus with the triterpene azadirachtin. Environmental Entomology, 25, 1210–1214.
Dayan, F. E., Cantrell, C. L., & Duke, S. O. (2009). Natural products in crop protection. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 17, 4022–4034.
Ericsson, J. D., Kabaluk, J. T., Goettel, S., & Myers, J. H. (2007). Spinosad interacts synergistically with the insect pathogen Metarhizium anisopliae against the exotic wireworms Agriotes lineatus and Agriotes obscurus (Coleoptera: Elateridae). Journal of Economic Entomology, 100, 31–38.
Escribano, A., Williams, T., Goulson, D., Cave, R. D., Chapman, J. W., & Caballero, P. (1999). Selection of a nucleopolyhedrovirus for control of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): structural, genetic and biological comparison of four isolates from the Americas. Journal of Economic Entomology, 92, 1079–1085.
Evans, H., & Shapiro, M. (1994). Viruses. In L. A. Lacey (Ed.), Manual of techniques in insect pathology (pp. 17–53). Toronto, Canada: Academic Press.
Finney, D. J. (1964). Probit analysis. London, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Fuxa, J. R. (1982). Prevalence of viral infection in populations of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, in southeastern Louisiana. Environmental Entomology, 11, 239–242.
García, J. F., Grisoto, E., Vendramim, J. D., & Machado, B. P. S. (2006). Bioactivity of neem, Azadirachta indica, against spittlebug Mahanarva fimbriolata (Hemiptera: Cercopidae) on sugarcane. Journal of Economic Entomology, 99, 2010–2014.
Hamm, J. J. (1999). Interactions in entomology: Enhanced infectivity of entomopathogenic viruses by fluorescent brighteners. Journal of Entomological Science, 34, 8–16.
Hamm, J. J., & Young, J. R. (1971). Value of virus presilk treatment for corn earworm and fall armyworm in sweet corn. Journal of Economic Entomology, 64, 144–146.
Hruska, A. J., & Gould, F. (1997). Fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and Diatraea lineolata (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): impact of larval population level and temporal occurrence on maize yield in Nicaragua. Journal of Economic Entomology, 90, 611–622.
Hummel, H. E., Hein, D. F., & Schmutterer, H. (2012). The coming of age of azadirachtins and related tetranortriterpenoids. Journal of Biopesticides, 5, 82–87.
Hummelbrunner, L. A., & Isman, M. B. (2001). Acute, sublethal, antifeedant, and synergistic effects of monoterpenoid essential oil compounds on tobacco cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49, 715–720.
Hunter-Fujita, F. R., Entwistle, P. F., Evans, H. F., & Crook, N. E. (1998). Insect viruses and pest management. Chichester, UK: John Wiley and Sons.
Juan, A., Sans, A., & Riba, M. (2000). Antifeedant activity and seed extracts of Melia azedarach and Azadiractha indica on larvae of Sesamia nonagrioides. Phytoparasitica, 28, 311–319.
Lacey, L. A., Frutos, R., Kaya, K. H., & Vails, P. (2001). Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Do they have a future? Biological Control, 21, 230–248.
Martínez, A. M., Goulson, D., Chapman, J. W., Caballero, P., Cave, R. D., & Williams, T. (2000). Is it feasible to use optical brightener technology with a baculovirus bioinsecticide for resource-poor maize farmers in Mesoamerica? Biological Control, 17, 174–181.
Martínez, A. M., Simón, O., Williams, T., & Caballero, P. (2003). Effect of optical brighteners on the insecticidal activity of a nucleopolyhedrovirus in three instars of Spodoptera frugiperda. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 109, 139–146.
Martínez, S. S., & van Emden, H. F. (1999). Sublethal concentrations of azadirachtin affect food intake, conversion efficacy and feeding behavior of Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera. Noctuidae). Bulletin of Entomological Research, 89, 65–71.
McConnell, R., & Hruska, A. (1993). An epidemic of pesticide poisoning in Nicaragua: Implications for prevention in developing countries. American Journal of Public Health, 83, 1559–1562.
Méndez, W. A., Valle, J., Ibarra, J. E., Cisneros, J., Penagos, D. I., & Williams, T. (2002). Spinosad and nucleopolyhedrovirus mixtures for control of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in maize. Biological Control, 25, 195–206.
Mordue, A. J., Simmonds, M. S. J., Ley, S. V., Blaney, W. M., Mordue, M., Nasiruddin, M., et al. (1998). Actions of azadirachtin, a plant allelochemical, against insects. Pesticide Science, 54, 277–284.
Morgan, E. D. (2009). Azadirachtin, a scientific gold mine. Bioorganic & Medical Chemistry, 17, 4096–4105.
Moscardi, F. (1999). Assessment of the application of baculoviruses for control of Lepidoptera. Annual Review of Entomology, 44, 257–289.
Pineda, S., Martínez, A. M., Figueroa, J. I., Schneider, M. I., Del Estal, P., Viñuela, E., et al. (2009). Influence of azadirachtin and methoxyfenozide on life parameters of Spodoptera littoralis. Journal of Economic Entomology, 102, 1490–1496.
Poitout, S., & Bues, R. (1974). Elevage de chenilles de vingt-huit espèces de lépidoptères Noctuidae. Annales de Zoologie Ecologie Animale, 6, 341–411.
Possee, R. D., Grififiths, C. M., Hichman, R. B., Chambers, A., Murguia-Meca, F., Danquah, J., et al. (2010). Baculoviruses: biology, replication, and exploitation. In S. Asgarim & K. Johnson (Eds.), Insect virology (pp. 35–57). Norfolk, UK: Caister Academic Press.
Raffa, K. F. (1987). Influence of host plant on deterrence by azadirachtin of feeding by fall armyworm larvae. Journal of Economic Entomology, 80, 384–387.
Robertson, J. L., & Preisler, H. K. (1992). Pesticide bioassays with arthropods. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press.
Schmutterer, H. (1990). Properties and potential of natural pesticides from the neem tree, Azadirachta indica. Annual Review of Entomology, 35, 271–297.
Senthil-Kumar, N., Murugan, K., & Zhang, W. (2008). Additive interaction of Helicoverpa armigera nucleopolyedrovirus and azadirachtin. BioControl, 53, 869–880.
Senthil-Nathan, S., & Kalaivani, K. (2005). Efficacy of nucleopolyhedrovirus (NPV) and azadirachtin on Spodoptera litura Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Biological Control, 34, 93–98.
Senthil-Nathan, S., & Kalaivani, K. (2006). Combined effects of azadirachtin and nucleopolyhedrovirus (SpltNPV) on Spodoptera litura Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. Biological Control, 36, 94–104.
Senthil-Nathan, S., Kalaivani, K., & Chung, P. G. (2005). The effects of azadirachtin and nucleopolyhedrovirus on midgut enzymatic profile of Spodoptera litura Fab. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 83, 46–57.
Shapiro, M., Robertson, J. L., & Webb, R. E. (1994). Effect of neem seed extract upon the gypsy moth (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) and its nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Journal of Economic Entomology, 87, 356–360.
Software, L. O. (1987). POLO-PC. A user’s guide to probit or logit analysis. Berkeley, CA, USA: LeOra Software.
Subrahmanyam, B., & Ramakrishnan, N. (1981). Influence of a baculovirus infection on molting and food consumption by Spodoptera litura. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 38, 161–168.
Szewczyk, B., Hoyos-Carvajal, L., Paluszek, M., Skrzecz, W., & De Souza, M. L. (2006). Baculoviruses – re-emerging biopesticides. Biotechnology Advances, 24, 143–160.
Trisyono, A., & Whalon, M. (1999). Toxicity of neem applied alone and in combinations with Bacillus thuringiensis to Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Journal of Economic Entomology, 92, 1281–1288.
Wanner, K. W., Helson, B. V., & Harris, B. J. (2000). Laboratory and field evaluation of spinosad against the gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar. Pest Management Science, 56, 855–860.
Wilcox, C. D., Brent, S., Dove, W., McDavid, D., & Greer, D. B. (2002). Image Tool version 3.0. San Antonio, TX, USA: University of Texas Health Science Center.
Williams, T., Goulson, D., Caballero, P., Cisneros, J., Martínez, A. M., Chapman, J. W., et al. (1999). Evaluation of a baculovirus bioinsecticide for small scale maize growers in Latin America. Biological Control, 14, 67–75.
Zamora, M. C., Martínez, A. M., Nieto, M. S., Schneider, M. I., Figueroa, J. I., & Pineda, S. (2008). Actividad de algunos insecticidas biorracionales contra el gusano cogollero. Revista Fitotecnia Mexicana, 31, 351–357.
Zamora-Avilés, N., Alonso-Vargas, J., Pineda, S., Isaac-Figueroa, J., & Martínez, A. M. (2013). Effects of a nucleopolyhedrovirus in mixtures with azadirachtin on Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae and viral occlusion body production. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 23, 521–534.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported financially by the Coordinación de la Investigación Científica, Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo. The authors are
grateful to Angel Rebollar Alviter, who helped to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pineda, S., Pérez-Robledo, C.A., Hernández, R.E. et al. Combined and individual effects of a nucleopolyhedrovirus and azadirachtin on the mortality and maize-leaf consumption of Spodoptera frugiperda . Phytoparasitica 42, 571–578 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-014-0395-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-014-0395-4