Abstract
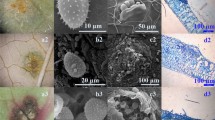
Epidemic outbreaks of rust disease have been observed in most of the black cottonwood (Populus trichocarpa) plantations in the south of China in recent years. However, the exact pathogens that cause rust disease in this area remain largely unknown. In this study we collected rust fungi from black cottonwood plantations at four different places in the south of China. Examination of these fungi by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and light microscopy (LM) revealed that the morphological characteristics of urediniospores for all the collected fungi were very close to that of Melampsora larici-populina. Using species-specific primers, these pathogens were confirmed to be M. larici-populina. In a survey on the resistance to rust disease for 88 genotypes of black cottonwood, nine potential candidate genotypes were detected that may be free from infection of rust pathogen. The results of this study provide essential information for breeding new rust-resistant black cottonwood cultivars.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyle, B., Hamelin, R. C., & Séguin, A. (2005). In vivo monitoring of obligate biotrophic pathogen growth by kinetic PCR. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 1546–1552.
Cao, Z. M., & Li, Z. Q. (1999). Rust fungi of Qinling Mountains. Beijing, China: China Forestry Publishing House [in Chinese].
Cervera, M. T., Sewell, M. M., Faivre-Rampant, P., Storme, V., & Boerjan, W. (2004). Genome mapping in Populus. In S. Kumar & M. Flandung (Eds.), Molecular genetics and breeding of forest trees (pp. 387–410). Binghamton, UK: Food Products Press.
Dowkiw, A., & Bastien, C. (2004). Characterization of two major genetic factors controlling quantitative resistance to Melampsora larici-populina leaf rust in hybrid poplars: strain-specificity, field expression, combined effects, and relationship with a defeated qualitative resistance gene. Phytopathology, 94, 1358–1367.
Fresa, R. (1936). Argentine Republic: Melampsora larici-populina in the Delta of Parana. International Bulletin of Plant Protection, 10, 145–146.
Gérard, P. R., Husson, C., Pinon, J., & Frey, P. (2006). Comparison of genetic and virulence diversity of Melampsora larici-populina populations on wild and cultivated poplar and influence of the alternate host. Phytopathology, 96, 1027–1036.
Gibson, I. A. S., & Waller, J. M. (1972). Notes from ODA plant pathology liaison offcers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 18, 336–337.
Hanley, S. J., Pei, M. H., Powers, S. J., Ruiz, C., Mallott, M. D., Barker, J. H. A., et al. (2011). Genetic mapping of rust resistance loci in biomass willow. Tree Genetics & Genomes, 7, 597–608.
Huo, J. F., & Wang, M. D. (1934). A preliminary list of fungi in north China. Annals of the Research Council National University of Peking, 1, 1–22.
Kern, F. D., & Thurston, H. W. (1954). Additional species of Uredinales from Colombia. Mycologia, 46, 354–357.
Kirk, P. M., Cannon, P. F., David, J. C., & Stalpers, J. A. (2001). Ainsworth & Bisby’s dictionary of the fungi (9th ed.). Wallingford, UK: CAB International.
Lefevre, F., Gouemourier, M. C., Faivre-Rampant, P., & Villar, M. (1998). A single gene cluster controls incompatibility and partial resistance to various Melampsora larici-populina races in hybrid poplars. Phytopathology, 88, 156–163.
Liu, T. N., & Wang, Y. Z. (1935). Materials for study on rusts of China (III). Contributions from the Institute of Botany, National Academy of Peking, 3, 353.
Lloyd, H. L. (1971). New records of Rhodesian fungi. 1. Melampsora larici-populina Klebahn. Kirkia, 8, 1–2.
Miura, M. (1928). Flora of Manchuria and East Mongolia. Part III, Cryptogams, fungi. South Manchuria Railway Co. (in Japanese).
Miyake, I. (1914). Uber Chinensiche Pilze. Botanical Magazine Tokyo, 28, 37–56.
Newcombe, G. (1996). The specificity of fungal pathogens of Populus. In R. F. Stettler, H. D. Bradshaw, P. E. Heilman, & T. M. Hinckley (Eds.), Biology of Populus and its implications for management and conservation (pp. 223–246). Ottawa, Canada: NRC Research Press.
Newcombe, G., & Chastagner, G. A. (1993a). First report of the Eurasian poplar leaf rust fungus, Melampsora larici-populina, in North America. Plant Disease, 77, 532–535.
Newcombe, G., & Chastagner, G. A. (1993b). A leaf rust epidemic of hybrid poplar along the lower Columbia River caused by Melamspora medusae. Plant Disease, 77, 528–531.
Pinon, J., & Frey, P. (2005). Interaction between poplar clones and Melampsora populations and their implication for breeding for durable resistance. In M. H. Pei & A. R. McCracken (Eds.), Rust diseases of willow and poplar (pp. 139–154). Cambridge, UK: CABI Publishing.
Pinon, J., Newcombe, G., & Chastagner, G. A. (1994). Identification of races of Melampsora larici-populina, the Eurasian rust fungus, on Populus species in California and Washington. Plant Disease, 78, 101.
Pinon, J., & Valadon, A. (1997). Comportement des cultivars de peupliers commercialisables dans l’Union européenne vis-à-vis de quelques parasites majeurs. Annals of Forest Science, 54, 19–38.
Pinon, J., van Dam, B. C., Genetet, I., & de Kam, M. (1987). Two pathogenic races of Melampsora larici-populina in northwestern Europe. European Journal of Forest Pathology, 17, 47–53.
Shang, Y. Z., Hao, J. Z., & Yuan, X. Y. (1990). Melampsora on poplars in NeiMonggol. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 5, 86–92 (in Chinese).
Shang, Y. Z., Pei, M. H., & Yuan, Z. W. (1986). A new rust fungus on poplars. Acta Mycologica Sinica Supplement, 1, 180–184.
Shang, Y. Z., Yuan, X. Y., & Hao, J. Z. (1986). Taxonomy of Melampsora on Populus. Journal of Inner Mongolia Forestry College, 8, 126–133 (in Chinese).
Spegazzini, C. (1918). Cuarta contribución a la Micología chilena. Revista Chilena de Historia Natural, 22, 95–104.
Spiers, A. G. (1998). Melampsora and Marssonina pathogens of poplars and willows in New Zealand. European Journal of Forest Pathology, 28, 233–240.
Stirling, B., Newcombe, G., Vrebalov, J., Bosdet, I., & Bradshaw, H. D., Jr. (2001). Suppressed recombination around the MXC3 locus, a major gene for resistance to poplar leaf rust. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 103, 1129–1137.
Tai, F. L. (1979). Sylloge Fungorum Sinicorum. Beijing, China: Science Press, Academia Sinica (in Chinese).
Tian, C. M., Shang, Y. Z., Zhuang, J. Y., Wang, Q., & Kakishima, M. (2004). Morphological and molecular phylogenetic analysis of Melampsora species on poplars in China. Mycoscience, 45, 56–66.
Tuskan, G. A., Difazio, S., Jansson, S., Bohlmann, J., Grigoriev, I., Hellsten, U., et al. (2006). The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science, 313, 1556–1604.
Villar, M., Lefevre, F., Bradshaw, H. D., Jr., & Ducros, E. T. (1996). Molecular genetics of rust resistance in poplars (Melampsora larici-populina Kleb./Populus sp.) by bulked segregant analysis in a 2 × 2 factorial mating design. Genetics, 143, 531–536.
Walker, J. (1975). Melampsora larici-populina. In Description of pathogenic fungi and bacteria. Kew, UK: Commonwealth Mycological Institute / Association of Applied Biology.
Walker, J., Hartigan, D., & Bertus, A. L. (1974). Poplar rusts in Australia with comments on potential conifer rusts. European Journal of Forest Pathology, 4, 100–118.
Wilkinson, A. G., & Spiers, A. G. (1976). Introduction of the poplar rusts Melampsora larici-populina and M. medusae to New Zealand and their subsequent distribution. New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science, 19, 195–198.
Xie, C. T., & Liu, X. F. (1997). Integrated control technique of poplar diseases in China. Journal of Forest Research, 8, 171–173.
Yin, T. M., DiFazio, S. P., Gunter, L. E., Jawdy, S. S., Boerjan, W., & Tuskan, G. A. (2004). Genetic and physical mapping of Melampsora rust resistance genes in Populus and characterization of linkage disequilibrium and flanking genomic sequence. New Phytologist, 164, 95–105.
Yu, Z. D., Liu, X. Y., & Cao, Z. M. (2006). ISSR marker and ITS sequence study of Melampsora larici-populina. Agricultural Sciences in China, 5, 847–854.
Yuan, Y. (1984). On identification of some species of Melampsora infecting poplar trees in China and a test of host range of M. pruinosae. Journal of Beijing Forestry College, 6, 48–82 (in Chinese).
Zhang, J., Steenackers, M., Storme, V., Neyrinck, S., Van Montagu, M., Gerats, T., et al. (2001). Fine mapping and identification of nucleotide binding site/leucine-rich repeat sequences at the MER locus in Populus deltoides S9-2. Phytopathology, 91, 1069–1073.
Acknowledgments
Funds for this work are provided by the Forestry Public Welfare Project (201204311), NSFC project (31125008), 973 project (2012CB114505) and the PCSIRT program funded by the Educational Department of China. It is also supported by the Doctorate Fellowship Foundation (2011YB018) and PAPD program at Nanjing Forestry University. Special thanks go to the editor and anonymous reviewers for their help in preparing the final revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhibing Wan and Yiran Li have contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Z., Li, Y., Chen, Y. et al. Melampsora larici-populina, the main rust pathogen, causes loss in biomass production of black cottonwood plantations in the south of China. Phytoparasitica 41, 337–344 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-013-0294-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-013-0294-0