Abstract
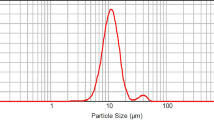
Using specially designed mechanochemical ball-mill equipment, ultramicro molybdenum carbide (MoC) powders were prepared by high-energy ball milling from pure molybdenum powders in civil coal gas atmosphere at room temperature. The structure and the particle size of the powders were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Transmission Electron microscopy (TEM). The results showed that after milling for 30 h, the MoC powders of hexagonal structure were obtained, and their average particle size was around 100 nm. It was found that chemisorption of CO in coal gas onto the fresh molybdenum surfaces created by milling was the predominant processes during the solid-gas reaction, and the energy input due to the introduction of highly dense grain boundaries and lattice defects provided the activation energy for the transition from Mo-C chemisorption to MoC. A coating was formed on the 40Cr steel base using plasma spray by mixing Ni60 alloy powders and ultramicro MoC powders of 5 wt.%, 10 wt.%, and 15 wt.%, respectively. Coating abrasion tests under the condition of dry-grinding, 2 h wear time, and 300 N load showed that the wear resistance property of the coating added with ultramicro MoC powders could be improved greatly, and the wear resistance property of the coating increased with the increase of ultramicro MoC content. The wear mechanisms of ultramicro MoC coating is mainly plough wear and flaking wear assisted. In the abrasion process, the evenly distributed ultramicro MoC particles play a dispersion strengthening and self-lubricating role in the coating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toth L.E., Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides, Academic Press, New York, 1971: 30.
Cao W.C., An G., and Liu G.J., The properties, applications and preparation methods of molybdenum carbide and molybdenum nitride, Chin. Moly. Ind., 2006, 30(5): 45.
Lee J.S., Yeom M.H., Park K.Y., Nam I.S., Chung J.S., Kim T.G., and Moon S.H., Preparation and benzene hydrogenation activity of supported molybdenum carbide catalysts, J. Catal., 1991, 128: 126.
Oyama S.T., The Chemistry of Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides, Blackie Academic and Professional, Glasgow, 1996: 25.
Sarangapani S., Tilak B.V., and Chen C.P., Materials for electrochemical capacitors, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, 143(11): 3791.
El-Eskandarany M.S., Sumiyama K., Aoki K., Masumoto T., and Suzuki K., Mechanism of solid-gas reaction for formation of metastable niobium-nitride alloy powders by reactive ball milling, J. Mater. Res., 1994, 9(11): 2891.
Yang H.M., Qiu G.Z., and Wang D.Z., Development of the mechano-chemistry of super-fine crushing, Met. Mine, 2000 (9): 21.
Xiong R.G., You X.Z, and Dong J.X., Mechanochemistry and its application, Chemistry, 1995, 4: 7.
Liu L., Study on nitriding reactions of Ta-N2 by mechanical activation, Acta Phys. Sin., 2002, 51(3): 603.
Wu X.M., Chen J., Zhuge L.T., and Yao W.G., Solid-gas reaction of Nb and N2 during ball milling procedure, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1999, 7(1): 83.
An G. and Liu G.J, Ultramicro molybdenum nitride powder prepared using high-energy mechanochemical method, Rare Met., 2008, 27(3): 303.
Wang Z.T and Chen H.H, Microstructure and wear-resistant properties of induction clad micro-nanostructured composite coating, Power Metall. Techol., 2006, 24(1): 32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, G., Liu, G. Preparation of ultramicro molybdenum carbide powders and study on wear properties of their coating. Rare Metals 30, 262–266 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-011-0379-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-011-0379-1