Abstract
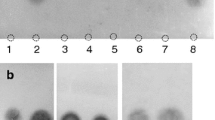
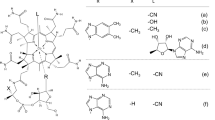
We determined the vitamin B12 content in both the muscles and head innards of various shrimp species [Argis lar (Owen, 1839); Togezako shrimp, Argis toyamaensis (Yokoya, 1933); Pandalopsis japonica, Balss, 1914; Pandalus eous Makarov, 1935] using a microbiological assay based on Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis ATCC7830. Approximately 2–4 µg vitamin B12/100 g wet weight—a considerable amount—was detected in shrimp muscles. The shrimp head innards contained significantly higher levels of vitamin B12 (~ 12–33 µg/100 g wet weight). Commercially available shrimp-innard products contained ~ 30 µg vitamin B12/100 g wet weight. We purified vitamin B12 compounds from the extracts of shrimp muscles and head innards using an immunoaffinity column. The muscle extract contained only one corrinoid compound, which was identified as vitamin B12 using liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization/tandem mass spectrometry, whereas the shrimp head innards contained three corrinoid compounds, which included large amounts of vitamin B12 and two smaller amounts of vitamin B12-d-monocarboxylic acid and tentatively identified vitamin B12 dicarboxylic acids.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton DL, Hogenkamp HPC, Walker TE, Matwiyoff NA (1980) Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the monocarboxylic acids of cyanocobalamin. Assignments of the b-, d-, and e-monocarboxylic acids. J Am Chem Soc 102:2215–2219
Bernhauer K, Wagner F, Beisbarth H, Rietz P, Vogelmann H (1966) Zur Chemie und Biochemie der Corrinoide XXVI. Darstellung und Charakterisierung von Corrinoidcarbonsauren. Biochem Z 344:289–309
Bito T, Tanioka Y, Watanabe F (2018) Characterization of vitamin B12 compounds from marine foods. Fish Sci 84:747–755
Bourre JME, Paquotte PM (2008) Contributions (in 2005) of marine and fresh water products (finfish and shellfish, seafood, wild and farmed) to the French dietary intakes of vitamins D and B12, selenium, iodine and docosahexaenoic acid: impact on public health. Int J Food Sci Nutr 59:491–501
Butcherine P, Benkendorff K, Kelaher B, Barkla BJ (2019) The risk of neonicotinoid exposure to shrimp aquaculture. Chemosphere 217:329–348
Heal KR, Qin W, Ribalet F, Bertagnolli AD, Coyote-Maestas W, Hmelo LR, Moffett JW, Devol AH, Armbrust EV, Stahl DA, Ingalls AE (2017) Two distinct pools of B12 analogs reveal community interdependencies in the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:364–369
Institute of Medicine (1998) Vitamin B12. Dietary reference intakes for thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, pantothenic acid, biotin, and choline. Institute of Medicine, National Academies Press, Washington, DC, pp 306–356
Kaymaci S, Altun BE (2016) Seasonal variation in the accumulation of trace elements and contaminants in five shrimp species from Iskenderun Bay and their consumibility as human food. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97:237–243
Kolhouse JF, Allen RH (1977) Absorption, plasma transport, and cellular retention of cobalamin analogues in rabbit: evidence for the existence of multiple mechanisms that prevent the absorption and tissue dissemination of naturally occurring cobalamin analogues. J Clin Invest 60:1381–1392
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (2010) In: Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan-2010. The Council for Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Tokyo, pp 174–176 (in Japanese)
Saido H, Watanabe F, Tamura Y, Manai Y, Nakano Y (1993) Effects of vitamin B12 analogues with alternations in the side chains of the corrin ring on urinary methylmalonate excretion in vitamin B12-deficient rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57:607–610
Scheers N, Lindqvist H, Langkilde AM, Undeland I, Sandberg AS (2014) Vitamin B12 as a potential compliance marker for fish intake. Eur J Nutr 53:1327–1333
Teng F, Tanioka Y, Hamaguchi N, Bito T, Takenaka S, Yabuta Y, Watanabe F (2015) Determination and characterization of vitamin B12 compounds in edible sea snails, ivory shell Babylonia japonica and turban shell Turdo Batillus cornutus. Fish Sci 81:1105–1111
Watanabe F, Bito T (2016) Corrinoids in food and biological samples. In: Atta-ur-Rahman X (ed) Frontiers in natural product chemistry, vol 2. Bentham, Sharjah, pp 229–244
Watanabe F, Bito T (2018a) Vitamin B12 sources and microbial interaction. Exp Biol Med 243:148–158
Watanabe F, Bito T (2018b) Determination of cobalamin and related compounds in foods. J AOAC Int 101:1308–1313
Watanabe F, Nakano Y, Stupperich E (1992) Different corrinoid specificities for cell growth and the cobalamin uptake system in Euglena gracilis Z. J Gen Microbiol 138:1807–1813
Watanabe F, Katsura H, Takenaka S, Fujita T, Abe K, Tamura Y, Nakatsuka T, Nakano Y (1999) Pseudovitamin B12 is the predominant cobamide of an algal health food, Spirulina tablets. J Agric Food Chem 47:4736–4741
Watanabe F, Yabuta Y, Bito T, Teng F (2014) Vitamin B12-containing plant food sources for vegetarians. Nutrients 6:1861–1873
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI grant number 16K07736 (to F. W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N. O. and N. H. performed most of the experiments. Y. U. and S. T. analyzed the B12 compounds using LC/ESI–MS/MS and interpreted the results. N. O., T. B., and F. W. designed the experiments, interpreted the results, and wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed and commented on the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okamoto, N., Hamaguchi, N., Umebayashi, Y. et al. Determination and characterization of vitamin B12 in the muscles and head innards of edible shrimp. Fish Sci 86, 395–406 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-019-01397-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-019-01397-x