Abstract
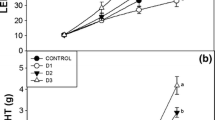
We conducted a 12-week feeding trial to evaluate the effects of total fishmeal replacement with different corn co-products on growth performance, feed utilization efficiency, and body composition in juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Five isonitrogenous diets were prepared. Fifty percent of the dietary protein was obtained from fishmeal (control diet) or from one of four corn co-products (experimental diets), namely corn protein concentrate, corn gluten meal, high-protein distillers’ dried grains (HPDDG), or distillers’ dried grains with solubles (DDGS). Fish with an initial mean weight of 4.5 g were fed one of the five diets twice a day to near satiety. Significantly higher (P < 0.05) specific growth rates and survival occurred in the fish fed the control diet or DDGS, followed by those fed the HPDDG; mean feed intakes by fish in these three groups were significantly greater than those in the others. Food conversion ratio, protein efficiency ratio, and total amino acid content of the whole body were not affected by changes in dietary ingredients. Whole-body and fillet protein contents were highest in the HPDDG group, whereas the lipid content was highest in those fed DDGS. DDGS can be used to fully replace the fishmeal components of Nile tilapia diets.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu YV, Rosati R, Sessa DJ, Brown P (1994) Utilization of protein-rich ethanol co-products from corn in tilapia feed. J Am Oil Chem Soc 71:1041–1043
Wu YV, Rosati RR, Brown PB (1996) Effect of diets containing various levels of protein and ethanol coproducts from corn on growth of tilapia fry. J Agric Food Chem 44:1491–1493
Tidwell JH, Coyle SD, VanArnum A, Weibel C, Harkins S (2000) Growth, survival, and body composition of cage-cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus fed pelleted and unpelleted distillers grains with solubles in polyculture with freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. J World Aquac Soc 31:627–631
Richter N, Siddhuraju P, Becker K (2003) Evaluation of nutritional quality of moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam.) leaves as an alternative protein source for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Aquaculture 217:599–611
Schaeffer TW, Brown ML, Rosentrater KA, Muthukumarappan K (2010) Utilization of diets containing graded levels of ethanol production co-products by Nile tilapia. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 94:e348–e354
Lu F, Haga Y, Satoh S (2015) Effects of replacing fish meal with rendered animal protein and plant protein sources on growth response, biological indices, and amino acid availability for rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Sci 81:95–105
Plaipetch P, Yakupitiyage A (2014) Effect of replacing soybean meal with yeast-fermented canola meal on growth and nutrient retention of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus 1758). Aquac Res 45:1744–1753
Xu Z, Lin X, Lin Q, Yang Y, Wang Y (2007) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and energy waste outputs of four marine cage-cultured fish fed with trash fish. Aquaculture 263:130–141
Pereira T, Oliva-Teles A (2003) Evaluation of corn gluten meal as a protein source in diets for gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) juveniles. Aquac Res 34:1111–1117
Robinson PH, Karges K, Gibson ML (2008) Nutritional evaluation of four co-product feedstuffs from the motor fuel ethanol distillation industry in the Midwestern USA. Anim Feed Sci Technol 146:345–352
Shiau S-Y, Chuang J-L, Sun C-L (1987) Inclusion of soybean meal in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus) diets at two protein levels. Aquaculture 65:251–261
Robinson EH, Li MH (2008) Replacement of soybean meal in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, diets with cottonseed meal and distiller’s dried grains with solubles. J World Aquacult Soc 39:521–527
Cheng ZJ, Hardy RW (2004) Nutritional value of diets containing distiller’s dried grain with solubles for rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. J Appl Aquac 15:101–113
Tacon AG, Metian M (2008) Global overview on the use of fish meal and fish oil in industrially compounded aquafeeds: trends and future prospects. Aquaculture 285:146–158
Twibell RG, Brown PB (1998) Optimal dietary protein concentration for hybrid tilapia Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus fed all-plant diets. J World Aquac Soc 29:9–16
Wu YV, Rosati RR, Sessa DJ, Brown PB (1995) Evaluation of corn gluten meal as a protein source in tilapia diets. J Agric Food Chem 43:1585–1588
Coyle SD, Mengel GJ, Tidwell JH, Webster CD (2004) Evaluation of growth, feed utilization, and economics of hybrid tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus, fed diets containing different protein sources in combination with distillers dried grains with solubles. Aquac Res 35:365–370
Jobling M (2012) National Research Council (NRC): nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. Aquac Int 20:601–602
AOAC International (1995) Official methods of analysis. AOAC International, Arlington
Boonyoung S, Haga Y, Satoh S (2013) Preliminary study on effects of methionine hydroxy analog and taurine supplementation in a soy protein concentrate-based diet on the biological performance and amino acid composition of rainbow trout [Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum)]. Aquac Res 44:1339–1347
Carter C, Houlihan D, Kiessling A, Médale F, Jobling M (2001) Chapter 13: Physiological effects of feeding. In: Food intake in fish. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp 297–331
De la Higuera M (2001) Effects of nutritional factors and feed characteristics on feed intake. Food Intake Fish 827:250–268
Santiago CB, Lovell RT (1988) Amino acid requirements for growth of Nile tilapia. J Nutr 118:1540–1546
Prachom N, Haga Y, Satoh S (2013) Impact of dietary high protein distillers dried grains on amino acid utilization, growth response, nutritional health status and waste output in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac Nutr 19:62–71
Gómez-Requeni P, Mingarro M, Calduch-Giner J, Médale F, Martin S, Houlihan D, Kaushik S, Pérez-Sánchez J (2004) Protein growth performance, amino acid utilisation and somatotropic axis responsiveness to fish meal replacement by plant protein sources in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 232:493–510
Wu YV, Rosati RR, Brown PB (1997) Use of corn-derived ethanol coproducts and synthetic lysine and tryptophan for growth of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fry. J Agric Food Chem 45:2174–2177
Weigel J, Loy D, Kilmer L (2005) Feed co-products of the dry corn milling process. Iowa State University/Iowa Corn Promotion Board, Ames/Johnston
Weigel JC, Loy D, Kilmer LH (1997) Feed co-products of the dry corn milling process. Iowa Corn Growers Association/Renewable Fuels Association/National Corn Growers Association, Johnston/Washington, DC/St. Louis
Belyea RL, Rausch KD, Tumbleson ME (2004) Composition of corn and distillers dried grains with solubles from dry grind ethanol processing. Bioresour Technol 94:293–298
Han J, Liu K (2010) Changes in composition and amino acid profile during dry grind ethanol processing from corn and estimation of yeast contribution toward DDGS proteins. J Agric Food Chem 58:3430–3437
Abdel-Tawwab M, Abdel-Rahman AM, Ismael NEM (2008) Evaluation of commercial live bakers’ yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a growth and immunity promoter for fry Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) challenged in situ with Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 280:185–189
Lim C, Garcia JC, Yildirim-Aksoy M, Klesius PH, Shoemaker CA, Evans JJ (2007) Growth response and resistance to Streptococcus iniae of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, fed diets containing distiller’s dried grains with solubles. J World Aquac Soc 38:231–237
He J-Y, Han B, Tian L-X, Yang H-J, Zeng S-L, Liu Y-J (2014) The sparing effect of cystine on methionine at a constant TSAA level in practical diets of juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac Res 47:2031–2039
Likongwe JS, Stecko TD, Stauffer JR Jr, Carline RF (1996) Combined effects of water temperature and salinity on growth and feed utilization of juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linneaus). Aquaculture 146:37–46
Fontainhas-Fernandes A, Gomes E, Reis-Henriques MA, Coimbra J (1999) Replacement of fish meal by plant proteins in the diet of Nile tilapia: digestibility and growth performance. Aquac Int 7:57–67
Furuya WM, Pezzato LE, Barros MM, Pezzato AC, Furuya VR, Miranda EC (2004) Use of ideal protein concept for precision formulation of amino acid levels in fish-meal-free diets for juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Aquac Res 35:1110–1116
Jobling M (2001) Feed composition and analysis. Food Intake Fish 827:1–24
Acknowledgments
The Scholarship received by the first author from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan for her doctoral degree is gratefully acknowledged. This study was partly funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research given to Shuichi Satoh from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology through the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (26252034) and the “Development of Aquaculture Technology for Food Security and Food Safety for the Next Generation” project of the SATREPS program of JST and JICA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herath, S.S., Haga, Y. & Satoh, S. Potential use of corn co-products in fishmeal-free diets for juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus . Fish Sci 82, 811–818 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-016-1008-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-016-1008-6