Abstract
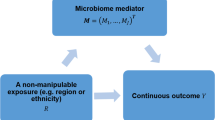
Mediation analysis has been commonly used to study the effect of an exposure on an outcome through a mediator. In this paper, we are interested in exploring the mediation mechanism of microbiome, whose special features make the analysis challenging. We consider the isometric logratio transformation of the relative abundance as the mediator variable. Then, we present a de-biased Lasso estimate for the mediator of interest and derive its standard error estimator, which can be used to develop a test procedure for the interested mediation effect. Extensive simulation studies are conducted to assess the performance of our method. We apply the proposed approach to test the mediation effect of human gut microbiome between the dietary fiber intake and body mass index.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitchison J (1986) The statistical analysis of compositional data. Chapman and Hall, London
Aitchison J (1999) Logratios and natural laws in compositional data analysis. Math Geol 31:563–580
Barfield R, Shen J, Just A, Vokonas P, Schwartz J, Baccarelli A, VanderWeele T, Lin X (2017) Testing for the indirect effect under the null for genome-wide mediation analyses. Genet Epidemiol 41:824–833
Baron R, Kenny D (1986) The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical consideration. J Personal Soc Psychol 51:1173–1182
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B 57:289–300
Boca S, Sinha R, Cross A, Moore S, Sampson J (2014) Testing multiple biological mediators simultaneously. Bioinformatics 30:214–220
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R et al (2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 10:57–9
Chai HT, Jiang HM, Lin L, Liu L (2018) A marginalized two-part beta regression model for microbiome compositional data. PLoS Comput Biol 14:e1006329
Cao Y, Lin W, Li H (2018) Large covariance estimation for compositional data via composition-adjusted thresholding. J Am Stat Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.2018.1442340
Chen EZ, Li H (2016) A two-part mixed-effects model for analyzing longitudinal microbiome compositional data. Bioinformatics 32:2611–2617
Chén O, Crainiceanu C, Ogburn E, Caffo B, Wager T, Lindquist M (2018) High-dimensional multivariate mediation with application to neuroimaging data. Biostatistics 19(2):121–136
Coffman D, Zhong W (2012) Assessing mediation using marginal structural models in the presence of confounding and moderation. Psychol Methods 17:642–664
Egozcue J, Pawlowsky-Glahn V, Mateu-Figueras G, Barceló-Vidal C (2003) Isometric logratio transformations for compositional data analysis. Math Geol 35:279–300
Fan J, Lv J (2008) Sure independence screening for ultrahigh dimensional feature space. J Royal Stat Soc 70:849–911
Fritz M, Kenny D, MacKinnon D (2016) The combined effects of measurement error and omitting confounders in the single-mediator model. Multivar Behav Res 51:681–697
Gu F, Preacher K, Ferrer E (2014) A state space modeling approach to mediation analysis. J Educ Behav Stat 39:117–143
Hron K, Filzmoser P, Thompson K (2012) Linear regression with compositional explanatory variables. J Appl Stat 39:1115–1128
Hr\(\mathring{{\rm u}}\)zová K, Todorov V, Hron K, Filzmoser P (2016) Classical and robust orthogonal regression between parts of compositional data. Statistics 50:1261–1275
Huang Y, Pan W (2016) Hypothesis test of mediation effect in causal mediation model with high-dimensional continuous mediators. Biometrics 72:402–413
Hochberg Y (1988) A sharper Bonferroni procedure for multiple tests of significance. Biometrika 75:800–802
Imai K, Keele L, Tingley D (2010) A general approach to causal mediation analysis. Psychol Methods 15:309–334
Ismail N, Ragab S, ElBaky A, Shoeib A, Alhosary Y, Fekry D (2011) Frequency of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in gut microbiota in obese and normal weight Egyptian children and adults. Arch Med Sci 7:501–507
Lin W, Shi P, Feng R, Li H (2014) Variable selection in regression with compositional covariates. Biometrika 101:785–797
Liu L, Shih YCT, Strawderman RL, Zhang DW, Johnson B, Chai H (2019) Statistical analysis of zero-inflated continuous data: a review. Stat Sci 34:253–279
MacKinnon D, Lockwood C, Hoffman J, West S, Sheets V (2002) A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychol Methods 7:83–104
MacKinnon D, Lockwood C, Williams J (2004) Confidence limits for the indirect effect: distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivar Behav Res 39:99–128
MacKinnon D (2008) Introduction to statistical mediation analysis. Erlbaum and Taylor Francis Group, New York
Mandal S, Treuren W, White R, Eggesbø M, Knight R, Peddada S (2015) Analysis of composition of microbiomes: a novel method for studying microbial composition. Microbial Ecol Health Dis 26(1):27663
Martín-Fernández J, Barceló-Vidal C, Pawlowsky-Glahnm V (2003) Dealing with zeros and missing values in compositional data sets using nonparametric imputation. Math Geol 35:253–278
Mert M, Filzmoser P, Endel G, Wilbacher I (2018) Compositional data analysis in epidemiology. Stat Methods Med Res 27:1878–1891
Morais J, Thomas-Agnan C, Simioni M (2018) Using compositional and Dirichlet models for market share regression. J Appl Stat 45:1670–1689
Preacher K, Hayes A (2008) Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods 40:879–891
Preacher K (2015) Advances in mediation analysis: a survey and synthesis of new developments. Annu Rev Psychol 66:825–852
Reid S, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (2016) A study of error variance estimation in lasso regression. Stat Sin 26:35–67
Sampson J, Boca S, Moore S, Heller R (2018) FWER and FDR control when testing multiple mediators. Bioinformatics 34:2418–2424
Sobel M (1982) Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. Sociol Methodol 13:290–312
Sohn M, Li H (2019) Compositional mediation analysis for microbiome studies. Ann Appl Stat 13:661–681
Tang Z, Chen G, Alekseyenko A, Li H (2017) A general framework for association analysis of microbial communities on a taxonomic tree. Bioinformatics 33:1278–1285
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B 58:267–288
Trompette A, Gollwitzer E, Yadava K et al (2014) Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat Med 20:159–166
Tsilimigras M, Fodor A (2016) Compositional data analysis of the microbiome: fundamentals, tools, and challenges. Ann Epidemiol 26:330–335
VanderWeele T (2009) Marginal structural models for the estimation of direct and indirect effects. Epidemiology 20:18–26
VanderWeele T (2016) Mediation analysis: a practitioner’s guide. Annu Rev Public Health 37:17–32
Wang T, Zhao H (2017) Constructing predictive microbial signatures at multiple taxonomic levels. J Am Stat Assoc 112:1022–1031
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen Y-Y, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R et al (2011) Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 334:105–108
Yun Y, Kim H, Kim S et al (2017) Comparative analysis of gut microbiota associated with body mass index in a large Korean cohort. BMC Microbiol 17:151
Zhang C-H (2010) Nearly unbiased variable selection under minimax concave penalty. Ann Stat 38:894–942
Zhang C-H, Zhang S (2014) Confidence intervals for low dimensional parameters in high dimensional linear models. J R Stat Soc Ser B 76:217–242
Zhang H, Zheng Y, Zhang Z, Gao T, Joyce B, Yoon G, Zhang W, Schwartz J, Just A, Colicino E, Vokonas P, Zhao L, Lv J, Baccarelli A, Hou L, Liu L (2016) Estimating and testing high-dimensional mediation effects in epigenetic studies. Bioinformatics 32:3150–3154
Zhang J, Wei Z, Chen J (2018) A distance-based approach for testing the mediation effect of the human microbiome. Bioinformatics 34:1875–1883
Zhao Y, Luo X (2016) Pathway Lasso: estimate and select sparse mediation pathways with high-dimensional mediators.arXiv:1603.07749v1, Preprint
Zou H, Hastie T (2005) Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J R Stat Soc Ser B 67:301–320
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Editor, the Associate Editor, and two reviewers for their constructive and insightful comments and suggestions that greatly improved the manuscript. Research reported in this publication was supported by the NIH R21 AG063370 and UL1 TR002345. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official view of the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Chen, J., Li, Z. et al. Testing for Mediation Effect with Application to Human Microbiome Data. Stat Biosci 13, 313–328 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12561-019-09253-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12561-019-09253-3