Abstract
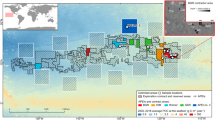
Sponge assemblages associated with coralligenous outcrops were studied with the aim of describing and comparing their composition, morphological features and distribution at different depths (shallow vs. deep) along the Apulian coasts. In addition, image analysis enabled the description of the main features of coralligenous outcrops and the detection of structuring species. The paper provides a significant contribution in terms of supplying new taxa of sponges associated to coralligenous assemblages and emphasising the importance of invertebrates in realising calcareous constructions. Most of the new finding came from deep sites, thus underlining the need to improve taxonomic studies on coralligenous communities at greater depths. A total of 153 taxa of sponges were recorded: 4 Calcarea, 6 Homoscleromorpha and 143 Demospongiae. Two species, Clathria (Microciona) macrochela and Thoosa armata, are new records for the Italian sponge fauna, with C. (M.) macrochela representing a new record for the whole Mediterranean. New findings for the Ionian and Adriatic Seas totalled 25 and 8 species, respectively. Thirty-nine species are endemic for the Mediterranean. Data analyses clustered sites into two groups, separated according to the depth. Deep sites, characterised by animal dominance, exhibit a heterogeneous substrate texture richer in cavities than the shallow and homogeneous algal ones. Differences in sponge species composition also correspond to differences in the distribution of sponge growth forms, with the insinuating cryptic species more abundant in deeper communities. Ten of 15 sponge species included in national and international wildlife protection laws and policy have been detected in the present study.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
AA VV (2014) Biocostruzioni Marine in Puglia (BIOMAP). P.O FESR 2007/2013- ASSE IV. Linea 4.4- Interventi per la rete ecologica. Final technical report
Annicchiarico R (1980) Poriferi del fondo coralligeno dei mari della Puglia. Thalass Salent 10:113–120
Balata D, Piazzi L, Cecchi E, Cinelli F (2005) Variability of Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages subject to local variation in sediment deposition. Mar Environ Res 60:403–421. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2004.12.005
Baldacconi R, Corriero G (2009) Effects of the spread of the alga Caulerpa racemosa Var. cylindracea on the sponge assemblage from coralligenous concretions of the Apulian coast (Ionian Sea, Italy). Mar Ecol 30:337–345
Ballesteros E (2006) Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages: a synthesis of present knowledge. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 44:123–195
Ballesteros E, Zabala M (1993) El bentos: el marc físic. In: Alcover JA et al (eds) Història Natural de l’Arxipèlag de Cabrera. CSIC-Ed. Moll, Palma de Mallorca, pp 663–685
Barcelona Convention (1978). Convention for the protecion of the Mediterranean Sea against Pollution, Annex II and III. February 12, 1978. Accessed 5 Dec 2016 at http://www.specieaspim.it
Bern Convention (1979). Convention on the conservation of European wildlife and natural habitats. September 19, 1979. Bern, Switzerland
Bertolino M, Cerrano C, Bavestrello G et al (2013) Diversity of Porifera in the Mediterranean coralligenous accretions, with description of a new species. ZooKeys 336:1–37
Bertolino M, Calcinai B, Cattaneo-Vietti R et al (2014) Stability of the sponge assemblage of the Mediterranean coralligenous along a millennial span of time. Mar Ecol 35:149–159. doi:10.1111/maec.12063
Boudouresque CF (2004) Marine biodiversity in the Mediterranean: status of species, populations and communities. Scientific Reports of Port-Cros National Park 20:97–146
Boury-Esnault N, Rützler K (1997) Thesaurus of sponge morphology. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington D.C. doi:10.5479/si.00810282.596
Calcinai B, Bertolino M, Bavestrello G et al (2015) Comparison between the sponge fauna living outside and inside the coralligenous bioconstruction: a quantitative approach. Mediterr Mar Sci 16(2):413–418
Campiani E, Foglini F, Fraschetti S et al (2014) Conservation and management of coralligenous habitat: experience from the BIOMAP Project. Habitat mapping for conservation and management purposes 5th - 9th May, 2014 Lorne, Victoria, Australia
Cánovas Molina AC, Montefalcone M, Vassallo P et al (2016) Combining literature review, acoustic mapping and in situ observations: an overview of coralligenous assemblages in Liguria (NW Mediterranean Sea). Sci Mar 80(1). doi:10.3989/scimar.04235.23A
Cerrano C, Bavestrello G, Bianchi CN et al (2001) The role of sponge bioerosion in Mediterranean coralligenous accretion. In: Faranda FM et al (eds) Mediterranean ecosystems: structures and processes. Springer, Italia, pp 235–240
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
CMEMS, Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service 2016. http://marine.copernicus.eu/. Accessed 10 Dec 2016
Cocito S, Lombardi C (2007) Competitive interactions in the coralligenous assemblages of S.M. Leuca (Ionian Sea). Biol Mar Mediterr 14(2):176–177
Coll M, Piroddi C, Steenbeek J et al (2010) The biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: estimates, patterns, and threats. PLoS ONE 5(8):e11842. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011842
Corriero G, Scalera Liaci L (1997) Cliona parenzani n. sp. (Porifera, Hadromerida) from the Ionian Sea. Ital J Zool 64(1):69–73
Corriero G, Scalera Liaci L, Ruggiero D, Pansini M (2000) The sponge community of a semi submerged Mediterranean cave. Mar Ecol 21(1):85–96
Corriero G, Gherardi M, Giangrande A et al (2004) Inventory and distribution of hard bottom fauna from the marine protected area of Porto Cesareo (Ionian Sea): Porifera and Polychaeta. Ital J Zool 71:237–245
Dring MJ (1981) Chromatic adaptation of photosynthesis in benthic marine algae: an examination of its ecological significance using a theoretical model. Limnol Oceanogr 26:271–284
Ferdeghini F, Acunto S, Cocito S, Cinelli F (2000) Variability at different spatial scales of a coralligenous assemblage at Giannutri Island (Tuscan archipelago, northwest Mediterranean). Hydrobiologia 440:27–36. doi:10.1023/A:1004124423718
Fredj G, Meinardi M, Manas R (2002) Medifaune: une banque de données sur la faune marine méditerranéenne. In: Fredj G (ed) Premières journées d’étude des producteurs français de banque de données biologiques factuelles. D’Olmo, Saint Laurent du Var, pp 115–145
Gerovasileiou V, Voultsiadou E (2012) Marine caves of the Mediterranean Sea: a sponge biodiversity reservoir within a biodiversity hotspot. PLoS ONE 7(7):e39873
Giakoumi S, Sini M, Gerovasileiou V et al (2013) Ecoregion-based conservation planning in the Mediterranean: dealing with large-scale heterogeneity. PLoS ONE 8(10):e76449
Gili JM, Ballesteros E (1991) Structure of cnidarian populations in Mediterranean sublittoral benthic communities as a result of adaptation to different environmental conditions. Oecol Aquat 10:243–254
Hong JS (1980) Étude faunistique d’un fond de concrétionnement de type coralligène soumis à un gradient de pollution en Méditerranée nord-occidentale (Golfe de Fos). PhD Thesis, University of Aix-Marseille II
Hong JS (1982) Contribution à l’étude des peuplements d’un fond coralligène dans la région marseillaise en Méditerranée Nord-Occidentale. Bull Korean Ocean Res Dev Inst 4:27–51
Kersting DK, Linares C (2012) Cladocora caespitosa biocostructions in the Columbretes Islands marine reserve (Spain, NW Mediterranean): distribution, size structure and growth. Mar Ecol 33:427–436
Kipson S, Fourt M, Teixidò N et al (2011) Rapid biodiversity assessment and monitoring method for highly diverse benthic communities: a case study of Mediterranean coralligenous outcrops. PLoS ONE 6(11):e27103
Labate M (1967) Poriferi del coralligeno adriatico pugliese. Boll Zool 34:127
Laborel J (1961) Le concretionnement algal “coralligène” et son importance géomorphologique en Méditerranée. Rec Trav St Mar Endoume 23(37):37–60
Laborel J (1987) Marine biogenic constructions in the Mediterranean. Scientific Reports of Port-Cros National Park 13:97–126
Laubier L (1966) Le coralligène des Albères: monographie biocénotique. Ann Inst Oceanogr (Paris) 43:139–316
Lüning K (1981) Light. In: Lobban CS, Wynne MJ (eds) The biology of seaweeds. Blackwell, London, pp 326–355
Martí R, Uriz MJ, Ballesteros E, Turon X (2004) Benthic assemblages in two Mediterranean caves: species diversity and coverage as a function of abiotic parameters and geographic distance. J Mar Biol Ass UK 84:557–572
Martí R, Uriz MJ, Ballesteros E, Turon X (2005) Seasonal variation in structure of three algal communities under different light conditions. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 64:613–622
Martin CS, Giannoulaki M, De Leo F et al (2014) Coralligenous and maërl habitats: predictive modelling to identify their spatial distributions across the Mediterranean Sea. Sci Rep 4:50–73. doi:10.1038/srep05073
Pansini M, Longo C (2003) A review of the Mediterranean Sea sponge biogeography with, in appendix, a list of the demosponges hitherto recorded from this sea. In: Nuova Immagine (ed) Biogeographia, marine biogeography of the Mediterranea Sea: patterns and dynamics of biodiversity, vol XXIV. Tavarnelle Val Di Pesa, Florence, pp 59–90
Pansini M, Longo C (2008) Porifera. In: Relini G (ed) Checklist della flora e della fauna dei mari italiani. Biol Mar Medit 15(1): 42–66
Pansini M, Pesce LG (1998) Higginsia ciccaresi sp. nov. (Porifera: Demospongiae) from a marine cave on the Apulian coast (Mediterranean Sea). J Mar Biol Ass UK 78:1083–1091
Peirano A, Morri C, Bianchi CN, Rodolfo-Metalta R (2001) Biomass, carbonate standing stock and production of the Mediterranean coral Cladocora caespitosa (L.) Facies 44:75–80
Pérès JM, Picard J (1964) Nouveau manuel de bionomie benthique de la Mer Méditerranée. Rec Trav St Mar Endoume 31:1–137
Sarà M (1968) Un coralligeno di piattaforma (coralligène de plateau) lungo il littorale pugliese. Arch Oceanogr Limnol 15(suppl):139–150
Sarà M (1969) Research on coralligenous formation: problems and perspectives. Pubbl Staz Zool Napoli 37:124–134
Sarà M (1973) Sponge population of the Apulian coralligenous formations. Rapporto Della Commissione Internazionale per Il mar Mediterraneo 21:613–615
Sarà M (1999) Il ruolo dei Poriferi nella biodiversità, struttura e dinamica del coralligeno Mediterraneo. Biol Mar Medit 6(1):144–150
Sartoretto S (1996) Vitesse de croissance et bioérosion des concrétionnements “coralligènes” de Méditerranée nord-occidentale. Rapport avec les variations Holocènes du niveau marin. Thèse Doctorat d’Écologie, Université d’Aix-Marseille II
Underwood AJ (1997) Experiments in ecology: their logical design and interpretation using analysis of variances. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
UNEP-MAP-RAC/SPA (2003) The coralligenous in the Mediterranean Sea. Regional Activity Centre for Specially Protected Areas, Tunis
UNEP-MAP-RAC/SPA (2008) Action plan for the conservation of the coralligenous and other calcareous bio-concretions in the Mediterranean Sea. Regional Activity Centre for Specially Protected Areas, Tunis
UNEP-MAP-RAC/SPA (2015) Updated Action plan for the conservation of the coralligenous and other calcareous bio-concretions in the Mediterranean Sea. Regional Activity Centre for Specially Protected Areas, Tunis
Van Soest RWM, Boury-Esnault N, Hooper JNA et al (2016) World Porifera Database. http://www.marinespecies.org/porifera. Accessed 2 Dec 2016
Virgilio M, Airoldi L, Abbiati M (2006) Spatial and temporal variations of assemblages in a Mediterranean coralligenous reef and relationships with surface orientation. Coral Reefs 25:265–272. doi:10.1007/s00338-006-0100-2
Voultsiadou E (2009) Reevaluating sponge diversity and distribution in the Mediterranean Sea. Hydrobiologia 628:1–12
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Robert Domin for critical reading and the English review of the manuscript. This work was partially funded by CoNISMa as part of Marine Strategy Framework Directive.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Piraino
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Longo, C., Cardone, F., Pierri, C. et al. Sponges associated with coralligenous formations along the Apulian coasts. Mar Biodiv 48, 2151–2163 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-017-0744-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-017-0744-x