Abstract
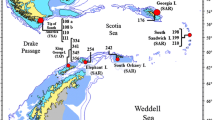
During the austral summer of 2005, the Weddell deep sea and adjacent basins were sampled in the course of the ANDEEP III project. In this study, 19 epibenthic-sledge stations are analyzed, with a focus on species diversity and distribution patterns of polychaetes. The polychaete fauna of the deep Southern Ocean has been found to be similarly speciose and diverse compared with deep-sea basins worldwide. Also, in depths below 2,000 m many polychaete species do not seem to be endemic for certain areas but are rather far spread within the Southern Ocean and beyond. Therefore, ongoing faunal exchanges between adjacent basins, even beyond the Antarctic convergence, are strongly suggested, ruling out a general isolation of the Southern Ocean deep-sea benthos. Driving forces behind species distribution patterns were investigated. The findings indicate that polychaete species’ distribution in the Southern Ocean deep sea is rather dependent on local environment than depths.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alongi DM (1992) Bathymetric patterns of deep-sea benthic communities from bathyal to abyssal depths in the western South Pacific (Solomon and Coral Seas). Deep-Sea Res 39(3/4):549–565. doi:10.1016/0198–0149(92)90088-B
Borowski C, Thiel H (1998) Deep-sea macrofaunal impacts of a large-scale physical disturbance experiment in the Southeast Pacific. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 45:55–81. doi:10.1016/S0967-0645(97)00073-8
Brandt A, Schnack K (1999) Macrofaunal abundance at 79°N off East Greenland: opposing data from epibenthic-sledge and box-corer samples. Polar Biol 22:75–81. doi:10.1007/s003000050392
Brandt A, Brenke N, Andres H-G et al (2005) Diversity of peracarid crustaceans (Malacostraca) from the abyssal plain of the Angola Basin. Org Divers Evol 5:105–112. doi:10.1016/j.ode.2004.10.007
Brandt A, Ebbe B, Gooday AJ (2007a) Introduction to ANDEEP, summary and outlook. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1645–1651. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.001
Brandt A, Gooday AJ, Brandao SN et al (2007b) First insights into the biodiversity and biogeography of the Southern Ocean deep sea. Nature 447(17):307–311. doi:10.1038/nature05827
Brandt A, Brix S, Brökeland W et al (2007c) Deep-sea isopoda biodiversity, abundance, and endemism in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean—Results from ANDEEP I-III expeditions. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1760–1775. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.015
Brandt A, De Broyer C, De Mesel I et al (2007d) The biodiversity of the deep Southern Ocean benthos. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B 362:39–66. doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.1952
Bray JR, Curtis JT (1957) An ordination of the upland forest of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol Monogr 27:225–349. doi:10.2307/1942268
Brenke N (2005) An epibenthic sledge for operations on marine soft bottom and bedrock. Mar Technol Soc 39(2):13–24
Brey T, Dahm C, Gorney M et al (1996) Do Antarctic benthic invertebrates show an extended level of eurybathy? Antarct Sci 8(1):3–6
Brökeland W, Choudhury M, Brandt A (2007) Composition, abundance and distribution of Peracarida from the Southern Ocean deep sea. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1752–1759. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.014
Clarke A, Crame JA (1992) The Southern Ocean benthic fauna and climate change: a historical perspective. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B 338:299–309. doi:10.1098/rstb.1992.0150
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006). Primer v6: user manual/tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth, pp 1–190
Cosson-Sarradin N, Sibuet M, Paterson GLJ et al (1998) Polychaete diversity at tropical Atlantic deep-sea sites: environmental effects. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 165:173–185. doi:10.3354/meps165173
Ellingsen KE, Brandt A, Ebbe B et al (2007) Diversity and species distribution of polychaetes, isopods and bivalves in the Atlantic sector of the deep Southern Ocean. Polar Biol 30(10):1265–1273. doi:10.1007/s00300–007–0287-x
Gallagher ED (1996) Compah 96: a users manual: 37 (http://www.es.umb.edu/edgwebp.htm)
Glover A, Paterson G, Bett B et al (2001) Patterns in polychaete abundance and diversity from the Madeira Abyssal Plain, northeast Atlantic. Deep Sea Res Part I Oceanogr Res Pap 48:217–236. doi:10.1016/S0967–0637(00)00053–4
Gooday AJ, Cedhagen T, Maneskaya OE et al (2007) The biodiversity and biogeography of komokiaceans and other enigmatic foraminiferan-like protests in the deep Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1691–1719. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.003
Hardy OJ (2007) BiodivR 1.0. A program to compute statistically unbiased indices of species diversity within sample and species similarity between samples using rarefaction principles. http://www.ulb.ac.be/sciences/ecoevol/biodivr.html
Hartman O (1964) Polychaeta Errantia of Antarctica. Antarct Res Ser 3:1–131
Hartman O (1966) Polychaeta Myzostomida and Sedentaria of Antarctica. Antarct Res Ser 7:1–158
Hartman O (1967) Polychaetous annelids collected by the USNS ELTANIN and Staten Island cruises, chiefly from Antarctic Seas. Allan Hancock Monogr Mar Biol 2:1–387
Hartman O (1978) Polychaeta from the Weddell Sea Quadrant, Antarctica. Paper 4 in: Biology of the Antarctic Seas VI. Antarct Res Ser 26:125–223
Hartmann-Schröder G, Rosenfeldt P (1988) Die Polychaeten der “Polarstern”-Reise ANT III/2 in die Antarktis 1984. Teil 1: Euphrosinidae bis Chaetopteridae. Mitt Hamb Zool Mus Inst 85:25–72
Hartmann-Schröder G, Rosenfeldt P (1989) Die Polychaeten der “Polarstern”-Reise ANT III/2 in die Antarktis 1984. Teil 2: Cirratulidae bis Serpulidae. Mitt Hamb Zool Mus Inst 86:65–106
Hartmann-Schröder G, Rosenfeldt P (1990) Die Polychaeten der “Walther Herwig”-Reise 68/1 nach Elephant Island (Antarktis) 1985. Teil 1: Aphroditidae bis Cirratulidae. Mitt Hamb Zool Mus Inst 87:89–122
Hartmann-Schröder G, Rosenfeldt P (1991) Die Polychaeten der “Walther Herwig”-Reise 68/1 nach Elephant Island (Antarktis) 1985. Teil 2: Acrocirridae bis Sabllidae. Mitt Hamb Zool Mus Inst 88:73–96
Hartmann-Schröder G, Rosenfeldt P (1992) Die Polychaeten der “Polarstern”-Reise ANT V/1 in die Antarktis 1986. Teil 1: Euphrosinidae bis Iphitimidae. Mitt Hamb Zool Mus Inst 89:85–124
Herring P (2002) The biology of the deep ocean.. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hessler RR, Jumars PA (1974) Abyssal community analysis from replicate box cores in the central north Pacific. Deep-Sea Res 21:185–209
Hessler RR, Sanders HL (1967) Faunal diversity in the deep-sea. Deep-Sea Res 14:65–78
Hilbig B (2001) Deep-sea polychaetes in the Weddell Sea and Drake Passage: first quantitative results. Polar Biol 24:538–544. doi:10.1007/s003000100259
Hilbig B (2004) Polychaetes of the deep Weddell and Scotia Seas- composition and zoogeographical links. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 51:1817–1825. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2004.07.015
Hilbig B, Blake JA (2006) Deep-sea Polychaete communities in the northeast Pacific ocean off the Gulf of the Farallones, California. Bull Mar Sci 78(2):243–269
Hilbig B, Gerdes D, Montiel A (2006) Distributional patterns and biodiversity in polychaete communities of the Weddell Sea and Antarctic Peninsula area (Southern Ocean). J Mar Biol Assoc U K 86:711–725. doi:10.1017/S0025315406013610
Howe JA, Wilson CR, Shimmield TM et al (2007) Recent deep-water sedimentation, trace metal and radioisotope geochemistry across the Southern Ocean and Northern Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1652–1681. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.007
Hurlbert SH (1971) The nonconcept of species diversity: a critique and alternative parameters. Ecology 52:577–586. doi:10.2307/1934145
Janussen D, Tendal OS (2007) Diversity and distribution of Porifera in the bathyal and abyssal Weddell Sea (Southern Ocean). Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1864–1875. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.012
Jumars PA (1975) Environmental grain and polychaete species’ diversity in a bathyal benthic community. Mar Biol (Berl) 30:253–266. doi:10.1007/BF00390748
Kröncke I, Türkay M (2003) Structural and functional aspects of the benthic communities in the deep Angola Basin. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 260:43–53. doi:10.3354/meps260043
Kruskal JB (1964) Multidimensioning scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Psychometrika 29:1–27. doi:10.1007/BF02289565
Levin LA, Edesa S (1997) The ecology of cirratulid mudballs on the Oman margin, northwest Arabian Sea. Mar Biol (Berl) 128:671–678. doi:10.1007/s002270050134
Linse K, Brandt A, Bohn J et al (2007) Macro- and megabenthic communities in the abyssal Weddell Sea (South Atlantic). Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1848–1863. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.011
Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of species diversity in different types of biological collections. J Theor Biol 13:131–144. doi:10.1016/0022–5193(66)90013–0
Rex MA (1981) Community structure in the deep-sea benthos. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 12:331–353. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.12.110181.001555
Rodriguez E, López-González PJ, Gili JM (2007) Biogeography of Antarctic sea anemones (Anthozoa, Actiniaria): What do they tell us about the origin of the Antarctic benthic fauna? Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1876–1904. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.013
Schüller M, Ebbe B (2007) Global distributional patterns of selected deep-sea polychaeta (Annelida) from the Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1737–1751. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.005
Schwabe E, Bohn JM, Engl W et al (2007) Rich and rare—First insights into species diversity and abundance of Antarctic abyssal Gastropoda (Mollusca). Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 54(16–17):1831–1847. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.010
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Smith CR, De Leo FC, Bernardino AF et al (2008) Abyssal food limitation, ecosystem structure and climate change. Trends Ecol Evol 962:1–11
Thistle D, Yingst JY, Fauchald K (1985) A deep-sea benthic community exposed to strong bottom currents on the Scotia Rise (Western Atlantic). Mar Geol 66:91–112. doi:10.1016/0025–3227(85)90024–6
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all crew members and participants of the ANDEEP III expedition aboard the RV Polarstern for their great effort and care while sampling the Southern Ocean. Further thanks are due to the Zoological Museum, University of Hamburg for pre-sorting and provision of polychaete samples, as well as to the DZMB, Wilhelmshaven, for the subsequent sample management. This study was funded by the German Science Foundation WA 530/29–1/2 and the Sloan Foundation through the Census of Marine Life field project CeDAMar. This is ANDEEP publication No. 116.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schüller, M., Ebbe, B. & Wägele, JW. Community structure and diversity of polychaetes (Annelida) in the deep Weddell Sea (Southern Ocean) and adjacent basins. Mar Biodiv 39, 95–108 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-009-0009-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-009-0009-4