Abstract
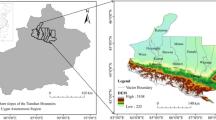
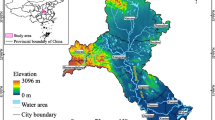
Fractional vegetation cover (FVC) is an important ecological parameter and indication for ecological environment change. As the main part of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Qinghai Province is a more sensitive area of climate change and fragile zone of ecology environment. In this study, multi-temporal satellite data were analyzed to estimate FVC from 2000 to 2013 in Qinghai Province using no-dense & dense model. When 1 < Leaf Area Index (LAI) < 3, the no-dense model was used and dense model was used under other conditions. This study explored the application of MODIS data in FVC estimation. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) data, Fraction of Photosynthetically Active Radiation (FPAR) and Leaf Area Index (LAI) products were acquired from MOD13A1 and MOD15A2. FVC highly related to LAI, light extinction coefficient and FPAR was estimated using no-dense & dense model. Slope map was calculated by multiple years FVC results. The increased tendency of FVC in this area illustrated the improving ecological environment. However, ecological and environmental problems of Qinghai Lake are still needed to be solved.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri, R., Weng, Q., Alimohammadi, A., & Alavipanah, S. K. (2009). Spatial–temporal dynamics of land surface temperature in relation to fractional vegetation cover and land use/cover in the Tabriz urban area, Iran. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(12), 2606–2617.
Asrar, G., Fuchs, M., Kanemasu, E. T., & Hatfield, J. L. (1984). Estimating absorbed photosynthetic radiation and leaf area index from spectral reflectance in wheat. Agronomy Journal, 76(2), 300–306.
Avissar, R., & Verstraete, M. M. (1990). The representation of continental surface processes in atmospheric models. Reviews of Geophysics, 28(1), 35–52.
Baret, F., & Guyot, G. (1991). Potentials and limits of vegetation indices for LAI and APAR assessment. Remote Sensing of Environment, 35(2), 161–173.
Guan, K., Wood, E. F., & Caylor, K. K. (2012). Multi-sensor derivation of regional vegetation fractional cover in Africa. Remote Sensing of Environment, 124, 653–665.
Gutman, G., & Ignatov, A. (1998). The derivation of the green vegetation fraction from NOAA/AVHRR data for use in numerical weather prediction models. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19(8), 1533–1543.
Hoffmann, W. A., & Jackson, R. B. (2000). Vegetation-climate feedbacks in the conversion of tropical savanna to grassland. Journal of Climate, 13(9), 1593–1602.
Hu, J. N., Su, Y., Tan, B., Huang, D., Yang, W. Z., Schull, M., Bull, M. A., Martonchik, J. V., Diner, D. J., Knyazikhin, Y., & Myneni, R. B. (2007). Analysis of the MISR LA/FPAR product for spatial and temporal coverage, accuracy and consistency. Remote Sensing of Environment, 107, 334–347.
Jiang, Z., Huete, A. R., Chen, J., Chen, Y., Li, J., Yan, G., & Zhang, X. (2006). Analysis of NDVI and scaled difference vegetation index retrievals of vegetation fraction. Remote Sensing of Environment, 101(3), 366–378.
Jiapaer, G., Chen, X., & Bao, A. (2011). A comparison of methods for estimating fractional vegetation cover in arid regions. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 151(12), 1698–1710.
Myneni, R. B., Asrar, G., Tanre, D., & Choudhury, B. J. (1992). Remote sensing of solar radiation absorbed and reflected by vegetated land surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 30(2), 302–314.
Peterson, D. L., Spanner, M. A., Running, S. W., & Teuber, K. B. (1987). Relationship of thematic mapper simulator data to leaf area index of temperate coniferous forests. Remote Sensing of Environment, 22(3), 323–341.
Ruimy, A., Kergoat, L., Bondeau, A., & Model, P. O. T. P. N. (1999). Comparing global models of terrestrial net primary productivity (NPP): analysis of differences in light absorption and light‐use efficiency. Global Change Biology, 5(S1), 56–64.
Running, S. W., Peterson, D. L., Spanner, M. A., & Teuber, K. B. (1986). Remote sensing of coniferous forest leaf area. Ecology, 67, 273–276.
Schimel, D. S., House, J. I., Hibbard, K. A., Bousquet, P., Ciais, P., Peylin, P., & Wirth, C. (2001). Recent patterns and mechanisms of carbon exchange by terrestrial ecosystems. Nature, 414(6860), 169–172.
Spanner, M. A., Pierce, L. L., Peterson, D. L., & Running, S. W. (1990). Remote sensing of temperate coniferous forest leaf area index The influence of canopy closure, understory vegetation and background reflectance. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 11(1), 95–111.
Wang, Y., & Zhou, G. (2012). Light use efficiency over two temperate steppes in Inner Mongolia, China. PloS One, 7(8), e43614.
Xiao, J., & Moody, A. (2005). A comparison of methods for estimating fractional green vegetation cover within a desert-to-upland transition zone in central New Mexico, USA. Remote Sensing of Environment, 98(2), 237–250.
Zeng, X., Dickinson, R. E., Walker, A., Shaikh, M., DeFries, R. S., & Qi, J. (2000). Derivation and evaluation of global 1-km fractional vegetation cover data for land modeling. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 39(6), 826–839.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Key Technology R&D Program (2012BAD16B0102); Forestry Public Benefit Scientific Research Special Project of PR China (201504420).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L., Jia, Z., Li, Q. et al. Fractional Vegetation Cover Estimation Based on MODIS Satellite Data from 2000 to 2013: a Case Study of Qinghai Province. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 44, 269–275 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-015-0492-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-015-0492-y