Abstract
Background
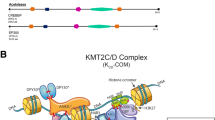
Kabuki syndrome (KS), is a infrequent inherited malformation syndrome caused by mutations in a H3 lysine 4 methylase (KMT2D) or an X-linked histone H3 lysine 27 demethylase (UTX/KDM6A). The characteristics in patients with KS have not yet been well recognized.
Data sources
We used databases including PubMed and Google Scholar to search for publications about the clinical features and the etiology of Kabuki syndrome. The most relevant articles to the scope of this review were chosen for analysis.
Results
Clinical diagnosis of KS is challenging in initial period, because many clinical characteristics become apparent only in subsequent years. Recently, the genetic and functional interaction between KS-associated genes and their products have been elucidated. New clinical findings were reported including nervous system and intellectual performance, endocrine-related disorders and immune deficiency and autoimmune disease. Cancer risks of Kabuki syndrome was reviewed. Meanwhile, we discussed the Kabuki-like syndrome. Digital clinical genetic service, such as dysmorphology database can improve availability and provide high-quality diagnostic services. Given the significant clinical relevance of KS-associated genes and epigenetic modifications crosstalk, efforts in the research for new mechanisms are thus of maximum interest.
Conclusions
Kabuki syndrome has a strong clinical and biological heterogeneity. The main pathogenesis of Kabuki syndrome is the imbalance between switch-on and -off of the chromatin. The direction of drug research may be to regulate the normal opening of chromatin. Small molecule inhibitors of histone deacetylases maybe helpful in treatment of mental retardation and reduce cancer risk in KS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niikawa N, Matsuura N, Fukushima Y. Kabuki makeup syndrome: a syndrome of mental retardation, unusual facies, large and protruding ears, and postnatal growth deficiency. J Pediatr. 1981;99:565–9.
Long A, Sinkovskaya ES, Edmondson AC, Zackai E, Schrier Vergano SA. Kabuki syndrome as a cause of non-immune fetal hydrops/ascites. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170:3333–7.
Ng SB, Bigham AW, Buckingham KJ. Exome sequencing identifies MLL2 mutations as a cause of Kabuki syndrome. Nat Genet. 2010;42:790–3.
Makrythanasis P, van Bon BW. MLL2 mutation detection in 86 patients with Kabuki syndrome: a genotype-phenotype study. Clin Genet. 2013;84:539–45.
Sattur A, Deshmukh PK, Abrahim L. Kabuki make-up syndrome—a case report with electromyographic study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8:ZD03–6.
Paděrová J, Holubová A, Simandlová M, Puchmajerová A. Molecular genetic analysis in 14 Czech Kabuki syndrome patients is confirming the utility of phenotypic scoring. Clin Genet. 2016;90:230–7.
Douzgou S, Pollalis YA, Vozikis A. Collaborative crowdsourcing for the diagnosis of rare genetic syndromes: the DYSCERNE experience. Public Health Genom. 2016;19:19–24.
Michot C, Corsini C, Sanlaville D. Finger creases lend a hand in Kabuki syndrome. Eur J Med Genet. 2013;56:556–60.
Adam MP, Banka S, Bjornsson HT, Bodamer O. Kabuki syndrome: international consensus diagnostic criteria. J Med Genet. 2019;56:89–95.
Kurahashi N, Miyake N, Mizuno S. Characteristics of epilepsy in patients with Kabuki syndrome with KMT2D mutations. Brain Dev. 2017;39:672–7.
Kim J, Lee CG. Coinheritance of novel mutations in SCN1A causing GEFS+ and in KDM6A causing Kabuki syndrome in a family. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2017;47:229–35.
Morgan AT, Mei C, Da Costa A. Speech and language in a genotyped cohort of individuals with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2015;167:1483–92.
Lehman N, Mazery AC, Visier A. Molecular, clinical and neuropsychological study in 31 patients with Kabuki syndrome and KMT2D mutations. Clin Genet. 2017;92:298–305.
Parisi L, Di Filippo T, Roccella M. Autism spectrum disorder in Kabuki syndrome: clinical, diagnostic and rehabilitative aspects assessed through the presentation of three cases. Minerva Pediatr. 2015;67:369–75.
Lin JL, Lee WI, Huang JL, Chen PK. Immunologic assessment and KMT2D mutation detection in Kabuki syndrome. Clin Genet. 2015;88:255–60.
Mock JR, Kolb TM, Illei PB. Bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue in Kabuki syndrome with associated hyper-IgM syndrome/common variable immunodeficiency. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194:514–5.
Lindsley AW, Saal HM, Burrow TA. Defects of B-cell terminal differentiation in patients with type-1 Kabuki syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137(179–87):e10.
Ming JE, Russell KL, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai EH. Autoimmune disorders in Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2005;132:260–2.
Giordano P, Lassandro G, Sangerardi M. Autoimmune haematological disorders in two Italian children with Kabuki syndrome. Ital J Pediatr. 2014;40:10.
Schott DA, Blok MJ, Gerver WJ. Growth pattern in Kabuki syndrome with a KMT2D mutation. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170:3172–9.
Penders B, Schott N, Gerver WJ, Stumpel CT. Body proportions in children with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170:610–4.
Gole H, Chuk R, Coman D. Persistent hyperinsulinism in Kabuki syndrome 2: case report and literature review. Clin Pract. 2016;6:848.
Subbarayan A, Hussain K. Hypoglycemia in Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2014;164A:467–71.
Gohda Y, Oka S, Matsunaga T, Watanabe S. Neonatal case of novel KMT2D mutation in Kabuki syndrome with severe hypoglycemia. Pediatr Int. 2015;57:726–8.
Toda N, Ihara K, Kojima-Ishii K. Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in Beckwith-Wiedemann, Sotos, and Kabuki syndromes: a nationwide survey in Japan. Am J Med Genet A. 2017;173:360–7.
Long A, Sinkovskaya ES, Edmondson AC. Kabuki syndrome as a cause of non-immune fetal hydrops/ascites. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170:3333–7.
Haanpää M, Schlecht H, Batra G, Clayton-Smith J. Interrupted/bipartite clavicle as a diagnostic clue in Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2017;173:1115–8.
Topa A, Samuelsson L, Lovmar L. On the significance of craniosynostosis in a case of Kabuki syndromewith a concomitant KMT2D mutation and 3.2 Mbp de novo 10q22.3q23.1 deletion. Am J Med Genet A. 2017;173:2219–25.
Siminas S, Baillie CT, Turnock R. Kabuki syndrome and anorectal malformations: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Eur J Pediatr Surg Rep. 2015;3:54–8.
McVeigh TP, Banka S, Reardon W. Kabuki syndrome: expanding the phenotype to include microphthalmia and anophthalmia. Clin Dysmorphol. 2015;24:135–9.
Liu S, Hong X, Shen C, Shi Q, Wang J, Xiong F, Qiu Z. Kabuki syndrome: a Chinese case series and systematic review of the spectrum of mutations. BMC Med Genet. 2015;16:26.
Kohei N, Takada H, Hishiki K, Nakashima Y. Spontaneous infection of an atrophic ureter with an ectopic ureteral opening after living-donor renal transplantation in a patient with Kabuki syndrome. Hinyokika Kiyo. 2016;62:455–8.
Bögershausen N, Altunoglu U, Beleggia F. An unusual presentation of Kabuki syndrome with orbital cysts, microphthalmia, and cholestasis with bile duct paucity. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170:3282–8.
Roma D, Palma P, Capolino R, Figà-Talamanca L. Spinal ependymoma in a patient with Kabuki syndrome: a case report. BMC Med Genet. 2015;16:80.
Karagianni P, Lambropoulos V, Stergidou D, Fryssira H. Recurrent giant cell fibroblastoma: malignancy predisposition in Kabuki syndrome revisited. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170A:1333–8.
Bernier FE, Schreiber A, Coulombe J, Hatami A. Pilomatricoma associated with Kabuki Syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:e26–e2727.
Schott DA, Gerver WJM, Stumpel CTRM. Growth hormone therapy in children with Kabuki syndrome: 1-year treatment results. Horm Res Paediatr. 2017;8:258–64.
Martinez SR, Gay MS. Epigenetic mechanisms in heart development and disease. Drug Discov Today. 2015;20:799–811.
Boland MJ, Nazor KL, Loring JF. Epigenetic regulation of pluripotency and differentiation. Circ Res. 2014;115:311–24.
Bevington S, Boyes J. Transcription-coupled eviction of histones H2A/H2B governs V(D)J recombination. EMBO J. 2013;32:1381–92.
Janzen WP, Wigle TJ, Jin J. Epigenetics: tools and technologies. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2010;7:e59–e65.
Kim JH, Lee JH, Lee IS, Lee SB. Histone lysine methylation and neurodevelopmental disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071404.
Ali M, Hom RA, Blakeslee W, Ikenouye L. Diverse functions of PHD fingers of the MLL/KMT2 subfamily. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1843:366–71.
Shinsky SA, Hu M, Vought VE, Ng SB, Bamshad MJ. A non-active-site SET domain surface crucial for the interaction of MLL1 and the RbBP5/Ash2L heterodimer within MLL family core complexes. J Mol Biol. 2014;426:2283–99.
Froimchuk E, Jang Y, Ge K. Histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferase KMT2D. Gene. 2017;627:337–42.
Rangasamy S, D'Mello SR, Narayanan V. Epigenetics, autism spectrum, and neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurotherapeutics. 2013;10:742–56.
Van Laarhoven PM, Neitzel LR, Quintana AM. Kabuki syndrome genes KMT2D and KDM6A: functional analyses demonstrate critical roles in craniofacial, heart and brain development. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24:4443–53.
Micale L, Augello B, Maffeo C, Selicorni A. Molecular analysis, pathogenic mechanisms, and readthrough therapy on a large cohort of Kabuki syndrome patients. Hum Mutat. 2014;35:841–50.
Lederer D, Grisart B, Digilio MC, Benoit V. Deletion of KDM6A, a histone demethylase interacting with MLL2, in three patients with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;13:119–24.
Banka S, Lederer D, Benoit V, Jenkins E. Novel KDM6A (UTX) mutations and a clinical and molecular review of the X-linked Kabuki syndrome (KS2). Clin Genet. 2015;87:252–8.
Miyake N, Koshimizu E, Okamoto N, Mizuno S, Ogata T, Nagai T, et al. MLL2 and KDM6A mutations in patients with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2013;161A:2234–43.
Yang P, Tan H, Xia Y, Yu Q, Wei X, Guo R, Peng Y. De novo exonic deletion of KDM6A in a Chinese girl with Kabuki syndrome: a case report and brief literature review. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170:1613–21.
Smith E, Lin C, Shilatifard A. The super elongation complex (SEC) and MLL in development and disease. Genes Dev. 2011;25:661–72.
Ang SY, Uebersohn A, Spencer CI, Huang Y. KMT2D regulates specific programs in heart development via histone H3 lysine 4 di-methylation. Development. 2016;143:810–21.
Froimchuk E, Jang Y, Ge K. Histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferase KMT2D. Gene. 2017;5:337–42.
Bjornsson HT, Benjamin JS, Zhang L, Weissman J. Histone deacetylase inhibition rescues structural and functional brain deficits in a mouse model of Kabuki syndrome. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:256ra135.
Lintas C, Persico AM. Unraveling molecular pathways shared by Kabuki and Kabuki-like syndromes. Clin Genet. 2018;94:283–95.
Lange L, Pagnamenta AT, Lise S, Clasper S. A de novo frameshift in HNRNPK causing a Kabuki-like syndrome with nodular heterotopia. Clin Genet. 2016;90:258–62.
Dentici ML, Barresi S, Niceta M, Pantaleoni F. Clinical spectrum of Kabuki-like syndrome caused by HNRNPK haploinsufficiency. Clin Genet. 2018;93:401–7.
Baer S, Afenjar A, Smol T, Piton A, Gérard B. Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome as a major cause of syndromic intellectual disability: a study of 33 French cases. Clin Genet. 2018;94:141–52.
Li N, Wang Y, Yang Y, Wang P, Huang H. Description of the molecular and phenotypic spectrum of Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome in Chinese patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018;13:178.
Pagon RA, Graham JM Jr, Zonana J. Coloboma, congenital heart disease, and choanal atresia with multiple anomalies: CHARGE association. J Pediatr. 1981;99:223–7.
Writzl K, Cale CM, Pierce CM, Wilson LC. Immunological abnormalities in CHARGE syndrome. Europ J Med Genet. 2007;50:338–45.
Bögershausen N, Gatinois V, Riehmer V. Mutation Update for Kabuki syndrome genes KMT2D and KDM6A and further delineation of X-linked Kabuki Syndrome subtype 2. Hum Mutat. 2016;37:847–64.
Bögershausen N, Tsai IC, Pohl E, Kiper PÖ, Beleggia F, Percin EF, et al. RAP1-mediated MEK/ERK pathway defects in Kabuki syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:3585–99.
Funding
This study was supported by the Clinical Research Promotion Project of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (no. JQ201810).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WYR collected and analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. XNX revised the layout of the manuscript and edited the format. WJ and WXM designed the study and supervised the drafting of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not needed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YR., Xu, NX., Wang, J. et al. Kabuki syndrome: review of the clinical features, diagnosis and epigenetic mechanisms. World J Pediatr 15, 528–535 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-019-00309-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-019-00309-4