Abstract
Background
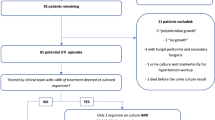
Hyperbilirubinemia is a frequently seen condition in neonates. This study was undertaken to determine the role of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in the etiology of indirect hyperbilirubinemia in neonates with jaundice in their first two weeks of life.
Methods
The study was conducted prospectively. The subjects were neonates aged 4–14 days with hyperbilirubinemia which could not be detected by routine tests and was sufficiently severe to necessitate phototherapy.
Results
The study was performed in 104 neonates, of whom 18% (n=19) had UTI. The most frequently identified micro-organism was Escherichia coli (43%). Phototherapy duration and rebound bilirubin level were higher in neonates with UTI (P<0.05).
Conclusion
UTI should be investigated in neonates with hyperbilirubinemia of unknown etiology in the first two weeks of life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pashapour N, Nikibahksh AA, Golmohammadlou S. Urinary tract infection in term neonates with prolonged jaundice. Urol J 2007;4:91–94.
Ghaemi S, Fesharaki RJ, Kelishadi R. Late onset jaundice and urinary tract infection in neonates. Indian J Pediatr 2007;74:139–141.
Garcia FJ, Nager AL. Jaundice as an early diagnostic sign of urinary tract infection in infancy. Pediatrics 2002;109:846–851.
Bilgen H, Ozek E, Unver T, Biyikli N, Alpay H, Cebeci D. Urinary tract infection and hyperbilirubinemia. Turk J Pediatr 2006;48:51–55.
American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Hyperbilirubinemia. Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics 2004;114:297–316.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Provisional Committee for Quality Improvement and Subcommittee on Hyperbilirubinemia. Practice parameter: management of hyperbilirubinemia in the healthy term newborn. Pediatrics 1994;94:558–565.
Lau AS, Uba A, Lehman D, Geertsma F, Supattapone S. Infectious disease: Urinary tract infections: dysuria and fever. In: Rudolph AM, Kamei RK, eds. Rudolph’s Fundamentals of Pediatrics, 2nd ed. Connecticut: Appleton and Lange, 1998: 301–303.
Nickavar A, Sotoudeh K. Treatment and prophylaxis in pediatric urinary tract infection. Int J Prev Med 2011;2:4–9.
Olusanya O, Owa JA, Olusanya OI. The prevalence of bacteriuria among high risk neonates in Nigeria. Acta Paediatr Scand 1989;78:94–99.
Maisels MJ, Newman TB. Neonatal Jaundice and Urinary Tract Infections. Pediatrics 2003;112:1213–1214.
Sarýcý SÜ, Kul M, Alpay F. Neonatal Jaundice Coinciding With or Resulting From Urinary Tract Infections? Pediatrics 2003;112:1212–1213.
Xinias I, Demertzidou V, Mavroudi A, Kollios K, Kardaras P, Papachristou F, et al. Bilirubin levels predict renal cortical changes in jaundiced neonates with urinary tract infection. World J Pediatr 2009;5:42–45.
Chavalitdhamrong PO, Escobedo MB, Barton LL, Zarkowsky H, Marshall RE. Hyperbilirubinaemia and bacterial infection in the newborn. A prospective study. Arch Dis Child 1975;50:652–654.
Wong RJ, Desandre GH, Sibley E, Stevenson DK. Neonatal Jaundice and Liver Disease. In: Martin R J, Fanoroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin’s Neonatal-Peinatal Medicine Diseases of the Fetus and Infant, 8th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier, 2006: 1419–1465.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mutlu, M., Çayır, Y. & Aslan, Y. Urinary tract infections in neonates with jaundice in their first two weeks of life. World J Pediatr 10, 164–167 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-013-0433-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-013-0433-1