Abstract
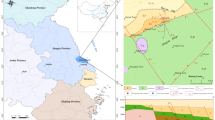
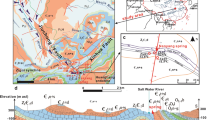
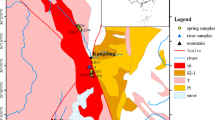
Geothermal water is plentiful in Changbai Mountain region, northeastern China, due to the volcanic activities and widespread faults. For the exploration of geothermal resources, this study uses quartz and cation geothermometer to estimate the temperatures of the geothermal reservoir and uses the tubular models to evaluate the thermal gradient. The hydrogeochemical characteristics of the geothermal resources were also evaluated by hydrogeochemical analysis. The results showed that the geothermal reservoir temperatures of the four major thermal springs in Changbai Mountain region range from 72 to 169 °C. The average geothermal reservoir temperatures of Jinjiang hot springs, Changbai hot springs I, Xianrenqiao hot springs, and Changbai hot springs II are 129.25, 169, 89, and 73.67 °C, respectively. The geothermal gradient values of the four major thermal springs have different characteristics. The geothermal gradient values of Jinjiang hot springs and Changbai hot springs I are 4.6 and 3.1 °C/100 m, respectively. The geothermal gradient values of Xianrenqiao thermal springs and Changbai thermal springs II are both lower than 1.5 °C/100 m, with the values of 1.1 and 1.4 °C/100 m. And the geothermal gradients are influenced by Changbai Mountain Tianchi volcano. In addition, the water chemical analyses showed that the geothermal water types are HCO3-Na with higher concentrations of Na+, Cl−, SO4 2−, TDS, and HCO3 − than the non-thermal waters, which suggested a deep and long water cycle of the thermal water, and therefore a sufficient water-rock interaction.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baioumy H, Nawawi M, Wagner K et al (2015) Geochemistry and geothermometry of non-volcanic hot springs in West Malaysia. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 290:12–22
Bülbül A (2015) Mixing of geothermal and non-geothermal fluids in shallow aquifers in the Germencik-Nazilli area, Büyük Menderes Basin (SW Turkey). Geodin Acta 27(1):67–81
Calmbach L (1997) Aquachem computer code-version 3.7.42. Lewis Publishers, New York
Chen ZQ, Wei HQ, Liu YS et al (2015) A historical pyroclastic flow emplaced within a pre-existing Pleistocene lava tube: Silidong, Tianchi volcano, Changbaishan, northeastern China. Bull Volcanol 77(6):48–58
Donaldson IG (2003) Heat and mass transfer in geothermal circulation systems. Annual review of earth & planetary sciences 10(1):13–17
Fournier RO, Potter RW (1982) Revised and expanded silica (quartz) geothermometer. Bulletin Geothermal Resources Council 11:3–12
Fournier RO, Truesdell AH (1973) An empirical Na-K-ca geothermometer for natural waters. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 37(5):1255–1275
Giggenbach WF (1988) Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-mg-ca geoindicators. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2749–2765
Guo F, Sun JC, Wu CZ et al (2010) The observation and research of escaping gas of hot springs in Tianchi volcanic. Energy and Environment 31:119–120
Jin DC, Cui TR, Jin ML (2003) Observation and research on hot and warm springs in Changbaishan Tianchi volcano. Seismology and Geology 2003(25):122–127
Li T, Liu JQ, Wang XB et al (2015) Geochemical characteristics and genesis of gases from Tianchi volcanic springs, Changbai Mountains, Jilin ,China. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem 34(6):1192–1202
Liu Q, Pan XD, Wei HQ et al (2008) A borehole study on the eruptive sequence from the Tianchi volcano, Changbai Mountain. Earth quake research in China 24(3):235–246
Liu H, Zhao Y, Rao WD et al (2015) Geothermal resource evaluation of Julong springs group in Changbai Mountains of Jilin Province. Jilin Geology 34(3):126–130
Marquer D, Burkhard M (1992) Fluid circulation, progressive deformation and mass-transfer processes in the upper crust: the example of basement-cover relationships in the external crystalline massifs, Switzerland. J Struct Geol 14(8):1047–1057
Qiu GG, Pei FG, Fang H et al (2014) Analysis of magma chamber at the Tianchi volcano area in Changbai Mountain. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014 57(10):3466–3477
Rybach L (1987) Geothermics and geothermal energy. Springer Basel AG 7:1–347
Shuang guan ZG, Zheng YQ, Dong JC (1997) Gas sources of geothermal region in Changbai Tianchi volcanic. China Science 27(4):318–324
Tian F, Tang DP (1989) Petrogenesis of the cenozoic volcanic rocks in the Changbaishan region. Acta Petrol Sin 5(2):49–64
Verma SP, Santoyo E (1997) New improved equations for Na/K, Na/li and SiO2 geothermometers by outlier detection and rejection. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 79:9–23
Wei H, Wang Y, Jin J et al (2007) Timescale and evolution of the intercontinental Tianchi volcanic shield and ignimbrite- forming eruption, Changbaishan, Northeast China. Lithos 96(2):315–324
Zhang YF, Tan HB, Zhang WJ et al (2015) A new geochemical perspective on hydrochemical evolution of the Tibetan geothermal system. Geochem Int 53(2):1090–1106
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the major scientific and technological projects of Jilin Province (0773-1441GNJL00390), by Scientific Research Initiation funds for PhD scholars (BQ2017011); Scientific Research Projects of the Higher University in Hebei (ZD2014023); a Hebei Province Science and Technology Plan Project (15273630); Youth Foundation of Hebei Province Department (QN2017026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, B., Qiu, S., Liu, Z. et al. Characteristics of the geothermal water in Changbai Mountain volcanic region, northeast of China. Arab J Geosci 10, 261 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3039-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3039-4