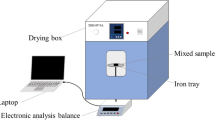
Abstract
Since the adverse factors such as deficient penetration and long reaction time have restricted the complete microwave-used drying of municipal sludge, the microwave-induced drying is considered, which has advantages in such aspects. The investigation of the microwave-induced drying to uncover the mechanism bears great meaning for its development and utilization. The effects of temperature and microwave cracking in municipal sewage sludge drying characteristics are studied through municipal sewage sludge drying experiment. Experiments shows that higher drying temperature would lead to a more acutely changing drying rate (D R). The D R had increased from 0.005 g/(g·min) to 0.060 g/(g·min), which was 12 times enlarged, while the temperature rose from 70 °C to 160 °C. The higher the temperature was, the earlier the peak value of D R appeared. The experiments indicated that the temperature was the decisive factor affecting the D R. The microwave-induced sludge reached the highest D R at the moisture rate (M R) of 40%, with a 20% grade promotion compared with that of the original one. The molecular fracture caused by microwave radiation had obviously accelerated the drying process and the DR was rising in proportion to the microwave radiation dose. The diffusion coefficient had been calculated according to Fick’s law. In comparison to that of the original one, the diffusion coefficient of microwave-induced sludge was obviously enlarged more than two times. By fit examinations, Model Weibull was proven to be the most fit one for thermal thin-layer drying of municipal sludge. By means of Arrhenius equation, the obtained average activation energy of municipal sludge was 37.1 kJ/(mol·K).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akgun N A, Doymaz I, 2005. Modelling of olive cake thin-layer drying process. Journal of Food Engineering, 68(4): 455–461.
Cui Z W, Xu D W, Sun S Y, 2004. Microwave-vacuum drying kinetics of carrot slices. Journal of Food Engineering, 65(2): 157–164.
Doymaz I, Gorel O, Akgun N A, 2004. Drying characteristics of the solid by-product of olive oil extraction. Biosystems Engineering, 88(2): 213–219.
Fonts I, Azuara M, Gea G, Murillo M B, 2009. Study of the pyrolysis liquids obtained from different sewage sludge. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 85(1–2): 184–191.
Hang S J, 2009. Sludge drying characteristics and application of new technologies. Construction Science and Technology, 23: 66–69.
Kahyaoglu T, Kaya S, 2006. Modeling of moisture, color and texture changes in sesame seeds during the conventional roasting. Journal of Food Engineering, 75(2):167–177.
Kong X J, He Q, Cai H X, 2009. Technological status and development for sludge treatment and disposal in municipal waste water treatment Plant. Construction Science and Technology, 19: 57–59.
Léonard A, 2008. Influence of back mixing on the convective drying of residual sludges in a fixed bed. Water Research, 42(10–11): 2671–2677.
Liu K, Ma X Q, Xiao H M, 2011. Experiment and kinetics model analysis on thin layer drying of paper mill sludge. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 39(2): 149–154.
McMinn W A M, 2006. Thin-layer modelling of the convective, microwave, microwave-convective and microwave vacuum drying of lactose powder. Journal of Food Engineering, 72(2): 113–123.
Menéndez J A, Domínguez A, Inguanzo M, Pis J J, 2004. Microwave pyrolysis of sewage sludge: Analysis of the gas fraction. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 71(2): 657–667.
Özbek B, Dadali G, 2007. Thin-layer drying characteristics and modelling of mint leaves undergoing microwave treatment. Journal of Food Engineering, 83(4): 541–549.
Ozkan I A, Akbudak B, Akbudak N, 2007. Microwave drying characteristics of spinach. Journal of Food Engineering, 78(2): 577–583.
Prabhanjan D G, Ramaswamy H S, Raghavan G S V, 1995. Microwave-assisted convective air drying of thin layer carrots. Journal of Food Engineering, 25(2): 283–293.
Ruiz T, Wisniewski C, 2008. Correlation between dewatering and hydro-textural characteristics of sewage sludge during drying. Separation and Purification Technology, 61(2): 204–210.
Wang K J, 2010. Insist on correctly technology direction, steady promoting sludge treatment and disposal work. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 36(10): 1–3, 18.
Wang R, 2010. Study on basic characteristics and technique of sludge drying. Shenyang Institute of Aeronautical Engineering, 5–10.
Wang Y H, Zhang S T, 2007. Advances and prospects of drying process of surplus sludge. Pollution Control Technology, (3): 51–53.
Xiao C L, Tang J L, Pan F, 2011. Effect of microwave irradiation on the penetrability and dewaterability of dewatered municipal sewage sludge. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 11(2): 215–220.
Xie S Z, Zheng X B, Xu C X, 2006. Analysis on the ingredients of the sludge and its recycle in sewage treatment plant. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 34(2): 54–57.
Zhang Y H, 2009. Analysis of the sludge drying and incinerating system. Energy and Environment, (4):76–77, 79.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (50930006)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Hx., Chen, Hp., Hu, Zf. et al. Study on microwave-induced thin-layer drying of municipal sludge for fuel reclamation. J Coal Sci Eng China 18, 307–312 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12404-012-0315-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12404-012-0315-5