Abstract
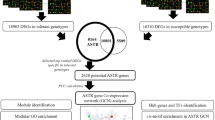
High-throughput transcriptome analyses such as oligonucleotide microarray technology are powerful tools for identifying an entire set of transcripts under given experimental conditions. However, it is not a simple process to interpret which information is important from those large gene sets. Using oligonucleotide arrays, more than 3000 rice microarray data have been produced; all are available for public users from the NCBI gene expression omnibus (GEO; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). In this study, we employed MapMan and RiceNet tools to drive systematic analyses of the early heat stress transcriptome in rice seedlings. We generated transcriptome data to identify 589 genes that respond to early during heat stress, and uploaded the list to various overviews installed in the MapMan tool. In the cellular-response overview, this investigation revealed that the heat stress MapMan term is the most dominant, fitting well to the purpose of transcriptome analysis for examining the early heat stress response. When we applied the regulation overview, we learned that genes associated with transcription factors, protein modification, and calcium regulation are more significantly coupled with early heat stress in rice seedlings. This suggests that essential components, comprising signaling pathways, are mediated by such stress. We also used RiceNet to determine the functional gene network mediated by this stress. This network development was based on genes with enriched MapMan terms, i.e., heat stress, transcription factors, protein modification, and calcium regulation. We expect that applications of MapMan and RiceNet to genome-wide transcriptome data will guide users to identify key elements for further analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affymetrix (2001) Affymetrix Microarray Suite User Guide, Ed, Vol version 5 edition. Affymetrix
AL-Quraan NA, Locy RD, Singh NK (2012) Heat and cold stresses phenotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana calmodulin mutants: regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid shunt pathway under temperature stress. Int J Plant Biol 3:10.4081/pb.2012.e4082
Chauhan H, Khurana N, Agarwal P, Khurana P (2011) Heat shock factors in rice (Oryza sativa L.): genome-wide expression analysis during reproductive development and abiotic stress. Mol Genet Genomics 286:171–187
Chen YJ, Inouye M (2008) The intramolecular chaperone-mediated protein folding. Curr Opin Struc Biol 18:765–770
Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Morsy MR, Song LH, Coutu A, Krizek BA, Lewis MW, Warren D, Cushman J, Connolly EL, Mittler R (2007) The EAR-motif of the Cys2/His2-type zinc finger protein Zat7 plays a key role in the defense response of Arabidopsis to salinity stress. J Biol Chem 282:9260–9268
Coghlin C, Carpenter B, Dundas SR, Lawrie LC, Telfer C, Murray GI (2006) Characterization and over-expression of chaperonin tcomplex proteins in colorectal cancer. J Pathol 210:351–357
Coppolino MG, Dedhar S (1998) Calreticulin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 30:553–558
Cuellar J, Martin-Benito J, Scheres SH, Sousa R, Moro F, Lopez-Vinas E, Gomez-Puertas P, Muga A, Carrascosa JL, Valpuesta JM (2008) The structure of CCT-Hsc70 NBD suggests a mechanism for Hsp70 delivery of substrates to the chaperonin. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:858–864
de la Fuente van Bentem S, Vossen JH, de Vries KJ, van Wees S, Tameling WI, Dekker HL, de Koster CG, Haring MA, Takken FL, Cornelissen BJ (2005) Heat shock protein 90 and its cochaperone protein phosphatase 5 interact with distinct regions of the tomato I-2 disease resistance protein. Plant J 43:284–298
Ding X, Richter T, Chen M, Fujii H, Seo YS, Xie M, Zheng X, Kanrar S, Stevenson RA, Dardick C, Li Y, Jiang H, Zhang Y, Yu F, Bartley LE, Chern M, Bart R, Chen X, Zhu L, Farmerie WG, Gribskov M, Zhu JK, Fromm ME, Ronald PC, Song WY (2009) A rice kinase-protein interaction map. Plant Physiol 149:1478–1492
Fenton WA, Horwich AL (2003) Chaperonin-mediated protein folding: fate of substrate polypeptide. Quart Rev Biophys 36:229–256
Ficklin SP, Luo F, Feltus FA (2010) The association of multiple interacting genes with specific phenotypes in rice using gene coexpression networks. Plant Physiol 154:13–24
Fujita Y, Yoshida T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012) Pivotal role of the AREB/ABF-SnRK2 pathway in ABRE-mediated transcription in response to osmotic stress in plants. Physiol Plant doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01635.x.
Genevaux P, Schwager F, Georgopoulos C, Kelley WL (2002) Scanning mutagenesis identifies amino acid residues essential for the in vivo activity of the Escherichia coli DnaJ (Hsp40) Jdomain. Genetics 162:1045–1053
Gu H, Zhu P, Jiao Y, Meng Y, Chen M (2011) PRIN: a predicted rice interactome network. BMC Bioinformatics 12:161
Guimaraes AJ, Nakayasu ES, Sobreira TJ, Cordero RJ, Nimrichter L, Almeida IC, Nosanchuk JD (2011) Histoplasma capsulatum heat-shock 60 orchestrates the adaptation of the fungus to temperature stress. PloS One 6:e14660
Guo L, Wang ZY, Lin H, Cui WE, Chen J, Liu M, Chen ZL, Qu LJ, Gu H (2006) Expression and functional analysis of the rice plasma-membrane intrinsic protein gene family. Cell Res 16:277–286
Homann U, Tester M (1997) Ca2+-independent and Ca2+/GTPbinding protein-controlled exocytosis in a plant cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:6565–6570
Hossain MA, Lee Y, Cho JI, Ahn CH, Lee SK, Jeon JS, Kang H, Lee CH, An G, Park PB (2010) The bZIP transcription factor OsABF1 is an ABA responsive element binding factor that enhances abiotic stress signaling in rice. Plant Mol Biol 72:557–566
Hu WH, Hu GC, Han B (2009) Genome-wide survey and expression profiling of heat shock proteins and heat shock factors revealed overlapped and stress specific response under abiotic stresses in rice. Plant Sci 176:583–590
Josine TL, Ji J, Wang G, Guan CF (2011) Advances in genetic engineering for plants abiotic stress control. Afr J Biotechnol 10:5402–5413
Jung K-H, An G, Ronald PC (2008a) Towards a better bowl of rice: assigning function to tens of thousands of rice genes. Nat Rev Genet 9:91–101
Jung KH, Dardick C, Bartley LE, Cao P, Phetsom J, Canlas P, Seo YS, Shultz M, Ouyang S, Yuan Q, Frank BC, Ly E, Zheng L, Jia Y, Hsia AP, An K, Chou HH, Rocke D, Lee GC, Schnable PS, An G, Buell CR, Ronald PC (2008b) Refinement of lightresponsive transcript lists using rice oligonucleotide arrays: evaluation of gene-redundancy. PLoS One 3:e3337
Jung KH, Cao P, Seo YS, Dardick C, Ronald PC (2010) The Rice Kinase Phylogenomics Database: a guide for systematic analysis of the rice kinase super-family. Trends Plant Sci 15:595–599
Jung KH, Jeon JS, An G (2011) Web Tools for Rice Transcriptome Analyses. J Plant Biol 54:65–80
Jung KH, KO HJ, Kim SR, Ronald PC, An G (2012) Genome-wide Identification and Analysis of Early Heat Stress Responsive Genes in Rice. J Plant Biol Accepted
Kaye FJ, Modi S, Ivanovska I, Koonin EV, Thress K, Kubo A, Kornbluth S, Rose MD (2000) A family of ubiquitin-like proteins binds the ATPase domain of Hsp70-like Stch. FEBS Letters 467:348–355
Lee I, Seo YS, Coltrane D, Hwang S, Oh T, Marcotte EM, Ronald PC (2011) Genetic dissection of the biotic stress response using a genome-scale gene network for rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:18548–18553
Lee JR, Lee SS, Jang HH, Lee YM, Park JH, Park SC, Moon JC, Park SK, Kim SY, Lee SY, Chae HB, Jung YJ, Kim WY, Shin MR, Cheong GW, Kim MG, Kang KR, Lee KO, Yun DJ (2009a) Heat-shock dependent oligomeric status alters the function of a plant-specific thioredoxin-like protein, AtTDX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:5978–5983
Lee TH, Kim YK, Pham TT, Song SI, Kim JK, Kang KY, An G, Jung KH, Galbraith DW, Kim M, Yoon UH, Nahm BH (2009b) RiceArrayNet: a database for correlating gene expression from transcriptome profiling, and its application to the analysis of coexpressed genes in rice. Plant Physiol 151:16–33
Li CG, Chen QJ, Gao XQ, Qi BS, Chen NZ, Xu SM, Chen J, Wang XC (2005a) AtHsfA2 modulates expression of stress responsive genes and enhances tolerance to heat and oxidative stress in Arabidopsis. Sci China Ser C 48:540–550
Li HY, Chang CS, Lu LS, Liu CA, Chan MT, Charng YY (2005b) Over-expression of Arabidopsis thaliana heat shock factor gene (AtHsfA1b) enhances chilling tolerance in transgenic tomato (vol 44, pg 129, 2003). Bot Bull Acad Sinica 46:91–91
Liu AL, Zou J, Zhang XW, Zhou XY, Wang WF, Xiong XY, Chen LY, Chen XB (2010) Expression Profiles of Class A Rice Heat Shock Transcription Factor Genes Under Abiotic Stresses. J Plant Biol 53:142–149
Liu HT, Gao F, Cui SJ, Han JL, Sun DY, Zhou RG (2006) Primary evidence for involvement of IP3 in heat-shock signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 16:394–400
Ma JF, Mitani N, Nagao S, Konishi S, Tamai K, Iwashita T, Yano M (2004) Characterization of the silicon uptake system and molecular mapping of the silicon transporter gene in rice. Plant Physiol 136:3284–3289
Miller G, Suzuki N, Rizhsky L, Hegie A, Koussevitzky S, Mittler R (2007) Double mutants deficient in cytosolic and thylakoid ascorbate peroxidase reveal a complex mode of interaction between reactive oxygen species, plant development, and response to abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol 144:1777–1785
Mishra SK, Tripp J, Winkelhaus S, Tschiersch B, Theres K, Nover L, Scharf KD (2002) In the complex family of heat stress transcription factors, HSfA1 has a unique role as master regulator of thermotolerance in tomato. Genes Dev 16:1555–1567
Mittal D, Chakrabarti S, Sarkar A, Singh A, Grover A (2009) Heat shock factor gene family in rice: Genomic organization and transcript expression profiling in response to high temperature, low temperature and oxidative stresses. Plant Physiol Bioch 47:785–795
Miyata Y, Yahara I (1992) The 90-kDa heat shock protein, HSP90, binds and protects casein kinase II from self-aggregation and enhances its kinase activity. J Biol Chem 267:7042–7047
Mogk A, Deuerling E, Vorderwulbecke S, Vierling E, Bukau B (2003) Small heat shock proteins, ClpB and the DnaK system form a functional triade in reversing protein aggregation. Mol Microbiol 50:585–595
Murshid A, Chou SD, Prince T, Zhang Y, Bharti A, Calderwood SK (2010) Protein kinase A binds and activates heat shock factor 1. PloS One 5:e13830
Nakashima K, Ito Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009) Transcriptional Regulatory Networks in Response to Abiotic Stresses in Arabidopsis and Grasses. Plant Physiol 149:88–95
Nguyen TO, Capra JD, Sontheimer RD (1996) Calreticulin is transcriptionally upregulated by heat shock, calcium and heavy metals. Mol Immunol 33:379–386
Nishizawa A, Yabuta Y, Yoshida E, Maruta T, Yoshimura K, Shigeoka S (2006) Arabidopsis heat shock transcription factor A2 as a key regulator in response to several types of environmental stress. Plant J 48:535–547
Noel LD, Cagna G, Stuttmann J, Wirthmuller L, Betsuyaku S, Witte CP, Bhat R, Pochon N, Colby T, Parker JE (2007) Interaction between SGT1 and cytosolic/nuclear HSC70 chaperones regulates Arabidopsis immune responses. Plant Cell 19:4061–4076
Ouyang S, Zhu W, Hamilton J, Lin H, Campbell M, Childs K, Thibaud-Nissen F, Malek RL, Lee Y, Zheng L, Orvis J, Haas B, Wortman J, Buell CR (2007) The TIGR Rice Genome Annotation Resource: improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D883–887
Peltier JB, Ytterberg AJ, Sun Q, van Wijk KJ (2004) New functions of the thylakoid membrane proteome of Arabidopsis thaliana revealed by a simple, fast, and versatile fractionation strategy. J Biol Chem 279:49367–49383
Ramsey AJ, Russell LC, Whitt SR, Chinkers M (2000) Overlapping sites of tetratricopeptide repeat protein binding and chaperone activity in heat shock protein 90. J Biol Chem 275:17857–17862
Rees DC, Johnson E, Lewinson O (2009) ABC transporters: the power to change. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:218–227
Rohila JS, Chen M, Chen S, Chen J, Cerny R, Dardick C, Canlas P, Xu X, Gribskov M, Kanrar S, Zhu JK, Ronald P, Fromm ME (2006) Protein-protein interactions of tandem affinity purification-tagged protein kinases in rice. Plant J 46:1–13
Saidi Y, Finka A, Goloubinoff P (2011) Heat perception and signalling in plants: a tortuous path to thermotolerance. New Phytol 190:556–565
Saitoh H, Cooke CA, Burgess WH, Earnshaw WC, Dasso M (1996) Direct and indirect association of the small GTPase ran with nuclear pore proteins and soluble transport factors: studies in Xenopus laevis egg extracts. Mol Biol Cell 7:1319–1334
Sato Y, Antonio BA, Namiki N, Takehisa H, Minami H, Kamatsuki K, Sugimoto K, Shimizu Y, Hirochika H, Nagamura Y (2011) RiceXPro: a platform for monitoring gene expression in japonica rice grown under natural field conditions. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D1141–1148
Scheufler C, Brinker A, Bourenkov G, Pegoraro S, Moroder L, Bartunik H, Hartl FU, Moarefi I (2000) Structure of TPR domain-peptide complexes: critical elements in the assembly of the Hsp70-Hsp90 multichaperone machine. Cell 101:199–210
Seo YS, Chern M, Bartley LE, Han M, Jung KH, Lee I, Walia H, Richter T, Xu X, Cao P, Bai W, Ramanan R, Amonpant F, Arul L, Canlas PE, Ruan R, Park CJ, Chen X, Hwang S, Jeon JS, Ronald PC (2011) Towards establishment of a rice stress response interactome. PLoS Genet 7:e1002020
Shack S, Gorospe M, Fawcett TW, Hudgins WR, Holbrook NJ (1999) Activation of the cholesterol pathway and Ras maturation in response to stress. Oncogene 18:6021–6028
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Smith DF, Sullivan WP, Marion TN, Zaitsu K, Madden B, McCormick DJ, Toft DO (1993) Identification of a 60-kilodalton stress-related protein, p60, which interacts with hsp90 and hsp70. Mol Cell Biol 13:869–876
Song HO, Lee W, An K, Lee HS, Cho JH, Park ZY, Ahnn J (2009) C. elegans STI-1, the homolog of Sti1/Hop, is involved in aging and stress response. J Mol Biol 390:604–617
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork P, Jensen LJ, von Mering C (2011) The STRING database in 2011: functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D561–568
Takabatake R, Ando Y, Seo S, Katou S, Tsuda S, Ohashi Y, Mitsuhara I (2007) MAP kinases function downstream of HSP90 and upstream of mitochondria in TMV resistance gene N-mediated hypersensitive cell death. Plant Cell Physiol 48:498–510
Urbanczyk-Wochniak E, Usadel B, Thimm O, Nunes-Nesi A, Carrari F, Davy M, Blasing O, Kowalczyk M, Weicht D, Polinceusz A, Meyer S, Stitt M, Fernie AR (2006) Conversion of MapMan to allow the analysis of transcript data from Solanaceous species: effects of genetic and environmental alterations in energy metabolism in the leaf. Plant Mol Biol 60:773–792
Usadel B, Nagel A, Thimm O, Redestig H, Blaesing OE, Palacios-Rojas N, Selbig J, Hannemann J, Piques MC, Steinhauser D, Scheible WR, Gibon Y, Morcuende R, Weicht D, Meyer S, Stitt M (2005) Extension of the visualization tool MapMan to allow statistical analysis of arrays, display of corresponding genes, and comparison with known responses. Plant Physiol 138:1195–1204
Wang C, Zhang Q, Shou HX (2009) Identification and expression analysis of OsHsfs in rice. J Zhejiang Univ-Sc B 10:291–300
Xing T, Higgins VJ, Blumwald E (1996) Regulation of Plant Defense Response to Fungal Pathogens: Two Types of Protein Kinases in the Reversible Phosphorylation of the Host Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase. Plant Cell 8:555–564
Yang SD, Lee SC, Chang HC (1997) Heat stress induces tyrosine phosphorylation/activation of kinase FA/GSK-3 alpha (a human carcinoma dedifferentiation modulator) in A431 cells. J Cell Biochem 66:16–26
Yokotani N, Ichikawa T, Kondou Y, Matsui M, Hirochika H, Iwabuchi M, Oda K (2008) Expression of rice heat stress transcription factor OsHsfA2e enhances tolerance to environmental stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 227:957–967
Zeng LR, Qu S, Bordeos A, Yang C, Baraoidan M, Yan H, Xie Q, Nahm BH, Leung H, Wang GL (2004) Spotted leaf11, a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, encodes a Ubox/armadillo repeat protein endowed with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Plant Cell 16:2795–2808
Zimmermann P, Laule O, Schmitz J, Hruz T, Bleuler S, Gruissem W (2008) Genevestigator transcriptome meta-analysis and biomarker search using rice and barley gene expression databases. Mol Plant 1:851–857
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, KH., An, G. Application of MapMan and RiceNet drives systematic analyses of the early heat stress transcriptome in rice seedlings. J. Plant Biol. 55, 436–449 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-012-0270-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-012-0270-0