Abstract
Introduction
Previous studies comparing insulin detemir versus insulin glargine showed conflicting results, and included only outpatients. This study compared the two insulin analogs once daily in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods
A total of 55 patients aged 18–80 years with hyperglycemia admitted to the endocrinology wards were screened between June 2014 and February 2015. Forty-two enrolled patients were randomly assigned to receive either insulin detemir followed by insulin glargine once daily (n = 21), or vice versa (n = 21). The two insulin analogs were titrated 0.1 U/kg once daily based on fasting blood glucose (FBG). After achieving FBG <7.8 mmol/L (the first period), subjects were switched from one analog to the other (the second period) with no change in the dose. The second period lasted for 3 days. When hypoglycemia occurred in the second period, the observation was discontinued. Six-point blood glucose including FBG, 2 h after breakfast, lunch, dinner, bedtime, and at 3:00 am was tested every day. The glucose profiles of the final days in the two periods were compared.
Results
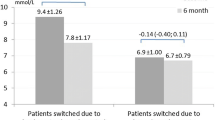
At the end of the first period, days for achieving FBG target (4.0 ± 0.5 days vs. 3.3 ± 0.4 days, t = 1.079, P = 0.286) and total daily dose (30.1 ± 2.4 U vs. 30.1 ± 2.9 U, t = 0.002, P = 0.999) between insulin detemir and insulin glargine were similar. There was no significant difference in the 24-h glucose control between the two analogs. No hypoglycemia occurred with both analogs in the first period. However, in the second period, when insulin glargine was switched to insulin detemir, two, three and, one patients had hypoglycemia events on day 1, day 2 and day 3 of the second period, respectively. One patient had severe hypoglycemia on day 1.
Conclusion
When both basal insulin analogs were given once daily in T2D, insulin detemir achieved similar efficacy to insulin glargine. On the other hand, there may be differences in action of the compared basal insulins. Further studies with larger patient samples are necessary to support evidence and reveal possible mechanisms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Draznin B, Gilden J, Golden SH, Inzucchi S. Response to comment on: Draznin et al. Pathways to quality inpatient management of hyperglycemia and diabetes: a call to action. Diabetes Care 2013;36:1807–1814. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(12):e220.
Umpierrez GE, Hellman R, Korytkowski MT, Kosiborod M, Maynard GA, Montori VM, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in hospitalized patients in non-critical care setting: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(1):16–38.
Tricco AC, Ashoor HM, Antony J, Beyene J, Veroniki AA, Isaranuwatchai W, et al. Safety, effectiveness, and cost effectiveness of long acting versus intermediate acting insulin for patients with type 1 diabetes: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014;349:g5459. doi:10.1136/bmj.g5459.
Rosenstock J, Davies M, Home PD, Larsen J, Koenen C, Schernthaner G. A randomised, 52-week, treat-to-target trial comparing insulin detemir with insulin glargine when administered as add-on to glucose-lowering drugs in insulin-naive people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2008;51(3):408–16.
Swinnen SG, Dain MP, Aronson R, Davies M, Gerstein HC, Pfeiffer AF, et al. A 24-week, randomized, treat-to-target trial comparing initiation of insulin glargine once-daily with insulin detemir twice-daily in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on oral glucose-lowering drugs. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(6):1176–8.
Raskin P, Gylvin T, Weng W, Chaykin L. Comparison of insulin detemir and insulin glargine using a basal-bolus regimen in a randomized, controlled clinical study in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009;25(6):542–8.
Meneghini L, Kesavadev J, Demissie M, Nazeri A, Hollander P. Once-daily initiation of basal insulin as add-on to metformin: a 26-week, randomized, treat-to-target trial comparing insulin detemir with insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(8):729–36.
Cander S, Dizdar OS, Oz Gul O, Guclu M, Unal OK, Tuncel E, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of once- versus twice-daily insulin detemir added on to oral antidiabetics in insulin-naive type 2 diabetes patients: 24-week, crossover, treat to target trial in a single center. Prim Care Diabetes. 2014;8(3):256–64.
Hollander P, Cooper J, Bregnhoj J, Pedersen CB. A 52-week, multinational, open-label, parallel-group, noninferiority, treat-to-target trial comparing insulin detemir with insulin glargine in a basal-bolus regimen with mealtime insulin aspart in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin Ther. 2008;30(11):1976–87.
King AB. No higher dose requirements with insulin detemir than glargine in type 2 diabetes: a crossover, double-blind, and randomized study using continuous glucose monitoring. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010;4(1):151–4.
Li X, Du T, Li W, Zhang T, Liu H, Xiong Y. Efficacy and safety of weight-based insulin glargine dose titration regimen compared with glucose level- and current dose-based regimens in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled study. Clin Ther. 2014;36(9):1269–75.
Heintjes EM, Thomsen TL, Penning-van Beest FJ, Christensen TE, Herings RM. Glycemic control and long-acting insulin analog utilization in patients with type 2 diabetes. Adv Therapy. 2010;27(4):211–22.
King AB. Once-daily insulin detemir is comparable to once-daily insulin glargine in providing glycaemic control over 24 h in patients with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind, randomized, crossover study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009;11(1):69–71.
Jakobsen M, Dalsgaard M, Hormann M, Moller DV. Insulin analogues dosing and costs—comparing real-life daily doses of insulin detemir and insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes patients. BMC Endocr Disord. 2012;12:21.
Klein O, Lynge J, Endahl L, Damholt B, Nosek L, Heise T. Albumin-bound basal insulin analogues (insulin detemir and NN344): comparable time-action profiles but less variability than insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007;9(3):290–9.
Luzio SD, Dunseath GJ, Atkinson MD, Owens DR. A comparison of the pharmacodynamic profiles of insulin detemir and insulin glargine: a single dose clamp study in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2013;39(6):537–42.
Lucidi P, Porcellati F, Rossetti P, Candeloro P, Cioli P, Marzotti S, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of therapeutic doses of basal insulins NPH, glargine, and detemir after 1 week of daily administration at bedtime in type 2 diabetic subjects: a randomized cross-over study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(6):1312–4.
Nelson SE. Detemir as a once-daily basal insulin in type 2 diabetes. Clin Pharmacol. 2011;3:27–37.
Porcellati F, Lucidi P, Rossetti P, Candeloro P, Andreoli AM, Marzotti S, et al. Differential effects of adiposity on pharmacodynamics of basal insulins NPH, glargine, and detemir in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(12):2521–3.
Fadini GP, de Kreutzenberg SV, Mariano V, Boscaro E, Bertolini F, Mancuso P, et al. Optimized glycaemic control achieved with add-on basal insulin therapy improves indexes of endothelial damage and regeneration in type 2 diabetic patients with macroangiopathy: a randomized crossover trial comparing detemir versus glargine. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(8):718–25.
Yenigun M, Honka M. Switching patients from insulin glargine-based basal-bolus regimens to a once daily insulin detemir-based basal-bolus regimen: results from a subgroup of the PREDICTIVE study. Int J Clin Pract. 2009;63(3):425–32.
Lavernia F. What options are available when considering starting insulin: premix or basal? Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011;13(Suppl 1):S85–92.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Science and Information Technology of Guangzhou (Grant 12C22021649). The article processing charges for this publication were supported by the authors. All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval for the version to be published.
Disclosures
Tong Zhang, Mingrun Lin, Wangen Li, Xiuyun Fan, Tao Du, Yunjuan Zhao, and Xiaodan Zhang have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines.
The study regimen was approved by the ethical board of each participating hospital. All patients provided written informed consent before participating in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Lin, M., Li, W. et al. Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Detemir and Insulin Glargine in Hospitalized Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Adv Ther 33, 178–185 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-016-0288-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-016-0288-7