Abstract
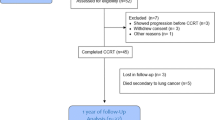
Although the deterioration in pulmonary functions is a well-known important problem due to the treatment of the Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients, the immediate and long term effects of the therapy and its distinctive components were not shown clearly yet. We planned to investigate effects of multiple agent chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy to pulmonary functions immediately and thereafter and the possible effects of the managing this situation. 34 patients were included the study. The patients were evaluated for peak expiratory flow (PEF), forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), forced expiratory vital capacity (FVC), mean total lung capacity (TLC) values, FEV1/FVC ratio, diffusing capacity for carbonmonoxide (DLco), diffusing capacity for carbonmonoxide corrected for hemoglobin concentration (DLCO) before and at 1, 6 and 12 months after the initiation of the treatment. Demographic characteristics; disease stages; chemotherapy protocols; whether radiotherapy is received; if yes, the region and the dose received were recorded. The tests were finally analysed in two separated groups; group A treated with only chemotherapy and group B; treated with combination therapy, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. In group A, FVC and FEV1 is similar before and after treatment. FEV1/FVC ratio was increased (P = 0.0001) in this group despite increasing in mean TLC values (P = 0.001). No meaningful changes were observed in PEF and DLCO values in group A. In group B, FVC, FEV1 and PEF were decreased after treatment (for FVC P = 0.028, for FEV1 P = 0.04). Despite a decrease in first month of the treatment in FEV1/FVC ratio and DLco these two parameters were recovered at the end of the first year in group B patients. TLC values were increased after treatment in group B as in group A (P = 0.035). We believe that, if these patients are managed well in 1 year; necessary precautions are provided; and patients are well-informed, then there wouldn’t be too much risk and mortality rate for long-term side effects of ABVD and mediastinal RT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klimm B, Engert A, Diehl V (2006) First-line treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 1(1):51–59
Lanzkowsky P (2005) Manuel of pediatric hematology and oncology, 4th edn. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, pp 453–490
Josting A, Franklin J, May M, Koch P, Beykirch MK, Heinz J, Rudolph C, Diehl V, Engert A (2002) New prognostic score based on treatment outcome of patients with relapsed Hodgkin’s lymphoma registered in the database of the German Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group. J Clin Oncol 20:221–230
Zubrod CG, Ipsen J, Frei E, Lasagna LC, Lipsett MB, Gehan E, Escher GC (1960) Newer techniques and some problems in cooperative group studies. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 3:277–292
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, McFadden ET, Carbone PP (1982) Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol 5:649–655
Cosset JM, Henry-Amar M, Meerwaldt JH (1991) Long-term toxicity of early stages of Hodgkin’s disease therapy: the EORTC experience. EORTC Lymphoma Cooperative Group. Ann Oncol 2(Suppl 2):77–82
Straus DJ (1995) High-risk Hodgkin’s disease prognostic factors. Leuk Lymphoma 15(Suppl 1):41–42
Hagberg H, Killander A, Simonsson B (1983) Serum β-2 microglobulin in malignant lymphoma. Cancer 51(12):2220–2225
Santoro A, Bonadonna G, Valagussa P, Zucali R, Viviani S, Villani F, Pagnoni AM, Bonfante V, Musumeci R, Crippa F (1987) Long-term results of combined chemotherapy-radiotherapy approach in Hodgkin’s disease: superiority of ABVD plus radiotherapy versus MOPP plus radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 5(1):27–37
Lagrange JL, Thyss A, Caldani C, Héry M, Schneider M, Bensadoun JR (1988) Toxicity of a combination of ABVD chemotherapy and mediastinal irradiation for Hodgkin’s disease patients with massive initial mediastinal involvement. Bull Cancer 75(8):801–806
Jules-Elysee K, White DA (1990) Bleomycin-induced pulmonary toxicity. Clin Chest Med 11(1):1–20
Evens AM, Helenowski I, Ramsdale E, Nabhan C, Karmali R, Hanson B, Parsons B, Smith S, Larsen A, McKoy JM, Jovanovic B, Gregory S, Gordon LI, Smith SM (2012) A retrospective multicenter analysis of elderly Hodgkin lymphoma: outcomes and prognostic factors in the modern era. Blood 119(3):692–695
Horning SJ, Adhikari A, Rizk N, Hoppe RT, Olshen RA (1994) Effect of treatment for Hodgkin’s disease on pulmonary function: results of a prospective study. J Clin Oncol 12(2):297–305
Bates NP, Williams MV, Bessell EM, Hudson GV, Hudson BV (1994) Efficacy and toxicity of vinblastine, bleomycin, and methotrexate with involved-field radiotherapy in clinical stage IA and IIA Hodgkin’s disease: a British National Lymphoma Investigation pilot study. J Clin Oncol 12(2):288–296
Hirsch A, Vander Els N, Straus DJ, Gomez EG, Leung D, Portlock CS, Yahalom J (1996) Effect of ABVD chemotherapy with and without mantle or mediastinal irradiation on pulmonary function and symptoms in early-stage Hodgkin’s disease. J Clin Oncol 14(4):1297–1305
Salloum E, Tanoue LT, Wackers FJ, Zelterman D, Hu GL, Cooper DL (1999) Assessment of cardiac and pulmonary function in adult patients with Hodgkin’s disease treated with ABVD or MOPP/ABVD plus adjuvant low-dose mediastinal irradiation. Cancer Invest 17(3):171–180
Villani F, Fede Catania A, Laffranchi A, Maffioli L, Viviani S, Bonfante V (2003) Effect of an intensive chemotherapy followed by mediastinal irradiation on pulmonary and cardiac function in advanced Hodgkin’s disease. Cancer Invest 21(2):185–192
Ho P, Sherman P, Grigg A (2012) Intermittent granulocyte colony-stimulating factor maintains dose intensity after ABVD therapy complicated by neutropenia. Eur J Haematol 88(5):416–421
Villani F, De Maria P, Bonfante V, Viviani S, Laffranchi A, Dell’oca I, Dirusso A, Zanini M (1997) Late pulmonary toxicity after treatment for Hodgkin’s disease. Anticancer Res 17(6D):4739–4742
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guner, S.I., Yanmaz, M.T., Selvi, A. et al. Chemotherapy and Radiation Induced Pulmonary Dysfunction in Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 32, 431–436 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-015-0619-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-015-0619-x