Abstract
Background
Immune responses play an important role in interrupting the progression of cancer cells. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are basic components of the immune system. In triple negative breast cancer, increased number of TILs is associated with excellent prognosis and response of chemotherapy. Here, we investigated whether TILs affect the efficacy of trastuzumab-based treatment in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer.
Methods
The study included 97 patients with stage I-III HER2-positive breast cancer. All patients were preoperatively treated with an anthracycline-based combination regimen, followed by taxane with trastuzumab from 2009 to 2013. Pathological complete response (pCR) was defined as the disappearance of invasive cancer cells regardless of the presence of in situ components. TILs were evaluated using pre-therapeutic needle biopsy specimens. We assessed the percentage of the breast stroma with TILs over the total intratumoral stroma and classified the specimens in three grades: TILs1+ < 30%, TILs2+ 30–50%, and TILs3+ > 50%.
Results
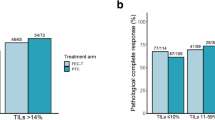
Overall, 80.4% of the specimens were TILs1+, 15.5% were TILs2+ and 4.1% were TILs3+. The pCR rate was 44.9% (35/78) in the TILs1+ cases, 80.0% (12/15) in the TILs2+ cases and 75.0% (3/4) in the TILs3+ cases. TILs were significantly associated with pCR (P = 0.0228). Multivariate analysis using TILs, hormone receptor (HR), nuclear grade (NG) and age indicated that TILs (OR 4.32, 95% CI 1.04–23.33, P = 0.0436) and HR (OR 8.76, 95% CI 3.30–25.44, P < 0.0001) were independent predictors for pCR.
Conclusion
TILs are associated with the efficacy of trastuzumab-based treatment in HER2-positive breast cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Blohmer JU, Costa SD, Eidtmann H, Fasching PA, et al. Definition and impact of pathologic complete response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1796–804.
Buzdar AU, Ibrahim NK, Francis D, Booser DJ, Thomas ES, Theriault RL, et al. Significantly higher pathologic complete remission rate after neoadjuvant therapy with trastuzumab, paclitaxel, and epirubicin chemotherapy: results of a randomized trial in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3676–85.
Valachis A, Mauri D, Polyzos NP, Chlouverakis G, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V. Trastuzumab combined to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast. 2011;20:485–90.
Buzdar AU, Valero V, Ibrahim NK, Francis D, Broglio KR, Theriault RL, et al. Neoadjuvant therapy with paclitaxel followed by 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy and concurrent trastuzumab in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive operable breast cancer: an update of the initial randomized study population and data of additional patients treated with the same regimen. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:228–33.
Bianchini G, Gianni L. The immune system and response to HER2-targeted treatment in breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e58–68.
Salgado R, Denkert C, Demaria S, Sirtaine N, Klauschen F, Pruneri G, et al. The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:259–71.
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, Sinn BV, Gade S, Kronenwett R, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without Carboplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive and triple-negative primary breast cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:983–91.
Issa-Nummer Y, Darb-Esfahani S, Loibl S, Kunz G, Nekljudova V, Schrader I, et al. Prospective validation of immunological infiltrate for prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-negative breast cancer—a substudy of the neoadjuvant GeparQuinto trial. PLoS One. 2013;8:e79775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079775.
Loi S, Michiels S, Salgado R, Sirtaine N, Jose V, Fumagalli D, et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: results from the FinHER trial. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1544–50.
Adams S, Gray RJ, Demaria S, Goldstein L, Perez EA, Shulman LN, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers from two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG 1199. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:2959–66.
International Union Against Cancer (UICC). TNM classification of malignant tumors. 7th ed. New York: Wiley; 2009.
The Japanese Breast Cancer Society. General rules for clinical and pathological recording of breast cancer. 17th ed. Tokyo: Kanehara & Co, Ltd; 2012.
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3997–4013.
Mao Y, Qu Q, Zhang Y, Liu J, Chen X, Shen K. The value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) for predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;12:e115103. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115103.
Seo AN, Lee HJ, Kim HJ, Jang MH, Lee HE, Kim YJ, et al. Tumour-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes as an independent predictive factor for pathological complete response to primary systemic therapy in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2705–13.
Lee HJ, Seo JY, Ahn JH, Ahn SH, Gong G. Tumor-associated lymphocytes predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. J Breast Cancer. 2013;16:32–9.
Ménétrier-Caux C, Curiel T, Faget J, Manuel M, Caux C, Zou W. Targeting regulatory T cells. Target Oncol. 2012;7:15–28.
Massarweh S, Schiff R. Unraveling the mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer: new therapeutic opportunities. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1950–4.
Denkert C, Huober J, Loibl S, Prinzler J, Kronenwett R, Esfahani SD, et al. HER2 and ESR1 mRNA expression levels and response to neoadjuvant trastuzumab plus chemotherapy in patients with primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15:R11. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3384.
Salgado R, Denkert C, Camphell C, Saras P, Nucifero P, Aura C, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and associations with pathological complete response and event-free survival in HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer treated with lapatinib and trastuzumab-a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO trial. JAMA Oncol. 2015;1:448–54. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.0830.
Swisher SK, Wu Y, Castaneda CA, Lyons GR, Yang F, Tapia C, et al. Interobserver agreement between pathologists assessing tumor-infiltration lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer using methodology proposed by the international TILs working group. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23:2242–8.
Denkert C, Wienert S, Poterie A, Loibl S, Budczies J, Badve S, et al. Standardized evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer: results of the ring studies of the international immune-oncology biomarker working group. Mod Pathol. 2016;29:1155–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yoshinori Ito received manuscript fees from Eisai, Novartis and Taiho. He also received research grants from MSD, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Parexel, Chugai and Lilly. Shinji Ohno received honoraria from Astra Zeneca, Eisai, Chugai, Taiho, Pfizer, Novartis and Kyowa-kirin. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, H., Horii, R., Ito, Y. et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes affect the efficacy of trastuzumab-based treatment in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer 25, 268–274 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0822-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0822-8