Abstract
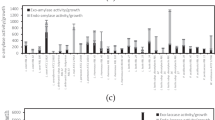
Aspergillus section Nigri is a fungus used industrially because of its ability to produce enzymes such as cellulolytic, amylolytic and proteolytic enzymes. In this study, we obtained twenty-eight strains of Aspergillus section Nigri from the traditional Korean fermentation starter, nuruk, which is known as a mixed culture of enzymatic filamentous fungi and yeasts. All strains were identified as Aspergillus section Nigri through combined phylogenetic analysis using partial β-tubulin and calmodulin gene sequences. The cellulase, amylase and protease activities of Korean strains were measured and compared with ten reference strains of Aspergillus niger. Most Korean strains showed higher cellulolytic activity than reference strains, and Aspergillus neoniger KCN5 showed the highest β-glucosidase activity. Two-thirds of the Korean strains showed similar levels of α- and glucoamylase activity as the reference strains. The protease activity of Aspergillus section Nigri strains was the highest at pH 3.0, and A. niger KSJ2 showed the highest acidic protease activity. By comparing ten reference strains and twenty-eight Korean strains, our results suggested useful Aspergillus section Nigri strains from nuruk with high enzyme activity, such as KCN5 and KSJ2, and their potential for industrial applications as enzyme producers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdella, A., El-Baz, A.F., Ibrahim, I.A., Mahrous, E.E., and Yang, S.T. 2018. Biotransformation of soy flour isoflavones by Aspergillus niger NRRL 3122 β-glucosidase enzyme. Nat. Prod. Res. 32, 2382–2391.
Aguilar-Pontes, M.V., Brandl, J., McDonnell, E., Strasser, K., Nguyen, T.T.M., Riley, R., Mondo, S., Salamov, A., Nybo, J.L., Vesth, T.C., et al. 2018. The gold-standard genome of Aspergillus niger NRRL 3 enables a detailed view of the diversity of sugar catabolism in fungi. Stud. Mycol. 91, 61–78.
Ahmed, A., Nasim, F.U., Batool, K., and Bibi, A. 2017. Microbial β-glucosidase: sources, production and applications. J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 5, 31–46.
Al-Hindi, R.R., Al-Najada, A.R., and Mohamed, S.A. 2011. Isolation and identification of some fruit spoilage fungi: screening of plant cell wall degrading enzymes. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 5, 443–448.
Andersen, M.R., Salazar, M.P., Schaap, P.J., van de Vondervoort, P.J., Culley, D., Thykaer, J., Frisvad, J.C., Nielsen, K.F., Albang, R., Albermann, K., et al. 2011. Comparative genomics of citric-acid-producing Aspergillus niger ATCC 1015 versus enzyme-producing CBS 513.88. Genome Res. 21, 885–897.
Bal, J., Yun, S.H., Song, H.Y., Yeo, S.H., Kim, J.H., Kim, J.M., and Kim, D.H. 2014. Mycoflora dynamics analysis of Korean traditional wheat-based nuruk. J. Microbiol. 52, 1025–1029.
Borin, G.P., Sanchez, C.C., de Santana, E.S., Zanini, G.K., Dos Santos, R.A.C., de Oliveira Pontes, A., de Souza, A.T., Dal’Mas, R.M.M.T.S., Riaño-Pachón, D.M., Goldman, G.H., et al. 2017. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals different strategies for degradation of steam-exploded sugarcane bagasse by Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma reesei. BMC Genomics 18, 501.
Cairns, T.C., Nai, C., and Meyer, V. 2018. How a fungus shapes biotechnology: 100 years of Aspergillus niger research. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 5, 13.
Carroll, E., Trinh, T.N., Son, H., Lee, Y.W., and Seo, J.A. 2017. Comprehensive analysis of fungal diversity and enzyme activity in nuruk, a Korean fermenting starter, for acquiring useful fungi. J. Microbiol. 55, 357–365.
Coronado-Ruiz, C., Avendaño, R., Escudero-Leyva, E., Conejo-Barboza, G., Chaverri, P., and Chavarría, M. 2018. Two new cellulolytic fungal species isolated from a 19th-century art collection. Sci. Rep. 8, 7492.
Cota-Sánchez, J.H., Remarchuk, K., and Ubayasena, K. 2006. Ready-to-use DNA extracted with a CTAB method adapted for herbarium specimens and mucilaginous plant tissue. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 24, 161.
Delmas, S., Pullan, S.T., Gaddipati, S., Kokolski, M., Malla, S., Blythe, M.J., Ibbett, R., Campbell, M., Liddell, S., Aboobaker, A., et al. 2012. Uncovering the genome-wide transcriptional responses of the filamentous fungus Aspergillus niger to lignocellulose using RNA sequencing. PLoS Genet. 8, e1002875.
Dojnov, B. and Vujčić, Z. 2012. Fast and reliable method for simultaneous zymographic detection of glucoamylase and α-amylase in fungal fermentation. Anal. Biochem. 421, 802–804.
Duarte, E.A.A., Damasceno, C.L., de Oliveira, T.A.S., Barbosa, L.O., Martins, F.M., de Queiroz Silva, J.R., de Lima, T.E.F., da Silva, R.M., Kato, R.B., Bortolini, D.E., et al. 2018. Putting the mess in order: Aspergillus welwitschiae (and not A. niger) is the etiological agent of sisal bole rot disease in Brazil. Front. Microbiol. 9, 1227.
Fungaro, M.H.P., Ferranti, L.S., Massi, F.P., da Silva, J.J., Sartori, D., Taniwaki, M.H., Frisvad, J.C., and Iamanaka, B.T. 2017. Aspergillus labruscus sp. nov., a new species of Aspergillus section Nigri discovered in Brazil. Sci. Rep. 7, 6203.
Gera, N., Uppaluri, R.V.S., Sen, S., and Dasu, V.V. 2008. Growth kinetics and production of glucose oxidase using Aspergillus niger NRRL 326. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 22, 315–320.
Gil-Serna, J., García-Díaz, M., Vázquez, C., González-Jaén, M.T., and Patiño, B. 2019. Significance of Aspergillus niger aggregate species as contaminants of food products in Spain regarding their occurrence and their ability to produce mycotoxins. Food Microbiol. 82, 240–248.
Gruben, B.S., Mäkelä, M.R., Kowalczyk, J.E., Zhou, M., Benoit-Gelber, I., and De Vries, R.P. 2017. Expression-based clustering of CAZyme-encoding genes of Aspergillus niger. BMC Genomics 18, 900.
Gurumallesh, P., Alagu, K., Ramakrishnan, B., and Muthusamy, S. 2019. A systematic reconsideration on proteases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 128, 254–267.
Jernejc, K. and Legiša, M. 2004. A drop of intracellular pH stimulates citric acid accumulation by some strains of Aspergillus niger. J. Biotechnol. 112, 289–297.
Kasana, R.C., Salwan, R., Dhar, H., Dutt, S., and Gulati, A. 2008. A rapid and easy method for the detection of microbial cellulases on agar plates using Gram’s iodine. Curr. Microbiol. 57, 503–507.
Khan, S., Nadir, S., Shah, Z.U., Shah, A.A., Karunarathna, S.C., Xu, J., Khan, A., Munir, S., and Hasan, F. 2017. Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane by Aspergillus tubingensis. Environ. Pollut. 225, 469–480.
Kumar, S. and Mutturi, S. 2020. Expression of a novel α-glucosidase from Aspergillus neoniger in Pichia pastoris and its efficient recovery for synthesis of isomaltooligosaccharides. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 141, 109653.
Logrieco, A., Ferracane, R., Haidukowsky, M., Cozzi, G., Visconti, A., and Ritieni, A. 2009. Fumonisin B2 production by Aspergillus niger from grapes and natural occurrence in must. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 26, 1495–1500.
Magnoli, C., Violante, M., Combina, M., Palacio, G., and Dalcero, A. 2003. Mycoflora and ochratoxin-producing strains of Aspergillus section Nigri in wine grapes in Argentina. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 37, 179–184.
Massi, F.P., Sartori, D., de Souza Ferranti, L., Iamanaka, B.T., Taniwaki, M.H., Vieira, M.L.C., and Fungaro, M.H.P. 2016. Prospecting for the incidence of genes involved in ochratoxin and fumonisin biosynthesis in Brazilian strains of Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus welwitschiae. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 221, 19–28.
Meijer, M., Houbraken, J.A.M.P., Dalhuijsen, S., Samson, R.A., and de Vries, R.P. 2011. Growth and hydrolase profiles can be used as characteristics to distinguish Aspergillus niger and other black aspergilli. Stud. Mycol. 69, 19–30.
Mienda, B.S., Yahya, A., Galadima, I.A., and Shamsir, M.S. 2014. An overview of microbial proteases for industrial applications. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 5, 388–396.
Narasimha, G., Sridevi, A., Buddolla, V., Subhosh, C.M., and Rajasekhar, R.B. 2006. Nutrient effects on production of cellulolytic enzymes by Aspergillus niger. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 5, 472–476.
Pailin, T., Kang, D.H., Schmidt, K., and Fung, D.Y. 2001. Detection of extracellular bound proteinase in EPS-producing lactic acid bacteria cultures on skim milk agar. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 33, 45–49.
Papagianni, M. and Moo-Young, M. 2002. Protease secretion in glucoamylase producer Aspergillus niger cultures: fungal morphology and inoculum effects. Process Biochem. 37, 1271–1278.
Paul, S., Ludeña, Y., Villena, G.K., Yu, F., Sherman, D.H., and Gutiérrez-Correa, M. 2017. High-quality draft genome sequence of a biofilm forming lignocellulolytic Aspergillus niger strain ATCC 10864. Stand. Genom. Sci. 12, 37.
Pel, H.J., de Winde, J.H., Archer, D.B., Dyer, P.S., Hofmann, G., Schaap, P.J., Turner, G., de Vries, R.P., Albang, R., Albermann, K., et al. 2007. Genome sequencing and analysis of the versatile cell factory Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 221–231.
Perrone, G., Stea, G., Epifani, F., Varga, J., Frisvad, J.C., and Samson, R.A. 2011. Aspergillus niger contains the cryptic phylogenetic species A. awamori. Fungal Biol. 115, 1138–1150.
Razzaq, A., Shamsi, S., Ali, A., Ali, Q., Sajjad, M., Malik, A., and Ashraf, M. 2019. Microbial proteases applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 7, 110.
Rodarte, M.P., Dias, D.R., Vilela, D.M., and Schwan, R.F. 2011. Proteolytic activities of bacteria, yeasts and filamentous fungi isolated from coffee fruit (Coffea arabica L.). Acta Sci. Agron. 33, 457–464.
Sajith, S., Priji, P., Sreedevi, S., and Benjamin, S. 2016. An overview on fungal cellulases with an industrial perspective. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 6, 461.
Samson, R.A., Visagie, C.M., Houbraken, J., Hong, S.B., Hubka, V., Klaassen, C.H.W., Perrone, G., Seifert, K.A., Susca, A., Tanney, J.B., et al. 2014. Phylogeny, identification and nomenclature of the genus Aspergillus. Stud. Mycol. 78, 141–173.
Show, P.L., Oladele, K.O., Siew, Q.Y., Aziz Zakry, F.A., Lan, J.C.W., and Ling, T.C. 2015. Overview of citric acid production from Aspergillus niger. Front. Life Sci. 8, 271–283.
Silveira, S.T., Oliveira, M.S., Costa, J.A.V., and Kalil, S.J. 2006. Optimization of glucoamylase production by Aspergillus niger in solid-state fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 128, 131–140.
Soares, I., Távora, Z., Barcelos, R.P., and Baroni, S. 2012. Microorganism-produced enzymes in the food industry, pp. 83–94. In Valdez, B. (ed.), Scientific, health and social aspects of the food industry. InTech, Rijeka, Croatia. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/scientific-health-and-social-aspects-of-the-food-industry/microorganismproduced-enzymes-in-the-food-industry.
Solanki, P., Putatunda, C., Kumar, A., Bhatia, R., and Walia, A. 2021. Microbial proteases: ubiquitous enzymes with innumerable uses. 3 Biotech 11, 428.
Song, P., Cheng, L., Tian, K., Zhang, M., McHunu, N.P., Niu, D., Singh, S., Prior, B., and Wang, Z.X. 2020. Biochemical characterization of two new Aspergillus niger aspartic proteases. 3 Biotech 10, 303.
Song, S.H., Lee, C., Lee, S., Park, J.M., Lee, H.J., Bai, D.H., Yoon, S.S., Choi, J.B., and Park, Y.S. 2013. Analysis of microflora profile in Korean traditional nuruk. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 23, 40–46.
Srilakshmi, J., Madhavi, J., Lavanya, S., and Ammani, K. 2015. Commercial potential of fungal protease: past, present and future prospects. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2, 218–234.
Srivastava, N., Rathour, R., Jha, S., Pandey, K., Srivastava, M., Thakur, V.K., Sengar, R.S., Gupta, V.K., Mazumder, P.B., Khan, A.F., et al. 2019. Microbial beta glucosidase enzymes: recent advances in biomass conversation for biofuels application. Biomolecules 9, 220.
Suganthi, R., Benazir, J.F., Santhi, R., Ramesh Kumar, V., Hari, A., Meenakshi, N., Nidhiya, K.A., Kavitha, G., and Lakshmi, R. 2011. Amylase production by Aspergillus niger under solid state fermentation using agroindustrial wastes. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 3, 1756–1763.
Tam, E.W., Chen, J.H., Lau, E.C., Ngan, A.H., Fung, K.S., Lee, K.C., Lam, C.W., Yuen, K.Y., Lau, S.K., and Woo, P.C. 2014. Misidentification of Aspergillus nomius and Aspergillus tamarii as Aspergillus flavus: characterization by internal transcribed spacer, β-tubulin, and calmodulin gene sequencing, metabolic fingerprinting, and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 52, 1153–1160.
van Munster, J.M., Daly, P., Delmas, S., Pullan, S.T., Blythe, M.J., Malla, S., Kokolski, M., Noltorp, E.C.M., Wennberg, K., Fetherston, R., et al. 2014. The role of carbon starvation in the induction of enzymes that degrade plant-derived carbohydrates in Aspergillus niger. Fungal Genet. Biol. 72, 34–47.
Varga, J., Frisvad, J.C., Kocsubé, S., Brankovics, B., Tóth, B., Szigeti, G., and Samson, R.A. 2011. New and revisited species in Aspergillus section Nigri. Stud. Mycol. 69, 1–17.
Vesth, T.C., Nybo, J.L., Theobald, S., Frisvad, J.C., Larsen, T.O., Nielsen, K.F., Hoof, J.B., Brandl, J., Salamov, A., Riley, R., et al. 2018. Investigation of inter- and intraspecies variation through genome sequencing of Aspergillus section Nigri. Nat. Genet. 50, 1688–1695.
Yang, S., Choi, S.J., Kwak, J., Kim, K., Seo, M., Moon, T.W., and Lee, Y.W. 2013. Aspergillus oryzae strains isolated from traditional Korean Nuruk: fermentation properties and influence on rice wine quality. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 22, 425–432.
Yang, S., Lee, J., Kwak, J., Kim, K., Seo, M., and Lee, Y.W. 2011. Fungi associated with the traditional starter cultures used for rice wine in Korea. Appl. Biol. Chem. 54, 933–943.
Yuan, X.L., van der Kaaij, R.M., van den Hondel, C.A.M.J.J., Punt, P.J., van der Maarel, M.J.E.C., Dijkhuizen, L., and Ram, A.F.J. 2008. Aspergillus niger genome-wide analysis reveals a large number of novel alpha-glucan acting enzymes with unexpected expression profiles. Mol. Genet. Genom. 279, 545–561.
Zulkifli, N.A. and Zakaria, L. 2017. Morphological and molecular diversity of Aspergillus from corn grain used as livestock feed. HAYATI J. Biosci. 24, 26–34.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture and Forestry (IPET) through the Agricultural Microbiome R&D Program, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA-918010-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Electric Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, E., Seo, JA. Enzyme activity of Aspergillus section Nigri strains isolated from the Korean fermentation starter, nuruk. J Microbiol. 60, 998–1006 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-022-2071-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-022-2071-6