Abstract
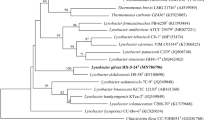
A Gram-negative, motile, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterial strain designated 119BY6-57T was isolated from spongin. The taxonomic position of the novel isolate was confirmed using the polyphasic approach. Strain 119BY6-57T grew well at 25–30°C on marine agar. On the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity, strain 119BY6-57T belongs to the family Xanthomonadaceae and is related to Lysobacter aestuarii S2-CT (99.8% sequence similarity), L. maris KMU-14T (97.5%), and L. daejeonensis GH1-9T (97.3%). Lower sequence similarities (97.0%) were found with all of the other recognized members of the genus Lysobacter. The G + C content of the genomic DNA was 69.9 mol%. The major respiratory quinone was Q-8 and the major fatty acids were C16:0 iso, C15:0 iso, summed feature 9 (comprising C17:1 iso ω9c and/or C16:0 10-methyl), summed feature 3 (comprising C16:1ω7c and/or C16:1ω6c), and C11:0 iso 3-OH. The polar lipids were phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, diphosphatidylglycerol, three unidentified phospholipids, and an unidentified polar lipid. DNADNA relatedness values between strain 119BY6-57T and its closest phylogenetically neighbors were below 48.0 ± 2.1%. Based on genotypic and phenotypic characteristics, it is concluded that strain 119BY6-57T is a new member within the genus Lysobacter, for which the name Lysobacter spongiae sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is 119BY6-57T (= KACC 19276T = LMG 30077T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas, R.M. 1993. Handbook of Microbiological Media. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
Bae, H.S., Im, W.T., and Lee, S.T. 2005. Lysobacter concretionis sp. nov., isolated from anaerobic granules in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 1155–1161.
Buck, J.D. 1982. Nonstaining (KOH) method for determination of Gram reactions of marine bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 44, 992–993.
Cappuccino, J.G. and Sherman, N. 2002. Microbiology: a laboratory manual, 6th ed. Pearson Education, Inc., California, USA.
Euzéby, J.P. 1997. List of bacterial names with standing in nomenclature: a folder available on the Internet. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47, 590–592.
Ezaki, T., Hashimoto, Y., and Yabuuchi, E. 1989. Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39, 224–229.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limit on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39, 783–791.
Fitch, W.M. 1971. Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool. 20, 406–416.
Hall, T.A. 1999. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 41, 95–98.
Hiraishi, A., Ueda, Y., Ishihara, J., and Mori, T. 1996. Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 42, 457–469.
Jeong, S.E., Lee, H.J., and Jeon, C.O. 2016. Lysobacter aestuarii sp. nov., isolated from estuary sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66, 1346–1351.
Kim, S.J., Ahn, J.H., Weon, H.Y., Hong, S.B., and Seok, S.J. 2016. Lysobacter terricola sp. nov., isolated from greenhouse soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66, 1401–1406.
Kim, J.K., Kang, M.S., Park, S.C., Kim, K.M., Choi, K., Yoon, M.H., and Im, W.T. 2015. Sphingosinicella ginsenosidimutans sp. nov., with ginsenoside converting activity. J. Microbiol. 53, 435–441.
Kimura, M. 1983. The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York, USA.
Luo, G., Shi, Z., and Wang, G. 2012. Lysobacter arseniciresistens sp. nov., an arsenite-resistant bacterium isolated from iron-mined soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 1659–1665.
Mesbah, M., Premachandran, U., and Whitman, W. 1989. Precise measurement of the G + C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high performance liquid chromatography. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39, 159–167.
Minnikin, D.E., O’Donnell, A.G., Goodfellow, M., Alderson, G., Athalye, M., Schaal, A., and Parlett, J.H. 1984. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 2, 233–241.
Moore, D.D. and Dowhan, D. 1995. Preparation and analysis of DNA, pp. 2–11. In Ausubel, F.W., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K. (eds.), Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley, New York, USA.
Park, J.H., Kim, R., Aslam, Z., Jeon, C.O., and Chung, Y.R. 2008. Lysobacter capsici sp. nov., with antimicrobial activity, isolated from the rhizosphere of pepper, and emended description of the genus Lysobacter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58, 387–392.
Perry, L.B. 1973. Gliding motility in some non-spreading flexibacteria. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 36, 227–232.
Saitou, N. and Nei, M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425.
Sasser, M. 1990. Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101, MIDI Inc., Newark, DE, USA.
Siddiqi, M.Z. and Im, W.T. 2016a. Lysobacter hankyongensis sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge and Lysobacter sediminicola sp. nov., isolated from freshwater sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66, 212–218.
Siddiqi, M.Z. and Im, W.T. 2016b. Lysobacter pocheonensis sp. nov., isolated from soil of a ginseng field. Arch. Microbiol. 198, 551–557.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., and Kumar, S. 2013. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 2725–2729.
Ten, L.N., Im, W.T., Kim, M.K., Kang, M.S., and Lee, S.T. 2004. Development of a plate technique for screening of polysaccharidedegrading microorganisms by using a mixture of insoluble chromogenic substrates. J. Microbiol. Methods 56, 375–382.
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D.G. 1997. The Clustal_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 4876–4882.
Wang, Y., Dai, J., Zhang, L., Luo, X., and Li, Y. 2009. Lysobacter ximonensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 786–789.
Wang, G.L., Wang, L., Chen, H.H., Shen, B., Li, S.P., and Jiang, J.D. 2011. Lysobacter ruishenii sp. nov., a chlorothalonil-degrading bacterium isolated from a long-term chlorothalonil-contaminated soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61, 674–679.
Wayne, L.G., Brenner, D.J., Colwell, R.R., Grimont, P.A.D., Kandler, O., Krichevsky, M.I., Moore, L.H., Moore, W.E.C., Murray, R.G.E., Stackebrandt, E., et al. 1987. International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37, 463–464.
Weon, H.Y., Kim, B.Y., Baek, Y.K., Yoo, S.H., Kwon, S.W., Stackebrandt, E., and Go, S.J. 2006. Two novel species, Lysobacter daejeonensis sp. nov. and Lysobacter yangpyeongensis sp. nov., isolated from Korean greenhouse soils. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 947–951.
Ye, X.M., Chu, C.W., Shi, C., Zhu, J.C., and He, Q. 2015. Lysobacter caeni sp. nov., isolated from the sludge of a pesticide manufacturing factory. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 65, 845–850.
Yoon, J. 2016. Polyphasic characterization of Lysobacter maris sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from seawater. Curr. Microbiol. 72, 282–287.
Yoon, S.H., Ha, S.M., Kwon, S., Lim, J., Kim, Y., Seo, H., and Chun, J. 2017. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67, 1613–1617.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain 119BY6-57T is KY451771.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, H., Im, WT. & Park, JS. Lysobacter spongiae sp. nov., isolated from spongin. J Microbiol. 56, 97–103 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-7462-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-7462-3