Abstract
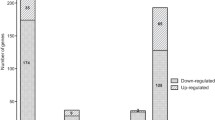
The type VI secretion system (T6SS) is a widespread and versatile protein secretion system found in most Gram-negative bacteria. Studies of T6SS have mainly focused on its role in virulence toward host cells and inter-bacterial interactions, but studies have also shown that T6SS4 in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis participates in the acquisition of zinc ions to alleviate the accumulation of hydroxyl radicals induced by multiple stressors. Here, by comparing the gene expression patterns of wild-type and zntR mutant Y. pseudotuberculosis cells using RNA-seq analysis, T6SS4 and 17 other biological processes were found to be regulated by ZntR. T6SS4 was positively regulated by ZntR in Y. pseudotuberculosis, and further investigation demonstrated that ZntR regulates T6SS4 by directly binding to its promoter region. T6SS4 expression is regulated by zinc via ZntR, which maintains intracellular zinc homeostasis and controls the concentration of reactive oxygen species to prevent bacterial death under oxidative stress. This study provides new insights into the regulation of T6SS4 by a zinc-dependent transcriptional regulator, and it provides a foundation for further investigation of the mechanism of zinc transport by T6SS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basler, M., Pilhofer, M., Henderson, G.P., Jensen, G.J., and Mekalanos, J.J. 2012. Type VI secretion requires a dynamic contractile phage tail-like structure. Nature 483, 182–186.
Bingle, L.E., Bailey, C.M., and Pallen, M.J. 2008. Type VI secretion: a beginner’s guide. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 11, 3–8.
Bobrov, A.G., Kirillina, O., Fetherston, J.D., Miller, M.C., Burlison, J.A., and Perry, R.D. 2014. The Yersinia pestis siderophore, yersiniabactin, and the ZnuABC system both contribute to zinc acquisition and the development of lethal septicaemic plague in mice. Mol. Microbiol. 93, 759–775.
Boyer, F., Fichant, G., Berthod, J., Vandenbrouck, Y., and Attree, I. 2009. Dissecting the bacterial type VI secretion system by a genome wide in silico analysis: what can be learned from available microbial genomic resources? BMC Genom. 10, 104.
Brown, N.L., Stoyanov, J.V., Kidd, S.P., and Hobman, J.L. 2003. The MerR family of transcriptional regulators. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27, 145–163.
Cascales, E. and Cambillau, C. 2012. Structural biology of type VI secretion systems. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 367, 1102–1111.
Cornelis, P., Wei, Q., Andrews, S.C., and Vinckx, T. 2011. Iron homeostasis and management of oxidative stress response in bacteria. Metallomics 3, 540–549.
Dong, T.G., Dong, S., Catalano, C., Moore, R., Liang, X., and Mekalanos, J.J. 2015. Generation of reactive oxygen species by lethal attacks from competing microbes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 2181–2186.
Faulkner, M.J. and Helmann, J.D. 2011. Peroxide stress elicits adaptive changes in bacterial metal ion homeostasis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 15, 175–189.
Grass, G., Wong, M.D., Rosen, B.P., Smith, R.L., and Rensing, C. 2002. ZupT is a Zn(II) uptake system in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 184, 864–866.
Guan, J., Xiao, X., Xu, S., Gao, F., Wang, J., Wang, T., Song, Y., Pan, J., Shen, X., and Wang, Y. 2015. Roles of RpoS in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis stress survival, motility, biofilm formation and type VI secretion system expression. J. Microbiol. 53, 633–642.
Gueguen, E., Durand, E., Zhang, X.Y., d’Amalric, Q., Journet, L., and Cascales, E. 2013. Expression of a Type VI secretion system is responsive to envelope stresses through the OmpR transcriptional activator. PLoS One 8, e66615.
Holland, I.B. 2010. The extraordinary diversity of bacterial protein secretion mechanisms. Methods Mol. Biol. 619, 1–20.
Ishikawa, T., Sabharwal, D., Broms, J., Milton, D.L., Sjostedt, A., Uhlin, B.E., and Wai, S.N. 2012. Pathoadaptive conditional regulation of the type VI secretion system in Vibrio cholerae O1 strains. Infect. Immun. 80, 575–584.
Jani, A.J. and Cotter, P.A. 2010. Type VI secretion: not just for pathogenesis anymore. Cell Host Microbe 8, 2–6.
Kanehisa, M., Araki, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Hirakawa, M., Itoh, M., Katayama, T., Kawashima, S., Okuda, S., Tokimatsu, T., et al. 2008. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D480–484.
Khan, S., Brocklehurst, K.R., Jones, G.W., and Morby, A.P. 2002. The functional analysis of directed amino-acid alterations in ZntR from Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 299, 438–445.
Li, B. and Dewey, C.N. 2011. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 12, 323.
Li, H. and Durbin, R. 2009. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25, 1754–1760.
Ma, L.S., Hachani, A., Lin, J.S., Filloux, A., and Lai, E.M. 2014. Agrobacterium tumefaciens deploys a superfamily of type VI secretion DNase effectors as weapons for interbacterial competition in planta. Cell Host Microbe 16, 94–104.
Ma, A.T., McAuley, S., Pukatzki, S., and Mekalanos, J.J. 2009. Translocation of a Vibrio cholerae type VI secretion effector requires bacterial endocytosis by host cells. Cell Host Microbe 5, 234–243.
Miller, J.H. 1992. A short course in bacterial genetics: a laboratory manual and handbook for Escherichia coli and related bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, N.Y., USA.
Mols, M. and Abee, T. 2011. Primary and secondary oxidative stress in Bacillus. Environ. Microbiol. 13, 1387–1394.
Mortazavi, A., Williams, B.A., McCue, K., Schaeffer, L., and Wold, B. 2008. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nature Methods 5, 621–628.
Mougous, J.D., Cuff, M.E., Raunser, S., Shen, A., Zhou, M., Gifford, C.A., Goodman, A.L., Joachimiak, G., Ordonez, C.L., Lory, S., et al. 2006. A virulence locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a protein secretion apparatus. Science 312, 1526–1530.
Mougous, J.D., Gifford, C.A., Ramsdell, T.L., and Mekalanos, J.J. 2007. Threonine phosphorylation post-translationally regulates protein secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nature Cell Biol. 9, 797–803.
Outten, C.E. and O’Halloran, T.V. 2001. Femtomolar sensitivity of metalloregulatory proteins controlling zinc homeostasis. Science 292, 2488–2492.
Outten, C.E., Outten, F.W., and O’Halloran, T.V. 1999. DNA distortion mechanism for transcriptional activation by ZntR, a Zn(II)-responsive MerR homologue in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37517–37524.
Panina, E.M., Mironov, A.A., and Gelfand, M.S. 2003. Comparative genomics of bacterial zinc regulons: enhanced ion transport, pathogenesis, and rearrangement of ribosomal proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 9912–9917.
Parsons, D.A. and Heffron, F. 2005. sciS, an icmF homolog in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, limits intracellular replication and decreases virulence. Infect. Immun. 73, 4338–4345.
Patzer, S.I. and Hantke, K. 1998. The ZnuABC high-affinity zinc uptake system and its regulator Zur in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 28, 1199–1210.
Permina, E.A., Kazakov, A.E., Kalinina, O.V., and Gelfand, M.S. 2006. Comparative genomics of regulation of heavy metal resistance in Eubacteria. BMC Microbiol. 6, 49.
Petrarca, P., Ammendola, S., Pasquali, P., and Battistoni, A. 2010. The Zur-regulated ZinT protein is an auxiliary component of the high-affinity ZnuABC zinc transporter that facilitates metal recruitment during severe zinc shortage. J. Bacteriol. 192, 1553–1564.
Pruteanu, M., Neher, S.B., and Baker, T.A. 2007. Ligand-controlled proteolysis of the Escherichia coli transcriptional regulator ZntR. J. Bacteriol. 189, 3017–3025.
Pukatzki, S., Ma, A.T., Sturtevant, D., Krastins, B., Sarracino, D., Nelson, W.C., Heidelberg, J.F., and Mekalanos, J.J. 2006. Identification of a conserved bacterial protein secretion system in Vibrio cholerae using the Dictyostelium host model system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 1528–1533.
Rensing, C., Mitra, B., and Rosen, B.P. 1997. The zntA gene of Escherichia coli encodes a Zn(II)-translocating P-type ATPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 14326–14331.
Russell, A.B., Hood, R.D., Bui, N.K., LeRoux, M., Vollmer, W., and Mougous, J.D. 2011. Type VI secretion delivers bacteriolytic effectors to target cells. Nature 475, 343–347.
Russell, A.B., Wexler, A.G., Harding, B.N., Whitney, J.C., Bohn, A.J., Goo, Y.A., Tran, B.Q., Barry, N.A., Zheng, H., Peterson, S.B., et al. 2014. A type VI secretion-related pathway in Bacteroidetes mediates interbacterial antagonism. Cell Host Microbe 16, 227–236.
Song, Y., Xiao, X., Li, C., Wang, T., Zhao, R., Zhang, W., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., and Shen, X. 2015. The dual transcriptional regulator RovM regulates the expression of AR3- and T6SS4-dependent acid survival systems in response to nutritional status in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Environ. Microbiol. 17, 4631–4645.
Tarazona, S., Garcia-Alcalde, F., Dopazo, J., Ferrer, A., and Conesa, A. 2011. Differential expression in RNA-seq: a matter of depth. Genome Res. 21, 2213–2223.
Wang, D., Hosteen, O., and Fierke, C.A. 2012. ZntR-mediated transcription of zntA responds to nanomolar intracellular free zinc. J. Inorg. Biochem. 111, 173–181.
Wang, T.T., Si, M.R., Song, Y.H., Zhu, W.H., Gao, F., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, W.P., Wei, G.H., Luo, Z.Q., et al. 2015. Type VI secretion system transports Zn2+ to combat multiple stresses and host immunity. PLoS Pathog. 11, e1005020.
Weber, B., Hasic, M., Chen, C., Wai, S.N., and Milton, D.L. 2009. Type VI secretion modulates quorum sensing and stress response in Vibrio anguillarum. Environ. Microbiol. 11, 3018–3028.
Wu, C.F., Lin, J.S., Shaw, G.C., and Lai, E.M. 2012. Acid-induced type VI secretion system is regulated by ExoR-ChvG/ChvI signaling cascade in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. PLoS Pathog. 8, e1002938.
Zhang, W., Wang, Y., Song, Y., Wang, T., Xu, S., Peng, Z., Lin, X., Zhang, L., and Shen, X. 2013. A type VI secretion system regulated by OmpR in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis functions to maintain intracellular pH homeostasis. Environ. Microbiol. 15, 557–569.
Zhang, W., Xu, S., Li, J., Shen, X., Wang, Y., and Yuan, Z. 2011. Modulation of a thermoregulated type VI secretion system by AHLdependent quorum sensing in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Arch. Microbiol. 193, 351–363.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Chen, K., Gao, F. et al. ZntR positively regulates T6SS4 expression in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis . J Microbiol. 55, 448–456 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-6540-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-6540-2