Abstract
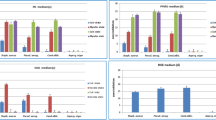
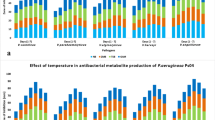
This study was undertaken to investigate the influence of culture conditions and medium components on production of antibacterial compounds by Serratia sp. WPRA3 (JX020764) which was isolated from marine water of Port Dickson, Malaysia. Biochemical, morphological, and molecular characteristics suggested that the isolate is a new candidate of the Serratia sp. The isolate showed strong antimicrobial activity against fungi, Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. This bacterium exhibited optimum antibacterial compounds production at 28°C, pH 7 and 200 rev/min aeration during 72 h of incubation period. Highest antibacterial activity was obtained when sodium chloride (2%), yeast extract (0.5%), and glucose concentration (0.75%) were used as salt, nitrogen, and carbon sources respectively. Different active fractions were obtained by Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) and Flash Column Chromatography (FCC) from ethyl acetate crude extracts namely OCE and RCE in different culture conditions, OCE (pH 5, 200 rev/min) and RCE (pH 7/without aeration). In conclusion, the results suggested different culture conditions have a significant impact on the types of secondary metabolites produced by the bacterium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S.F., Madden, T.L., Schäffer, A.A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., and Lipman, D.J. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-LAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3389–3402.
Anand, T.P., Bhat, A.W., Shouche, Y.S., Roy, U., Siddharth, J., and Sarma, S.P. 2006. Antimicrobial activity of marine bacteria associated with sponges from the waters off the coast of South East India. Microbiol. Res. 161, 252–262.
Bauer, A.W., Kirby, W.M., Sherris, J.C., and Turck, M. 1966. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45, 493–496.
Bennet, J.W. and Bentley, R. 2000. Seeing Red: The story of prodigiosin. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 47, 1–32.
D’Alessio, R., Bargiotti, A., Carlini, O., Colotta, F., Ferrari, M., Gnocchi, P., Isetta, A., Mongelli, N., Motta, P., Rossi, A., and et al. 2000. Synthesis and immunosuppressive activity of novel prodigiosin derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 43, 2557–2565.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Estimation of confidence in phylogeny: the complete-and-partial bootstrap technique. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 39, 783–791.
Giri, A.V., Anandkumar, N., Muthukumaran, G., and Pennathur, G. 2004. A novel medium for the enhanced cell growth and production of prodigiosin from Serratia marcescens isolated from soil. BMC Microbiol. 4, 11.
Grimont, P.A.D., Grimont, F., Dulong D.E Rosnay, H.L.C., and Sneathp, H.A. 1977. Taxonomy of the genus Serratia. J. Gen. Microbiol. 98, 39–66.
Hall, T.A. 1999. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 41, 95–98.
Han, S.B., Kim, H.M., Kim, Y.H., Lee, C.W., Jang, E.S., Son, K.H., Kim, S.U., and Kim, Y.K. 1998. T-cell specific immunosuppression by prodigiosin isolated from Serratia marcescens. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 20, 1–13.
Jonas, D., Schultheis, B., Klas, C., Krammer, P.H., and Bhakdi, S. 1993. Cytocidal effects of Escherichia coli hemolysin on human T lymphocytes. Infect. Immun. 61, 1715–1721.
Leone, S., Silipo, A.L., Nazarenko, E., Lanzetta, R., Parrilli, M., and Molinaro, A. 2007. Molecular structure of endotoxins from Gramnegative marine bacteria. Mar. Drugs 5, 85–112.
Lynch, D.L., Worthy, T.E., and Kresheck, G.C. 1968. Chromatographic separation of the pigment fractions from a Serratia marcescens strain. Appl. Microbiol. 16, 13–20.
Mbosso, E.J., Ngouelaa, S., Nguediac, J.C., Bengc, V.P., Rohmerb, M., and Tsamoa, E. 2010. In vitro antimicrobial activity of extracts and compounds of some selected medicinal plants from Cameroon. J. Ethnopharmacol. 128, 476–481.
Montaner, B., Navarro, S., Pique, M., Vilaseca, M., Martinell, M., Giralt, E., Gil, J., and Pérez-Tomás, R. 2000. Prodigiosin from the supernatant of Serratia marcescens induces apoptosis in haematopoietic cancer cell lines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 131, 585–593.
Montaner, B. and Pérez-Tomás, R. 2003. The prodigiosins: a new family of anticancer drugs. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 3, 57–65.
Moraes, C.S., Seabra, S.H., Albuquerque-Cunha, J.M., Castro, D.P., Genta, F.A., de Souza, W., Brazil, R.P., Garcia, E.S., and Azambuja, P. 2009. Prodigiosin is not a determinant factor in lysis of Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis after interaction with Serratia marcescens d-mannose sensitive fimbriae. Exp. Parasitol. 122, 84–90.
Pridham, T.G. and Gottlieb, D. 1948. The utilization of carbon compounds by some Actinomycetales as an aid for species determination. J. Bacteriol. 56, 107–114.
Samrot, A.V., Chandana, K., Senthilkumar, P., and Narendra, K.G. 2011. Optimization of prodigiosin production by Serratia marcescens SU-10 and evaluation of its bioactivity. Int. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2, 128–133.
Schwartsmann, G., Brondani da Rocha, A., Berlinck, R.G., and Jimeno, J. 2001. Marine organisms as a source of new anticancer agants. Lancet Oncol. 2, 221–225.
Song, M.J., Bae, J., Lee, D.S., Kim, C.H., Kim, J.S., Kim, S.W., and Hong, S.I. 2006. Purification and characterization of prodigiosin produced by integrated bioreactor from Serratia sp. KH-95. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 101, 157–161.
Spröer, C., Mendrock, U., Swiderski, J., Lang, E., and Stackebrandt, E. 1999. The phylogenetic position of Serratia, Buttiauxella and some other genera of the familiy Enterobacteriaceae. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49, 1433–1438.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., and Kumar, S. 2007. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1596–1599.
Thompson, J.D., Higgins, D.G., and Gibson, T.J. 1994. Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 4673–4680.
Weiss, C.M. 1949. Spectrophotometric and chromatographic analyses of the pigment produced by members of the genus Serratia. J. Cell Physiol. 34, 467–492.
Williams, R.P., Green, J.A., and Rappo-port, D.A. 1956. Studies on pigmentation of Serratia marcescens. I. Spectral and paper chromatographic properties of prodigiosin. J. Bacteriol. 71, 115–120.
Zhang, C.X., Yang, S.Y., Xu, M.X., Sun, J., Liu, H., Liu, J.R., Liu, H., Kan, F., Sun, J., Lai, R., and et al. 2009. Serratia nematodiphila sp. nov., associated symbiotically with the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditidoides chongmingensis (Rhabditida: habditidae). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 1603–1608.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafarzade, M., Yahya, N.A., Shayesteh, F. et al. Influence of culture conditions and medium composition on the production of antibacterial compounds by marine Serratia sp. WPRA3. J Microbiol. 51, 373–379 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2440-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2440-2