Abstract
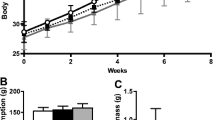
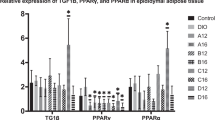
We investigated the weight-gain suppressive effect of Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 isolated from human breast milk. Rats were fed a high-carbohydrate diet and administered BNR17 (BNR17 group) twice daily for twelve weeks. Changes were observed in body weight and white adipose tissue mass. The percent increase in body weight (P=0.0331) and fat pad mass (P<0.01) was significantly lower in the BNR17 group, and the FER was moderately lower (P=0.0769). These data suggest that BNR17 can prevent diet-induced overweight and may become an alternative method for treating weight problems and obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altunkaynak, B.Z. and E. Ozbek. 2009. Overweight and structural alterations of the liver in female rats fed a high-fat diet: a stereological and histological study. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 20, 93–103.
Bhathena, J., C. Martoni, A. Kulamarva, A.M. Urbanska, M. Malhotra, and S. Prakash. 2009. Orally delivered microencapsulated live probiotic formulation lowers serum lipids in hypercholesterolemic hamsters. J. Med. Food 12, 310–319.
Cusi, K. 2010. The role of adipose tissue and lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 10, 306–315.
Delzenne, N. and G. Reid. 2009. No causal link between obesity and probiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7, 901; author reply 901.
Ehrlich, S.D. 2009. Probiotics-little evidence for a link to obesity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7, 901; author reply 901.
Guandalini, S. 2008. Probiotics for children with diarrhea: an update. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 42, S53–S57.
Isolauri, E. and S. Salminen. 2008. Probiotics: use in allergic disorders: a Nutrition, Allergy, Mucosal Immunology, and Intestinal Microbiota (NAMI) research group report. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 42, S91–S96.
Kumar, M., A. Kumar, R. Nagpal, D. Mohania, P. Behare, V. Verma, P. Kumar, D. Poddar, P.K. Aggarwal, C.J. Henry, S. Jain, and H. Yadav. 2010. Cancer-preventing attributes of probiotics: an update. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 61, 473–496.
Lee, K., K. Paek, H.Y. Lee, J.H. Park, and Y. Lee. 2007. Antiobesity effect of trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid-producing Lactobacillus plantarum PL62 on diet-induced obese mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 103, 1140–1146.
Ley, R.E., F. Bäckhed, P. Turnbaugh, C.A. Lozupone, R.D. Knight, and J.I. Gordon. 2005. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 11070–11075.
Ley, R.E., P.J. Turnbaugh, S. Klein, and J.I. Gordon. 2006. Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444, 1022–1023.
Lye, H.S., C.Y. Kuan, J.A. Ewe, W.Y. Fung, and M.T. Liong. 2009. The improvement of hypertension by probiotics: effects on cholesterol, diabetes, renin, and phytoestrogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 10, 3755–3775.
Mennigen, R. and M. Bruewer. 2009. Effect of probiotics on intestinal barrier function. Ann. NY. Acad. Sci. 1165, 183–189.
Nguyen, T.D., J.H. Kang, and M.S. Lee. 2007. Characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum PH04, a potential probiotic bacterium with cholesterol-lowering effects. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 113, 358–361.
Olivares, M., M.A. Díaz-Ropero, N. Gómez, F. Lara-Villoslada, S. Sierra, J.A. Maldonado, R. Martín, E. López-Huertas, J.M. Rodríguez, and J. Xaus. 2005. Oral administration of two probiotic strains, Lactobacillus gasseri CECT5714 and Lactobacillus coryniformis CECT5711, enhances the intestinal function of healthy adults. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 107, 104–111.
Owen, C.G., R.M. Martin, P.H. Whincup, G.D. Smith, and D.G. Cook. 2006. Does breastfeeding influence risk of type 2 diabetes in later life? A quantitative analysis of published evidence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 84, 1043–1054.
Owen, C.G., R.M. Martin, P.H. Whincup, G.D. Smith, and M.W. Gillman. 2008. The effect of breastfeeding on mean body mass index throughout life: a quantitive review of published and unpublished observational evidence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 82, 1298–1307.
Perdigón, G., R. Fuller, and R. Raya. 2001. Lactic acid bacteria and their effect on the immune system. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2, 27–42.
Raoult, D. 2009. Probiotics and obesity: a link? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7, 616.
Turnbaugh, P.J., R.E. Ley, M.A. Mahowald, V. Magrini, E.R. Mardis, and J.I. Gordon. 2006. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444, 1027–1031.
Yun, S.I., H.O. Park, and J.H. Kang. 2009. Effect of Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 on blood glucose levels and body weight in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 107, 1681–1686.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, JH., Yun, SI. & Park, HO. Effects of Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 on body weight and adipose tissue mass in diet-induced overweight rats. J Microbiol. 48, 712–714 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0363-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0363-8