Abstract
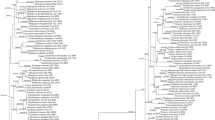
Based on morphological examination, two species of Polyporus, P. dictyopus, and P. tuberaster, were identified, which constitutes the first record of these species in South Korea. To confirm their affinity within the genus Polyporus, the phylogenetic relationships of Polyporus and allied genera were established from nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA (nLSU rDNA) sequences, and a morphological diagnostic key is presented to clarify the Korean species of Polyporus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adanson, M. 1763. Familles des plantes. Vol. 2. Fungi Sect V. Paris: Chez Vincen.
Buchanan, P.K. and L. Ryvarden. 1998. New Zealand polypore fungi (Aphyllophorales): three new species and a new record. NZ. J. Bot 36, 219–231.
Clements, F.E. and C.L. Shear. 1931. The genera of fungi. New York: The H.W. Wilson Co.
Corner, E.J.H. 1984. Ad Polyporaceas II: Polyporus, Mycobonia and Echinochaete. Beih. Nova Hedwigia 78, 1–29.
Dai, Y.C. 1996. Changbai wood-rotting fungi 5. Study on Polyporus mongolicus and P. tubaeformis. Ann. Bot. Fennici 33, 153–163.
Dai, Y.C. 1999. Changbai wood-rotting fungi 11. Species of Polyporus sensu stricto. Fung. Sci. 14, 67–77.
Donk, M.A. 1933. Revision de Niederlandischen Homobasidiomycetes. Aphyllophoraceae II. Meded. Bot. Mus. Herb. Rijks. Univ. Utrecht. 9, 1–141.
Donk, M.A. 1964. The generic names proposed for Polyporaceae. Persoonia 1, 173–302.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39, 783–791.
Fries, E.M. 1815. Observationes mycologicae. Vol. 1. Havniae. p. 230.
Fries, E.M. 1821. Systema Mycologicum. Vol. 1. Mauritius: Greifswald. p. 520.
Gilbertson, R.L. and L. Ryvarden. 1987. North American polypores, Vol. 2. Fungiflora, Oslo.
Hattori, T. 2000. Type studies of the polypores described by E.J.H. Corner from Asia and west Pacific I. Species described in Polyporus, Buglossoporus, Melipilus, Daedalea, and Flabellophora. Mycoscience 41, 339–349.
Imazeki, R. and T. Hongo. 1989. Colored illustrations of mushrooms of Japan. Vol. 2. Osaka, Japan: Hoikusha. p. 315.
Jahn, H. 1980. Polyporus arcularius (Batsch) ex Fries, der Borstrandige Porling. Westf. Pilzbr. 11, 162–180.
Jeon, Y.S., H. Chung, S. Park, I. Hur, J.H. Lee, and J. Chun. 2005. jPHYDIT: a JAVA-based integrated environment for molecular phylogeny of ribosomal RNA sequences. Bioinformatics 21, 3171–3173.
Jung, H.S. 1975. Revision of the Korean Aphyllophorales. M.Sc. Thesis. Seoul National University, p. 34. Seoul, Korea.
Jung, H.S. 1992. Fungal Flora of Ullung Island (III) — on some polyporoid fungi. Kor. J. Mycol. 20, 1–10.
Jung, H.S. 1994. Floral Studies on Korean Wood-rotting Fungi (II) — on the flora of the Aphyllophorales (Basidiomycotina). Kor. J. Mycol. 22, 62–99.
Ko, K.S. and H.S. Jung. 2002. Phylogenetic evaluation of Polyporus s. str. based on molecular sequences. Mycotaxon 82, 315–322.
Krüger, D. and A. Gargas. 2004. The basidiomycete genus Polyporus — an emendation based on phylogeny and putative secondary structure of ribosomal RNA molecules. Feddes Repert 115, 530–546.
Largent, D.L., D. Johnson, and R. Watling. 1977. How to identify mushrooms to genus, III. Microscopic features. Mad River Press, Eureka, CA, USA.
Lee, J.Y. 1975. The Common Names of Korean Higher Fungi. Kor. J. Mycol. 3, 27–30.
Lee, J.Y. 1988. Coloured Korean Mushrooms, pp. 204–213. Academic Publishing Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
Lee, T.S. 1990. The Full List of Recorded Mushrooms in Korea. Kor. J. Mycol. 18, 233–259.
Lee, E.R. and H.S. Jung. 1972. Taxonomic study of basidiomycetes. Ministry of Science and Technology R-72-82.
Lee, J.S. and H.S. Jung. 2005. List of Recorded Korean Aphyllophorales. Kor. J. Mycol. 33, 38–53.
Lee, J.Y., Y.W. Lee, and J.H. Lim. 1959. Coloured illustration of fungi of Korea, Baemungak, Seoul, Korea.
Lim, J.H. and B.G. Kim. 1972. Taxonomic investigations on Korean higher fungi (I). Kor. J. Pharmacog. 3, 11–20.
McNeill, J., F.R. Barrie, H.M. Burdet, V. Demoulin, D.J. Hawksworth, K. Marhold, D.H. Nicolson, and et al. 2006. International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (Vienna Code) adopted by the 17th International Botanical Congress, Vienna, Austria, July 2005. Regnum Veget 146:(i)xviii, 1–568.
Micheli, P. 1729. Nova plantarum genera. Richmond Publishing, Surrey, UK. Reprint 1976. p. 233.
Murrill, W.A. 1903. A historical review of the genera of the Polyporaceae. J. Mycol. 9, 87–102.
Núñez, M. and L. Ryvarden. 1995. Polyporus (Basidiomycotina) and related genera. Syn. Fung. 10, 1–85.
Park, W.H. and H.D. Lee. 1999. Illustrated book of Korean medicinal mushrooms, pp. 524–527. Kyo-Hak Publishing Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
Popoff, O.F. and J.E. Wright. 1998. Fungi of Paraguay. 1. Preliminary checklist of wood-inhabiting polypores (Aphyllophorales, Basidiomycota). Mycotaxon 67, 323–340.
Posada, D. and K.A. Crandall. 1998. Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14, 817–818.
Rehner, S.A. and G.J. Samuels. 1994. Taxonomy and phylogeny of Gliocladium analyzed from nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol. Res. 98, 625–634.
Ryvarden, L. 1991. Genera of polypores: nomenclature and taxonomy. Synopsis Fungorum 5, 1–363.
Ryvarden, L. and R.L. Gilbertson. 1994. European polypores. Vol. 2. Fungiflora. Oslo.
Ryvarden, L. and I. Johansen. 1980. A preliminary polypore flora of East Africa. Fungiflora. Oslo, Norway.
Salamin, N., M.W. Chase, T.R. Hodkinson, and V. Savolainen. 2003. Assessing internal support with large phylogenetic DNA matrices. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 27, 528–539.
Silveira, R.M.B. and J.E. Wright. 2005. The taxonomy of Echinochaete and Polyporus s. str. in South America. Mycotaxon 93, 1–59.
Sotome, K., T. Hattori, and M. Kakishima. 2007. Polyporus phyllostachydis sp. Nov. with notes on other rhizophilic species of Polyporus. Mycoscience 48, 42–46.
Sotome, K., T. Hattori, Y. Ota, C. To-anun, B. Salleh, and M. Kakishima. 2008. Phylogenetic relationships of Polyporus and morphologically allied genera. Mycologia 100, 603–615.
Swofford, D.L. 2002. PAUP*4.0b Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (* and other method), version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA.
Thorn, R.G. 2000. Some polypores misclassified in Piptoporus. Karstenia 40, 181–187.
Vilgalys, R. and M. Hester. 1990. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 172, 4238–4246.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.S., Woo, E.J., Oh, K.H. et al. The first report of two species of Polyporus (Polyporaceae, Basidiomycota) from South Korea. J Microbiol. 48, 748–753 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0105-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0105-y