Abstract
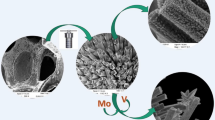
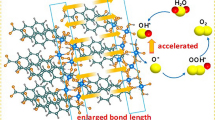
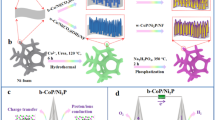
Rational design of highly active transition-metal phosphides for electrocatalyzing overall water splitting in a wide pH range assisted by first-principle calculations can efficiently save the developing cost and hence is quite attractive. Under the guidance of density-functional theory (DFT) calculations that the introduction of dopants (Fe, Mn, and Ni) into CoP could promote the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) performances, a series of binder-free CoMxP/carbon cloth (CC; M = Fe, Mn, and Ni; x = 0, 0.05, 0.2, 0.5, and 1) were fabricated. Both experimental measurements and DFT calculations confirm the electronic modulation of dopants. DFT calculations further reveal that the modulated electronic structure promotes the electronic conductivity, favors the adsorption of key species, and consequently promotes the electrochemical performances. As predicted, the bimetallic phosphides demonstrate excellent HER performances in alkaline, acidic, and alkaline simulated seawater solutions and also deliver excellent oxygen evolution reaction (OER) performances, overwhelming the commercial RuO2. Benefiting from the modulated electronic structure and the hierarchical structure with massive CoFe0.05P zero-dimensional (0D) quantum dots anchored on two-dimensional (2D) N-doped porous carbon, CoFe0.05P delivered the best HER in four kinds of electrolytes (η10 of 73 mV in an alkaline simulated seawater solution) and OER in two kinds of electrolytes (η10 of 264 mV in an alkaline solution) with excellent stability of 45 h in the alkaline solution. The assembled CoFe0.05P/CC//CoFe0.05P/CC with the electrodes folded by 180° can still maintain a low cell potential of 1.62 V at 10 mA·cm−2. This work proves the feasibility of the reported rational design strategy of developing efficient electrocatalysts for overall water splitting in a wide pH range.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu, L.; Zhu, Q.; Song, S. W.; McElhenny, B.; Wang, D. Z.; Wu, C. Z.; Qin, Z. J.; Bao, J. M.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S. et al. Non-noble metal-nitride based electrocatalysts for high-performance alkaline seawater electrolysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5106.
Zhang, J.; Huang, S. S.; Ning, P.; Xin, P. J.; Chen, Z. W.; Wang, Q.; Uvdal, K.; Hu, Z. J. Nested hollow architectures of nitrogen-doped carbon-decorated Fe, Co, Ni-based phosphides for boosting water and urea electrolysis. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1916–1925.
Xue, Y. R.; Wang, X. D.; Zhang, X. Q.; Fang, J. J.; Xu, Z. Y.; Zhang, Y. F.; Liu, X. R.; Liu, M. Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, Z. B. Cost-effective hydrogen oxidation reaction catalysts for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2021, 37, 2009103.
Jin, S. Are metal chalcogenides, nitrides, and phosphides oxygen evolution catalysts or bifunctional catalysts? ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1937–1938.
Liu, R. Q.; Xu, S. S.; Shao, X. X.; Wen, Y.; Shi, X. R.; Huang, L. P.; Hong, M.; Hu, J.; Yang, Z. Defect-engineered NiCo-S composite as a bifunctional electrode for high-performance supercapacitor and electrocatalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 47717–47727.
Zhang, L. P.; Zhang, J. T.; Fang, J. J.; Wang, X. Y.; Yin, L. K.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, Z. B. Cr-doped CoP nanorod arrays as high-performance hydrogen evolution reaction catalysts at high current density. Small 2021, 17, 2100832.
Huang, M. R.; Sun, C. Y.; Zhang, X. R.; Wang, P. J.; Xu, S. S.; Shi, X. R. The surface structure, stability, and catalytic performances toward O2 reduction of CoP and FeCoP2. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 10420–10431.
Cao, X. Y.; Jia, D. D.; Li, D.; Cui, L.; Liu, J. Q. One-step co-electrodeposition of hierarchical radial NixP nanospheres on Ni foam as highly active flexible electrodes for hydrogen evolution reaction and supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 310–318.
Wang, Y.; Zheng, X. B.; Wang, D. S. Design concept for electrocatalysts. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1730–1752.
Wang, Y. N.; Yang, Z. J.; Yang, D. H.; Zhao, L.; Shi, X. R.; Yang, G. C.; Han, B. H. FeCoP2 nanoparticles embedded in N and P co-doped hierarchically porous carbon for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 8832–8843.
Wang, M. S.; Fu, W. Y.; Du, L.; Wei, Y. S.; Rao, P.; Wei, L.; Zhao, X. S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S. H. Surface engineering by doping manganese into cobalt phosphide towards highly efficient bifunctional HER and OER electrocatalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 515, 146059.
Hu, X. M.; Zhang, S. L.; Sun, J. W.; Yu, L.; Qian, X. Y.; Hu, R. D.; Wang, Y. N.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, J. W. 2D Fe-containing cobalt phosphide/cobalt oxide lateral heterostructure with enhanced activity for oxygen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 109–117.
Liu, K. W.; Zhang, C. L.; Sun, Y. D.; Zhang, G. H.; Shen, X. C.; Zou, F.; Zhang, H. C.; Wu, Z. W.; Wegener, E. C.; Taubert, C. J. et al. High-performance transition metal phosphide alloy catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 158–167.
Yu, W. L.; Gao, Y. X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z. X.; Wang, L. Strategies on improving the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution performances of metal phosphides. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 1876–1902.
Shi, J. H.; Qiu, F.; Yuan, W. B.; Guo, M. M.; Lu, Z. H. Nitrogen-doped carbon-decorated yolk-shell CoP@FeCoP micro-polyhedra derived from MOF for efficient overall water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126312.
Zhan, J.; Cao, X.; Zhou, J. M.; Xu, G.; Lei, B.; Wu, M. H. Porous array with CoP nanoparticle modification derived from MOF grown on carbon cloth for effective alkaline hydrogen evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 128943.
Huang, S. M.; Shi, X. R.; Sun, C. Y.; Zhang, X. R.; Huang, M. R.; Liu, R. Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, S. S. Template-controlled in-situ growing of NiCo-MOF nanosheets on Ni foam with mixed linkers for high performance asymmetric supercapacitors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 572, 151344.
Zhang, B. W.; Li, C. J.; Hu, J.; Peng, D. D.; Huang, K.; Wu, J. S.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y. Z. Cobalt tungsten phosphide with tunable W-doping as highly efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 4073–4078.
Yan, L. T.; Cao, L.; Dai, P. C.; Gu, X.; Liu, D. D.; Li, L. J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. B. Metal-organic frameworks derived nanotube of nickel-cobalt bimetal phosphides as highly efficient electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1703455.
Yang, G. C.; Jiao, Y. Q.; Yan, H. J.; Xie, Y.; Wu, A. P.; Dong, X.; Guo, D. Z.; Tian, C. G.; Fu, H. G. Interfacial engineering of MoO2-FeP heterojunction for highly efficient hydrogen evolution coupled with biomass electrooxidation. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000455.
Zhang, B. S.; Xu, W. W.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Ma, T. F.; Wang, G. H.; Lu, Z. Y.; Sun, J. Enhanced interface interaction in Cu2S@Ni core-shell nanorod arrays as hydrogen evolution reaction electrode for alkaline seawater electrolysis. J. Power Sources 2021, 506, 230235.
Duan, Z. C.; Shi, X. R.; Sun, C. Y.; Lin, W. S.; Huang, S. M.; Zhang, X. R.; Huang, M. R.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S. S. Interface engineered hollow Co3O4@CoNi2S4 nanostructure for high efficiency supercapacitor and hydrogen evolution. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 412, 140139.
Zhang, S. L.; Guan, B. Y.; Lu, X. F.; Xi, S. B.; Du, Y. H.; Lou, X. W. Metal atom-doped Co3O4 hierarchical nanoplates for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002235.
Kong, D. Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S. Z.; Hu, J. P.; von Lim, Y.; Liu, B.; Fan, S.; Shi, Y. M.; Yang, H. Y. 3D self-branched zinc-cobalt oxide@N-doped carbon hollow nanowall arrays for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors and oxygen electrocatalysis. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 23, 653–663.
Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186.
Steinmann, S. N.; Corminboeuf, C. A generalized-gradient approximation exchange hole model for dispersion coefficients. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 044117.
Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868.
Sun, C. Y.; Duan, Z. C.; Wang, P. J.; Zhang, X. R.; Huang, M. R.; Cao, F.; Lin, W. S.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y. Y.; Shi, X. R. Modulation of graphene and graphdiyne by metaln (n = 1–5) adsorption and nucleation and the effect on hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 580, 152197.
Yang, X. L.; Lu, A. Y.; Zhu, Y. H.; Hedhili, M. N.; Min, S. X.; Huang, K. W.; Han, Y.; Li, L. J. CoP nanosheet assembly grown on carbon cloth: A highly efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen generation. Nano Energy 2015, 15, 634–641.
Han, D. D.; Wei, J. H.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Pan, Y. F.; Wei, Y.; Mao, L. C. Metal-organic framework derived petal-like Co3O4@CoNi2S4 hybrid on carbon cloth with enhanced performance for supercapacitors. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 1428–1436.
Ji, P. X.; Luo, X.; Chen, D.; Jin, H. H.; Pu, Z. H.; Zeng, W. H.; He, J. W.; Bai, H. W.; Liao, Y. C.; Mu, S. C. Significantly improved water oxidation of CoP catalysts by electrochemical activation. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 17851–17859.
Elshahawy, A. M.; Guan, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y. T.; Wu, H. J.; Pennycook, S. J.; Wang, J. Sulfur-doped cobalt phosphide nanotube arrays for highly stable hybrid supercapacitor. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 162–171.
Butt, G.; Sammes, N.; Tompsett, G.; Smirnova, A.; Yamamoto, O. Raman spectroscopy of superionic Ti-doped Li3Fe2(PO4)3 and LiNiPO4 structures. J. Power Sources 2004, 134, 72–79.
Zhou, D.; Wang, Z.; Long, X.; An, Y. M.; Lin, H.; Xing, Z.; Ma, M.; Yang, S. H. One-pot synthesis of manganese oxides and cobalt phosphides nanohybrids with abundant heterointerfaces in an amorphous matrix for efficient hydrogen evolution in alkaline solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 22530–22538.
Yao, R.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M. H.; Li, N.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J. P.; Liu, G. Amorphous CoFeP/NC hybrids as highly efficient electrocatalysts for water oxidation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 30196–30207.
Guo, T.; Xu, X. J.; Wang, X. K.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H. L.; Shi, Z. C.; Huang, M. H. Enabling the full exposure of Fe2P@NixP heterostructures in tree-branch-like nanoarrays for promoted urea electrolysis at high current densities. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128067.
Goryachev, A.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Rohling, R. Y.; Vervuurt, R. H. J.; Bol, A. A.; Hofmann, J. P.; Hensen, E. J. M. Stability of CoPx electrocatalysts in continuous and interrupted acidic electrolysis of water. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 1230–1239.
Jiang, D. L.; Xu, S. J.; Quan, B.; Liu, C. C.; Lu, Y. K.; Zhu, J. J.; Tian, D.; Li, D. Synergistically coupling of Fe-doped CoP nanocubes with CoP nanosheet arrays towards enhanced and robust oxygen evolution electrocatalysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 591, 67–75.
Feng, Z. P.; Sui, Y.; Sun, Z.; Qi, J. Q.; Wei, F. X.; Ren, Y. J.; Zhan, Z. Z.; Zhou, M. H.; Meng, D. M.; Zhang, L. J. et al. Controllable synthesis of flower-like Mn-Co-P nanosheets as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 615, 126265.
Li, X. M.; Hu, Q. Y.; Wang, H. Y.; Chen, M.; Hao, X. G.; Ma, Y. F.; Liu, J.; Tang, K. Y.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Q. Charge induced crystal distortion and morphology remodeling: Formation of Mn-CoP nanowire@Mn-CoOOH nanosheet electrocatalyst with rich edge dislocation defects. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 292, 120172.
Duan, D. H.; Feng, J. R.; Guo, D. S.; Gao, J.; Liu, S. B.; Wang, Y. F.; Zhou, X. X. MOF-derived cobalt manganese phosphide as highly efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 12927–12936.
Song, S. Y.; Guo, M. J.; Zhang, S. S.; Zhan, K.; Yan, Y.; Yang, J. H.; Zhao, B.; Xu, M. Plasma-assisted synthesis of hierarchical NiCoxPy nanosheets as robust and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in both acidic and alkaline media. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 331, 135431.
Dong, Y. M.; Kong, L. G.; Jiang, P. P.; Wang, G. L.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, H. Z.; Tang, B. A general strategy to fabricate NixP as highly efficient cocatalyst via photoreduction deposition for hydrogen evolution. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6845–6853.
Indra, A.; Acharjya, A.; Menezes, P. W.; Merschjann, C.; Hollmann, D.; Schwarze, M.; Aktas, M.; Friedrich, A.; Lochbrunner, S.; Thomas, A. et al. Boosting visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution with an integrated nickel phosphide-carbon nitride system. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1653–1657.
Murthy, A. P.; Theerthagiri, J.; Madhavan, J. Insights on tafel constant in the analysis of hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 23943–23949.
Wang, Z. P.; Xiao, B. B.; Lin, Z. P.; Shen, S. J.; Xu, A. J.; Du, Z. X.; Chen, Y. C.; Zhong, W. W. In-situ surface decoration of RuO2 nanoparticles by laser ablation for improved oxygen evolution reaction activity in both acid and alkali solutions. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 54, 510–518.
Ren, Z. G.; Ren, X. C.; Zhang, L.; Fu, C. H.; Li, X. F.; Zhang, Y. X.; Gao, B.; Yang, L. J.; Chu, P. K.; Huo, K. F. Tungsten-doped CoP nanoneedle arrays grown on carbon cloth as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 5229–5236.
Wu, T. L.; Pi, M. Y.; Wang, X. D.; Guo, W. M.; Zhang, D. K.; Chen, S. J. Developing bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting using three-dimensional porous CoP3 nanospheres integrated on carbon cloth. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 729, 203–209.
Du, Y. M.; Qu, H. Q.; Liu, Y. R.; Han, Y.; Wang, L.; Dong, B. Bimetallic CoFeP hollow microspheres as highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting in alkaline media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 465, 816–823.
Kang, Q. L.; Li, M. Y.; Shi, J. W.; Lu, Q. Y.; Gao, F. A universal strategy for carbon-supported transition metal phosphides as high-performance bifunctional electrocatalysts towards efficient overall water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19447–19456.
Wang, H. F.; Chen, L. Y.; Pang, H.; Kaskel, S.; Xu Q. MOF-derived electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction, oxygen evolution and hydrogen evolution reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1414–1448.
Wang, C.; Li, W.; Wang, X. D.; Yu, N.; Sun, H. X.; Geng, B. Y. Open N-doped carbon coated porous molybdenum phosphide nanorods for synergistic catalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1824–1830.
Valizadeh, A.; Najafpour, M. M. Is nickel phosphide an efficient catalyst for the oxygen-evolution reaction at low overpotentials? New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 19630–19641.
Wang, P. Y.; Pu, Z. H.; Li, Y. H.; Wu, L.; Tu, Z. K.; Jiang, M.; Kou, Z. K.; Amiinu, I. S.; Mu, S. C. Iron-doped nickel phosphide nanosheet arrays: An efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26001–26007.
Lin, Z. S.; Liu, S. L.; Liu, Y. G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S. D.; Zhang, X. F.; Tian, Y.; Tang, Z. H. Rational design of Ru aerogel and RuCo aerogels with abundant oxygen vacancies for hydrogen evolution reaction, oxygen evolution reaction, and overall water splitting. J. Power Sources 2021, 514, 230600.
Yang, M.; Xie, J. Y.; Lin, Z. Y.; Dong, B.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Wen, M. L.; Zhou, Y. N.; Wang, L.; Chai, Y. M. N-doped FeP nanorods derived from Fe-MOFs as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 507, 145096.
Jiao, J. Q.; Yang, W. J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S. J.; Chen, C.; Wang, D. S. Interface engineering of partially phosphidated Co@Co-P@NPCNTs for highly enhanced electrochemical overall water splitting. Small 2020, 16, 2002124.
Zhang, Y. L.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Li, S.; Cui, M. Y.; Ma, L.; Zhou, H.; Su, D.; Zhang, S. Programmable synthesis of multimetallic phosphide nanorods mediated by core/shell structure formation and conversion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 8490–8497.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFB1311605), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21703137), and the Shanghai Sailing Program (No. 20YF1416100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4771_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
DFT-assisted rational design of CoMxP/CC (M = Fe, Mn, and Ni) as efficient electrocatalyst for wide pH range hydrogen evolution and oxygen evolution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Sun, C., Xu, S. et al. DFT-assisted rational design of CoMxP/CC (M = Fe, Mn, and Ni) as efficient electrocatalyst for wide pH range hydrogen evolution and oxygen evolution. Nano Res. 15, 8897–8907 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4771-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4771-y