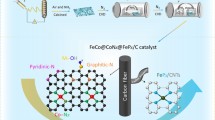
Abstract
Carbon materials featuring hierarchical pores and atomically dispersed metal sites are promising catalysts for energy storage and conversion applications. Herein, we developed a facile strategy to construct functional carbon materials with a fluffy peony-like structure and dense binary FeCo-Nx active sites (termed as f-FeCo-CNT). By regulating the metal content in precursors, a three-dimensional (3D) interconnected conductive carbon nanotubes network was in-situ formed throughout the atomically dispersed FeCo-NC matrix during pyrolysis. Taking advantage of rich pore hierarchy and co-existence of highly active FeCo-Nx sites and beneficial FeCo alloy nanoparticles, the f-FeCo-CNT material exhibited excellent bifunctional performance towards oxygen reduction reaction/oxygen evolution reactions (ORR/OER) with respect to the atomically dispersed FeCo-NC (SA-f-FeCo-NC) and commercial Pt/C+RuO2 mixture, surpassing the SA-f-FeCo-NC with a 20 mV higher ORR half-wave potential and a 100 mV lower OER overpotential (at 10.0 mA/cm2). Remarkably, the f-FeCo-CNT-assembled Zn-air battery (ZAB) possessed a maximum specific power of 195.8 mW/cm2, excellent rate capability, and very good cycling stability at large current density of 20.0 mA/cm2. This work provides a facile and feasible synthetic strategy of constructing low-cost cathode materials with excellent comprehensive ZAB performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neburchilov, V.; Wang, H. J.; Martin, J. J.; Qu, W. A review on air cathodes for zinc-air fuel cells. J. Power Sources2010, 195, 1271–1291.
Lee, J. S.; Kim, S. T.; Cao, R. G.; Choi, N. S.; Liu, M. L.; Lee, K. T.; Cho, J. Metal-air batteries: Metal-air batteries with high energy density: Li-Air versus Zn-Air. Adv. Energy Mater.2011, 1, 2.
Li, H. F.; Ma, L. T.; Han, C. P.; Wang, Z. F.; Liu, Z. X.; Tang, Z. J.; Zhi, C. Y. Advanced rechargeable zinc-based batteries: Recent progress and future perspectives. Nano Energy2019, 62, 550–587.
Cheng, F. Y.; Chen, J. Metal-air batteries: from oxygenreduction electrochemistry to cathode catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev.2012, 41, 2172–2192.
Fu, J.; Cao, Z. P.; Park, M. G.; Yu, A. P.; Fowler, M.; Chen, Z. W. Electrically rechargeable zinc-air batteries: Progress, challenges, and perspectives. Adv. Mater.2017, 29, 1604685.
Li, Y. G.; Dai, H. J. Recent advances in zinc-air batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev.2014, 43, 5257–5275.
Lu, Y. C.; Xu, Z. C.; Gasteiger, H. A.; Chen, S.; Hamad- Schifferli, K.; Shao-Horn, Y. Platinum-gold nanoparticles: A highly active bifunctional electrocatalyst for rechargeable lithium-air batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2010, 132, 12170–12171.
Wang, H. F.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Q. A review of precious-metal-free bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts: Rational design and applications in Zn-Air batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater.2018, 28, 1803329.
Peng, Y.; Lu, B. Z.; Chen, S. W. Carbon-supported single atom catalysts for electrochemical energy conversion and storage. Adv. Mater.2018, 30, 1801995.
Mao, S.; Wen, Z. H.; Huang, T. Z.; Hou, Y.; Chen, J. H. Highperformance bi-functional electrocatalysts of 3D crumpled graphenecobalt oxide nanohybrids for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Energy Environ. Sci.2014, 7, 609–616.
Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, C.; Zou, L. L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, B.; Zou, Z. Q.; Yang H. Fe2N nanoparticles boosting FeNx moieties for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction in Fe-N-C porous catalyst. Nano Res.2019, 12, 1651–1657.
Wang, J.; Wu, H. H.; Gao, D. F.; Miao, S.; Wang, G. X.; Bao, X. H. High-density iron nanoparticles encapsulated within nitrogen-doped carbon nanoshell as efficient oxygen electrocatalyst for zinc-air battery. Nano Energy2015, 13, 387–396.
Lin, L.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, A. W. Noble-metal-free Fe-N/C catalyst for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction under both alkaline and acidic conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2014, 136, 11027–11033.
Jiang, W. J.; Gu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. J.; Wang, J. Q.; Hu, J. S.; Wei, Z. D.; Wan, L. J. Understanding the high activity of Fe-N-C electrocatalysts in oxygen reduction: Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles boost the activity of Fe–Nx. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2016, 138, 3570–3578.
Mamtani, K.; Singh, D.; Tian, J.; Millet, J. M. M.; Miller, J. T.; Co, A. C.; Ozkan, U. S. Evolution of N-coordinated iron-carbon (FeNC) catalysts and their Oxygen Reduction (ORR) performance in acidic media at various stages of catalyst synthesis: An attempt at benchmarking. Catal. Lett.2016, 146, 1749–1770.
Han, L.; Dong, S. J.; Wang, E. K. Transition-metal (Co, Ni, and Fe)-based electrocatalysts for the water oxidation reaction. Adv. Mater.2016, 28, 9266–9291.
Bae, S. H.; Kim, J. E.; Randriamahazaka, H.; Moon, S. Y.; Park, J. Y.; Oh, I. K. Seamlessly conductive 3D nanoarchitecture of core-shell Ni-Co nanowire network for highly efficient oxygen evolution. Adv. Energy Mater.2017, 7, 1601492.
Sun, Y. H.; Zhu, Y. H.; Jiang, H. L.; Shen, J. H.; Yang, X. L.; Zou, W. J.; Chen, J. D.; Li, C. Z. Cobalt nanoparticles embedded in N-doped carbon as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Nanoscale2014, 6, 15080–15089.
Louie, M. W.; Bell, A. T. An investigation of thin-film Ni-Fe oxide catalysts for the electrochemical evolution of oxygen. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2013, 135, 12329–12337.
Chen, Y. J.; Ji, S. F.; Chen, C.; Peng, Q.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Single-atom catalysts: Synthetic strategies and electrochemical applications. Joule2018, 2, 1242–1264.
Chung, H. T.; Cullen, D. A.; Higgins, D.; Sneed, B. T.; Holby, E. F.; More, K. L.; Zelenay, P. Direct atomic-level insight into the active sites of a high-performance PGM-free ORR catalyst. Science2017, 357, 479–484.
Xu, H. X.; Cheng, D. J.; Cao, D. P.; Zeng, X. C. A universal principle for a rational design of single-atom electrocatalysts. Nat. Catal.2018, 1, 339–348.
Yang, X. F.; Wang, A. Q.; Qiao, B. T.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Y.; Zhang, T. Single-atom catalysts: A new frontier in heterogeneous catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res.2013, 46, 1740–1748.
Wang, A. Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, T. Heterogeneous single-atom catalysis. Nat. Rev. Chem.2018, 2, 65–81.
Fei, H. L.; Dong, J. C.; Feng, Y. X.; Allen, C. S.; Wan, C. Z.; Volosskiy, B.; Li, M. F.; Zhao, Z. P.; Wang, Y. L.; Sun, H. T. et al. General synthesis and definitive structural identification of MN4C4 single-atom catalysts with tunable electrocatalytic activities. Nat. Catal.2018, 1, 63–72.
Zang, W. J.; Sumboja, A.; Ma, Y. Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wu, S. S.; Wu, H. J.; Liu, Z. L.; Guan, C.; Wang, J. et al. Single Co atoms anchored in porous N-doped carbon for efficient Zinc-Air battery cathodes. ACS Catal.2018, 8, 8961–8969.
Tang, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, H. F.; Zhang, Q. Defect engineering toward atomic Co-Nx-C in hierarchical graphene for rechargeable flexible solid Zn-Air batteries. Adv. Mater.2017, 29, 1703185.
Yang, L.; Cheng, D. J.; Xu, H. X.; Zeng, X. F.; Wan, X.; Shui, J. L.; Xiang, Z. H.; Cao, D. Unveiling the high-activity origin of single-atom iron catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA2018, 115, 6626–6631.
Kramm, U. I.; Herrmann-Geppert, I.; Behrends, J.; Lips, K.; Fiechter, S.; Bogdanoff, P. On an easy way to prepare Metal-Nitrogen doped Carbon with exclusive presence of MeN4-type sites active for the ORR. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2016, 138, 635–640.
Zhang, D. Y.; Chen, W. X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y. J.; Zheng, L. R.; Gong, Y.; Li, Q. H.; Shen, R. A.; Han, Y. H.; Cheong, W. C. et al. Isolated Fe and Co dual active sites on nitrogen-doped carbon for a highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Commun.2018, 54, 4274–4277.
Wan, G.; Lin, X. M.; Wen, J. G.; Zhao, W. P.; Pan, L. Y.; Tian, J.; Li, T.; Chen, H. R.; Shi, J. L. Tuning the performance of single-atom electrocatalysts: Support-induced structural reconstruction. Chem. Mater.2018, 30, 7494–7502.
Su, C. Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Q.; Li, N.; Hou, Z. F.; Bai, F. Q.; Zhang, H. X.; Ma, T. Y. Zinc-air batteries: Atomic modulation of FeCo-nitrogen-carbon bifunctional oxygen electrodes for rechargeable and flexible all-solid-state zinc-air battery (Adv. Energy Mater. 13/2017). Adv. Eng. Mater.2017, 13, 1602420.
Zhang, G. X.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, X. Y.; Sun, K.; Chen, R. D.; Chen, W. X.; Kuang, Y.; Zheng, L. R.; Tang, H. L. et al. A general route via formamide condensation to prepare atomically dispersed metal-nitrogen-carbon electrocatalysts for energy technologies. Energy Environ. Sci.2019, 12, 1317–1325.
Li, S.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, X. J.; Schmidt, J.; Thomas, A. Active salt/silica-templated 2D mesoporous FeCo-Nx-carbon as bifunctional oxygen electrodes for zinc-air batteries. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2018, 57, 1856–1862.
Li, C. L.; Wu, M. C.; Liu, R. High-performance bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts for zinc-air batteries over mesoporous Fe/Co-N-C nanofibers with embedding FeCo alloy nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B: Environ.2019, 244, 150–158.
Wang, H. F.; Tang, C.; Zhu, X. L.; Zhang, Q. A “point-line-point ” hybrid electrocatalyst for bi-functional catalysis of oxygen evolution and reduction reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A2016, 4, 3379–3385.
Lai, C. L.; Wang, J.; Wen, L.; Xuan, C. J.; Xiao, W. P.; Zhao, T. H.; Huang, T.; Chen, L. X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, D. L. Restricting growth of Ni3Fe nanoparticles on heteroatom-doped carbon nanotube/graphene nanosheets as air-electrode electrocatalyst for Zn-air battery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2018, 10, 38093–38100.
Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, H. D.; Li, J.; Ma, P.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J. T. Two-step synthesis of cobalt iron alloy nanoparticles embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheets/carbon nanotubes for the oxygen evolution reaction. ChemSusChem2018, 11, 2358–2366.
Chen, B. H.; He, X. B.; Yin, F. X.; Wang, H.; Liu, D. J.; Shi, R. X.; Chen, J. N.; Yin, H. W. MO-Co@N-doped carbon (M = Zn or Co): Vital roles of inactive Zn and highly efficient activity toward oxygen reduction/evolution reactions for rechargeable Zn-Air battery. Adv. Funct. Mater.2017, 27, 1700795.
Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, P.; Tian, C. G.; Sun, F. F.; Ma, J. Y.; Li, W.; Fu, H. G. A stable bifunctional catalyst for rechargeable zinc-air batteries: Iron-cobalt nanoparticles embedded in a nitrogen-doped 3D carbon matrix. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2018, 130, 16398–16402.
Fu, G. T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. F.; Tang Y. W.; Goodenough, J. B.; Lee, J. M. Robust N-doped carbon aerogels strongly coupled with iron-cobalt particles as efficient bifunctional catalysts for rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Nanoscale2013, 10, 19937–19944.
Niu, W. H.; Pakhira, S.; Marcus, K.; Li, Z.; Mendoza- Cortes, J. L.; Yang, Y. Apically dominant mechanism for improving catalytic activities of N-doped carbon nanotube arrays in rechargeable Zinc-Air battery. Adv. Energy Mater.2018, 8, 1800480.
Chen, Y. M.; Li, X. Y.; Zhou, X. Y.; Yao, H. M.; Huang, H. T.; Mai, Y. W.; Zhou, L. M. Hollow-tunneled graphitic carbon nanofibers through Ni-diffusion-induced graphitization as high-performance anode materials. Energy Environ. Sci.2014, 7, 2689–2696.
Zhu, C. Y.; Kim, C.; Aoki, Y.; Habazaki, H. Nitrogen-doped hierarchical porous carbon architecture incorporated with cobalt nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes as efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. Interfaces2017, 4, 1700583.
Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A. V.; Olivier, J. P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K. S. W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem.2015, 87, 1051–1069.
Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. B.; Dai, L. M.; Yao, J. N. Scalable fabrication of nanoporous carbon fiber films as bifunctional catalytic electrodes for flexible Zn-Air batteries. Adv. Mater.2016, 28, 3000–3006.
Zeng, M.; Liu, Y. L.; Zhao, F. P.; Nie, K. Q.; Han, N.; Wang, X. X.; Huang, W. J.; Song, X. N.; Zhong, J.; Li, Y. G. Metallic cobalt nanoparticles encapsulated in nitrogen-enriched graphene shells: Its bifunctional electrocatalysis and application in zinc-air batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater.2016, 26, 4397–4404.
Shen, H. J.; Gracia-Espino, E.; Ma, J. Y.; Tang, H. D.; Mamat, X.; Wagberg, T.; Hu, G. Z.; Guo, S. J. Atomically FeN2 moieties dispersed on mesoporous carbon: A new atomic catalyst for efficient oxygen reduction catalysis. Nano Energy2017, 35, 9–16.
Nam, G.; Son, Y.; Park, S. O.; Jeon, W. C.; Jang, H.; Park, J.; Chae, S.; Yoo, Y.; Ryu, J.; Kim, M. G. et al. A ternary Ni46Co40Fe14 nanoalloy-based oxygen electrocatalyst for highly efficient rechargeable zinc-air batteries. Adv. Mater.2018, 30, 1803372.
Wang, J.; Huang, Z. Q.; Liu, W.; Chang, C. R.; Tang, H. L.; Li, Z. J.; Chen, W. X.; Jia, C. J.; Yao, T.; Wei, S. Q. et al. Design of N-coordinated dual-metal sites: A stable and active Pt-free catalyst for acidic oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2017, 139, 17281–17284.
Chen, Y. J.; Ji, S. F.; Wang, Y. G.; Dong, J. C.; Chen, W. X.; Li, Z.; Shen, R. A.; Zheng, L. R.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Wang, D. S. et al. Isolated single iron atoms anchored on N-doped porous carbon as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2017, 129, 7041–7045.
Yin, P. Q.; Yao, T.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, L. R.; Lin, Y.; Liu, W.; Ju, H. X.; Zhu, J. F.; Hong, X.; Deng, Z. X. et al. Single cobalt atoms with precise N-coordination as superior oxygen reduction reaction catalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2016, 128, 10958–10963.
Su, C. Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Q.; Li, N.; Hou, Z. F.; Bai, F. Q.; Zhang, H. X.; Ma, T. Y. Atomic modulation of FeCo-nitrogen-carbon bifunctional oxygen electrodes for rechargeable and flexible all-solidstate zinc-air battery. Adv. Energy Mater.2017, 7, 1602420.
Han, S. C.; Hu, X. Y.; Wang, J. C.; Fang, X. S.; Zhu, Y. F. Novel route to Fe-based cathode as an efficient bifunctional catalysts for rechargeable Zn-Air battery. Adv. Energy Mater.2018, 8, 1800955.
Jiang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Z.; Li, J. Co nanoparticles confined in 3D nitrogen-doped porous carbon foams as bifunctional electrocatalysts for long-life rechargeable Zn-Air batteries. Small2018, 14, 1703739.
Yang, D. J.; Zhang, L. J.; Yan, X. C.; Yao, X. D. Recent progress in oxygen electrocatalysts for zinc-air batteries. Small Methods2017, 1, 1700209.
Gong, M.; Dai, H. J. A mini review of NiFe-based materials as highly active oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts. Nano Res.2015, 8, 23–39.
Stern, M.; Geary, A. L. Electrochemical polarization: I. A theoretical analysis of the shape of polarization curves. J. Electrochem. Soc.1957, 104, 56.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21701101), the National Key Research and Development Project (Nos. 2018YFE0118200 and 2016YFF0204402), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 18CX06063A), the Long-Term Subsidy Mechanism from the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Education of China, the Shandong Key Research and Development Project (No. 2019JZZY010506), the Shandong Scientific Research Awards Foundation for Outstanding Young Scientists (No. ZR2018JL010), the Shandong Joint Fund of Outstanding Young Talents (No. ZR2017BB018), the Scientific Research Foundation of Shandong University of Science and Technology for Recruited Talents (No. 2017RCJJ059), and the Program for Tsingtao Al-ion Power and Energy-Storage Battery Research Team in the University (No. 17-2-1-1-zhc).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2020_2751_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Hierarchical peony-like FeCo-NC with conductive network and highly active sites as efficient electrocatalyst for rechargeable Zn-air battery
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Kumar, A., Ma, M. et al. Hierarchical peony-like FeCo-NC with conductive network and highly active sites as efficient electrocatalyst for rechargeable Zn-air battery. Nano Res. 13, 1090–1099 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2751-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2751-7