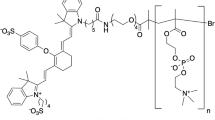
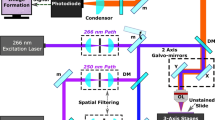
Abstract
Distinguishing a tumor from non-neoplastic tissue is a challenging task during cancer surgery. Several attempts have been made to use visible or fluorescent agents to aid in the visualization of a tumor during surgery. We describe a novel method to delineate brain tumors, using a highly sensitive photoacoustic imaging technique that is enhanced by tumor-targeting blue nanoparticles serving as a contrast agent. Experiments on phantoms and on rat brains, ex vivo, demonstrate the high sensitivity of photoacoustic imaging in delineating tumors containing contrast agent at a concentration much lower than needed for visualization by the naked eye. The limit of detection of the system for the nanoparticles is about 0.77 μg/mL in water (equivalent to 0.84 μmol/L Coomassie Blue dye). The present exploratory study suggests that photoacoustic imaging, when used with strongly optical absorbing contrast agents, could facilitate cancer surgery intraoperatively by revealing the distribution and extent of the tumor.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanai, N.; Berger, M. S. Glioma extent of resection and its impact on patient outcome. Neurosurgery 2008, 62(4), 753–766.
Orringer D. A.; Chen T.; Huang D. L.; Armstead W. M.; Hoff B. A.; Koo Y. E.; Keep R. F.; Philbert M. A.; Kopelman R.; Sagher O. The brain tumor window model: A combined cranial window and implanted glioma model for evaluating intraoperative contrast agents. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 736–743.
Ozawa T.; Britz G. W.; Kinder D. H.; Spence A. M.; VandenBerg S.; Lamborn K. R.; Deen D. F.; Berger M. S. Bromophenol blue staining of tumors in a rat glioma model. Neurosurgery 2005, 57(5), 1041–1047.
Britz G. W.; Ghatan S.; Spence A. M.; Berger M. S. Intracarotid RMP-7 enhanced indocyanine green staining of tumors in a rat glioma model. J. Neurooncol. 2002, 56(3), 227–232.
Hansen D. A.; Spence A. M.; Carski T.; Berger M. S. Indocyanine green (ICG) staining and demarcation of tumor margins in a rat glioma model. Surg. Neurol. 1993, 40(6), 451–456.
Shinoda J.; Yano H.; Yoshimura S.; Okumura A.; Kaku Y.; Iwama T.; Sakai N. Fluorescence-guided resection of glioblastoma multiforme by using high-dose fluorescein sodium. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99(3), 597–603.
Stummer W.; Pichlmeier U.; Meinel T.; Wiestler O. D.; Zanella F.; Reulen H. J. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: A randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7(5), 392–401.
Moore G. E. Fluorescein as an agent in the differentiation of normal and malignant tissues. Science 1947, 106(2745), 130–131.
Veiseh M.; Gabikian P.; Bahrami S. B.; Veiseh O.; Zhang M.; Hackman R. C.; Ravanpay A. C.; Stroud M. R; Kusuma Y.; Hansen S. J.; Kwok D.; Munoz N. M.; Sze R. W.; Grady W. M.; Greenberg N. M.; Ellenbogen R. G.; Olson J. M. Tumor paint: A chlorotoxin:Cy5.5 bioconjugate for intraoperative visualization of cancer foci. Cancer Res. 2007, 67(14), 6882–6888.
Xu M.; Wang L. V. Time-domain reconstruction for thermoacoustic tomography in a spherical geometry. IEEE T. Med. Imaging 2002, 21(7), 814–822.
Wang X.; Ku G.; Wegiel M. A.; Bornhop D. J.; Stoica G.; Wang L. V. Noninvasive photoacoustic angiography of animal brains in-vivo with near-infrared light and an optical contrast agent. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29(7), 730–732.
Kim C.; Song K. H.; Gao F.; Wang L. V. Sentinel lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels: Noninvasive dual-modality in-vivo mapping by using indocyanine green in rats-volumetric spectroscopic photoacoustic imaging and planar fluorescence imaging. Radiology 2010, 255(2), 442–450.
Kim, C.; Cho, E. C.; Chen, J.; Song, K. H.; Au, L.; Favazza, C.; Zhang, Q.; Cobley, C. M.; Gao, F.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L. V. In vivo molecular photoacoustic tomography of melanomas targeted by bioconjugated gold nanocages. ACS Nano 2010, 4(8), 4559–4564.
De la Zerda, A.; Zavaleta, C.; Keren, S.; Vaithilingam, S.; Bodapati, S.; Liu, Z.; Levi, J.; Smith, B. R.; Ma, T.; Oralkan, O.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, X.; Dai, H.; Khuri-Yakub, B. T.; Gambhir, S. S. Carbon nanotubes as photoacoustic molecular imaging agents in living mice. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3(9), 557–562.
Li, P.; Shieh, D.; Wang, C.; Shieh, D.; Wei, C.; Liao, C.; Ding, A.; Wu, Y.; Poe, C.; Jhan, S. In vivo photoacoustic molecular imaging with simultaneous multiple selective targeting using antibody-conjugated gold nanorods. Opt. Express 2008, 16(23), 18605–18615.
Lee, Y. E. K.; Kopelman, R.; Smith, R. Nanoparticle PEBBLE sensors in live cells and in vivo. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 2, 57–76.
Orringer, D. A.; Koo, Y. E. L.; Chen, T.; Kopelman, R.; Sagher, O. Small solutions for big problems: The application of nanoparticles to brain tumor diagnosis and therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 85(5), 531–534.
Reddy, G. R.; Bhojani, M. S.; McConville, P.; Moody, J.; Moffat, B. A.; Hall, D. E.; Kim, G.; Koo, Y. E.; Woolliscroft, M. J.; Sugai, J. V.; Johnson, T. D.; Philbert, M. A.; Kopelman, R.; Rehemtulla, A.; Ross, B. D. Vascular targeted nano-particles for imaging and treatment of brain tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12(22), 6677–6686.
Winer, I.; Wang, S.; Lee, Y. E. K.; Fan, W.; Gong, Y.; Burgos-Ojeda, D.; Spahlinger, G.; Kopelman, R.; Buckanovich, R. J. F3-Targeted Cisplatin-Hydrogel nanoparhticles as an effective therapeutic that targets both murine and human ovarian tumor endothelial cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 2010, 70(21), 8674–8683.
Orringer, D. A.; Sagher, O.; Kopelman, R.; Koo, Y. E. L. Dye loaded nanoparticle. U.S. Patent 20,100,098,637, April 22, 2010.
Xu, M.; Wang, L. V.; Universal back-projection algorithm for photoacoustic-computed tomography. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71(1), 016706.
Wang, X.; Pang, Y.; Ku, G.; Xie, X.; Stoica, G.; Wang, L. V. Non-invasive laser-induced photoacoustic tomography for structural and functional imaging of the brain in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21(7), 803–806.
Porkka, K.; Laakkonen, P.; Hoffman, J. A.; Bernasconi, M.; Ruoslahti, E. A fragment of the HMGN2 protein homes to the nuclei of tumor cells and tumor endothelial cells in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2002, 99(11), 7444–7449.
Akerman, M. E.; Chan, W. C.; Laakkonen, P.; Bhatia, S. N.; Ruoslahti, E. Nanocrystal targeting in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2002, 99(20), 12617–12621.
Ruoslahti, E.; Duza, T.; Zhang, L. Vascular homing peptides with cell-penetrating properties. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11(28), 3655–3660.
Orringer, D. A.; Koo, Y. E. L.; Chen, T.; Kim, G.; Hah, H. J.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Keep, R.; Philbert, M. A.; Kopelman, R.; Sagher, O. In-vitro characterization of a targeted, dyeloaded nanodevice for intraoperative tumor delineation. Neurosurgery 2009, 64(5), 965–972.
Koo, Y. E. L.; Reddy, G. R.; Bhojani, M.; Schneider, R.; Philbert, M. A.; Rehemtulla, A.; Ross, B. D.; Kopelman, R. Brain cancer diagnosis and therapy with nano-platforms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58(14), 1556–1577.
Wenger, Y.; Schneider II, R. J.; Reddy, G. R.; Kopelman, R.; Jolliet, O.; Philbert, M. A. Tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics of stable polyacrylamide nanoparticles following intravenous injection in the rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 251(3), 181–190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ray, A., Wang, X., Lee, YE.K. et al. Targeted blue nanoparticles as photoacoustic contrast agent for brain tumor delineation. Nano Res. 4, 1163–1173 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0166-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0166-1