Abstract
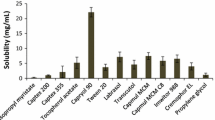
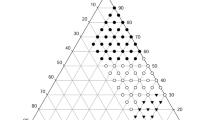
In order to characterize the in situ intestinal permeability and in vivo oral bioavailability of celecoxib (CXB), a poorly water-soluble cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor, various formulations including the self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) and supersaturating SEDDS (S-SEDDS) were compared. The S-SEDDS formulation was obtained by adding Soluplus as a precipitation inhibitor to SEDDS, composed of Capryol 90 as oil, Tween 20 as surfactant, and Tetraglycol as cosurfactant (1:4.5:4.5 in volume ratio). An in situ single pass intestinal perfusion study in rats was performed with CXB-dissolved solutions at a concentration of 40 μg/mL. The effective permeability (Peff) of CXB in the control solution (2.5 v/v% Tween 20-containing PBS) was 6.39 × 10−5 cm/s. The Peff value was significantly increased (P < 0.05) by the lipid-based formulation, yielding 1.5- and 2.9-fold increases for the SEDDS and S-SEDDS solutions, respectively, compared to the control solution. After oral administration of various formulations to rats at the equivalent dose of 100 mg/kg of CXB, the plasma drug level was measured by LC–MS/MS. The relative bioavailabilities of SEDDS and S-SEDDS were 263 and 355 %, respectively, compared to the CXB suspension as a reference. In particular, S-SEDDS revealed the highest Cmax and the smallest Tmax, indicating rapid and enhanced absorption with this formulation. This study illustrates the potential use of the S-SEDDS formulation in the oral delivery of poorly water-soluble compounds.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amidon, G.L., H. Lennernas, V.P. Shah, and J.R. Crison. 1995. A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharmaceutical Research 12: 413–420.
Arai, H., M. Murata, and J. Shinoda. 1971. The interaction between polymer and surfactant: the composition of the complex between polyvinylpyrrolidone and sodium alkyl sulfate as revealed by surface tension, dialysis, and solubilization. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 37: 223–227.
Attwood, D., and A.T. Florence. 1983. Surfactant systems: their chemistry, pharmacy and biology. New York: Chapman and Hall.
Berggren, S., J. Hoogstraate, U. Fagerholm, and H. Lennernas. 2004. Characterization of jejunal absorption and apical efflux of ropivacaine, lidocaine and bupivacaine in the rat using in situ and in vitro absorption models. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 21: 553–560.
Brouwers, J., M.E. Brewster, and P. Augustijns. 2009. Supersaturating drug delivery systems: the answer to solubility-limited oral bioavailability? Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 98: 2549–2572.
Brusewitz, C., A. Schendler, A. Funke, T. Wagner, and R. Lipp. 2007. Novel poloxamer-based nanoemulsions to enhance the intestinal absorption of active compounds. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 329: 173–181.
Charman, S.A., W.N. Charman, M.C. Rogge, T.D. Wilson, F.J. Dutko, and C.W. Pouton. 1992. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: formulation and bio-pharmaceutical evaluation of an investigational lipophilic compound. Pharmaceutical Research 9: 87–93.
Chen, L., X. Sha, X. Jiang, Y. Chen, Q. Ren, and X. Fang. 2013. Pluronic P105/F127 mixed micelles for the delivery of docetaxel against Taxol resistant non-small cell lung cancer: optimization and in vitro, in vivo evaluation. International Journal of Nanomedicine 8: 73–84.
Chiou, W.L., and A. Barve. 1998. Linear correlation of the fraction of oral dose absorbed of 64 drugs between humans and rats. Pharmaceutical Research 15: 1792–1795.
Clemett, D., and K.L. Goa. 2000. Celecoxib: a review of its use in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and acute pain. Drugs 59: 957–980.
de Vries, N.A., J. Zhao, E. Kroon, T. Buckle, J.H. Beijnen, and O. van Tellingen. 2007. P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein: two dominant transporters working together in limiting the brain penetration of topotecan. Clinical Cancer Research 13: 6440–6449.
Dressman, J.B., and C. Reppas. 2000. In vitro-in vivo correlations for lipophilic, poorly water-soluble drugs. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 11: S73–S80.
Fagerholm, U., M. Johansson, and H. Lennernas. 1996. Comparison between permeability coefficients in rat and human jejunum. Pharmaceutical Research 13: 1336–1342.
Gao, P., B.D. Rush, W.P. Pfund, T. Huang, J.M. Bauer, W. Morozowich, M.S. Kuo, and M.J. Hageman. 2003. Development of a supersaturable SEDDS(S-SEDDS) formulation of paclitaxel with improved oral bioavailability. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 92: 2386–2398.
Gursoy, R.N., and S. Benita. 2004. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for improved oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 58: 173–182.
Guzman, H.R., M. Tawa, Z. Zhang, P. Ratanabanangkoon, P. Shaw, C.R. Gardner, H. Chen, J.P. Moreau, O. Almarsson, and J.F. Remenar. 2007. Combined use of crystalline salt forms and precipitation inhibitors to improve oral absorption of celecoxib from solid oral formulations. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 96: 2686–2702.
Hillgren, K.M., A. Kato, and R.T. Borchardt. 1995. In vitro systems for studying intestinal drug absorption. Medicinal Research Reviews 15: 83–109.
Jones, M.N. 1968. Dye solubilization by a polymer-surfactant complex. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 26: 532–533.
Kang, M.J., H.S. Kim, H.S. Jeon, J.H. Park, B.S. Lee, B.K. Ahn, K.Y. Moon, and Y.W. Choi. 2012. In situ intestinal permeability and in vivo absorption characteristics of olmesartan medoxomil in self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 38: 587–596.
Khan, K.A., and C.T. Rhodes. 1975. The concept of dissolution efficiency. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 27: 48–49.
Karlsson, J., and P. Artursson. 1991. A method for the determination of cellular permeability coefficients and aqueous boundary layer thickness in monolayers of intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells grown in permeable filter chambers. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 71: 55–64.
Komiya, I., J.Y. Park, A. Kamani, N.F.H. Ho, and W.I. Higuchi. 1980. Quantitative mechanistic studies in simultaneous fluid flow and intestinal absorption using steroids as model solutes. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 4: 249–262.
Lennernas, H., O. Ahrenstedt, R. Hallgren, L. Knutson, M. Ryde, and L.K. Paalzow. 1992. Regional jejunal perfusion, a new in vivo approach to study oral drug absorption. Pharmaceutical Research 9: 1243–1251.
Linn, M., E.M. Collnot, D. Djuric, K. Hempel, E. Fabian, K. Kolter, and C.M. Lehr. 2012. Soluplus® as an effective absorption enhancer of poorly soluble drugs in vitro and in vivo. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 45: 336–343.
O’driscoll, C.M., and B.T. Griffin. 2008. Biopharmaceutical challenges associated with drugs with low aqueous solubility—the potential impact of lipid-based formulations. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 60: 617–624.
Paulson, S.K., M.B. Vaughn, S.M. Jessen, Y. Lawal, C.J. Gresk, B. Yan, T.J. Maziasz, C.S. Cook, and A. Karim. 2001. Pharmacokinetics of celecoxib after oral administration in dogs and humans: effect of food and site of absorption. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 297: 638–645.
Pouton, C.W. 2006. Formulation of poorly water-soluble drugs for oral administration: physicochemical and physiological issues and the lipid formulation classification system. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 29: 278–287.
Rubas, W., N. Jezyk, and G.M. Grass. 1993. Comparison of the permeability characteristics of a human colonic epithelial (Caco-2) cell line to colon of rabbit, monkey, and dog intestine and human drug absorption. Pharmaceutical Research 10: 113–118.
Saito, S. 1967. Solubilization properties of polymer-surfactant complexes. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 24: 227–234.
Salphati, L., K. Childers, L. Pan, K. Tsutsui, and L. Takahashi. 2001. Evaluation of a single-pass intestinal-perfusion method in rat for the prediction of absorption in man. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 53: 1007–1013.
Shah, N.H., M.T. Carvajal, C.I. Patel, M.H. Infeld, and A.W. Malick. 1994. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems with polyglycolyzed glycerides for improving in vitro dissolution and oral absorption of lipophilic drugs. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 106: 15–23.
Shakeel, F., S. Baboota, A. Ahuja, J. Ali, M. Aqil, and S. Shafiq. 2007. Nanoemulsions as vehicles for transdermal delivery of aceclofenac. AAPS PharmSciTech 8: 191–199.
Song, W.H., J.H. Park, D.W. Yeom, B.K. Ahn, K.M. Lee, S.G. Lee, H.S. Woo, and Y.W. Choi. 2013. Enhanced dissolution of celecoxib by supersaturating self-emulsifying drug delivery system (S-SEDDS) formulation. Archives of Pharmacal Research 36: 69–78.
Subramanian, N., S. Ray, S.K. Ghosal, R. Bhadra, and S.P. Moulik. 2004. Formulation design of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems for improved oral bioavailability of celecoxib. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 27: 1993–1999.
Swenson, E.S., and W.J. Curatolo. 1992. Intestinal permeability enhancement for proteins, peptides and other polar drugs: mechanisms and potential toxicity. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 8: 39–92.
Ullah, I., M.K. Baloch, and G.F. Durrani. 2011. Solubility of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in aqueous solution of non-ionic surfactants. Journal of Solution Chemistry 40: 1341–1348.
Vasconcelos, T., B. Sarmento, and P. Costa. 2007. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discovery Today 12: 1068–1075.
Yao, J., Y. Lu, and J.P. Zhou. 2008. Preparation of nobiletin in self-microemulsifying systems and its intestinal permeability in rats. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 11: 22–29.
Zakeri-Milani, P., M. Barzegar-Jalali, H. Tajerzadeh, Y. Azarmi, and H. Valizadeh. 2005. Simultaneous determination of naproxen, ketoprofen and phenol red in samples from rat intestinal permeability studies: HPLC method development and validation. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 39: 624–630.
Zakeri-Milani, P., H. Valizadeh, H. Tajerzadeh, Y. Azarmi, Z. Islambolchilar, S. Barzergar, and M. Barzegar-Jalali. 2007. Predicting human intestinal permeability using single-pass intestinal perfusion in rat. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 10: 368–379.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Chung-Ang University Research Scholarship Grants in 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
W. H. Song and D. W. Yeom have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W.H., Yeom, D.W., Lee, D.H. et al. In situ intestinal permeability and in vivo oral bioavailability of celecoxib in supersaturating self-emulsifying drug delivery system. Arch. Pharm. Res. 37, 626–635 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0202-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0202-7