Abstract
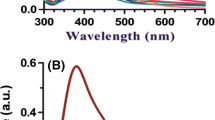
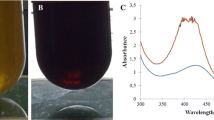
The stability of citrate-capped silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and the embryonic developmental toxicity were evaluated in the fish test water. Serious aggregation of AgNPs was observed in undiluted fish water (DM-100) in which high concentration of ionic salts exist. However, AgNPs were found to be stable for 7 days in DM-10, prepared by diluting the original fish water (DM-100) with deionized water to 10 %. The normal physiology of zebrafish embryos were evaluated in DM-10 to see if DM-10 can be used as a control vehicle for the embryonic fish toxicity test. As results, DM-10 without AgNPs did not induce any significant adverse effects on embryonic development of zebrafish determined by mortality, hatching, malformations and heart rate. When embryonic toxicity of AgNPs was tested in both DM-10 and in DM-100, AgNPs showed higher toxicity in DM-10 than in DM-100. This means that the big-sized aggregates of AgNPs were low toxic compared to the nano-sized AgNPs. AgNPs induced delayed hatching, decreased heart rate, pericardial edema, and embryo death. Accumulation of AgNPs in the embryo bodies was also observed. Based on this study, citrate-capped AgNPs are not aggregated in DM-10 and it can be used as a control vehicle in the toxicity test of fish embryonic development.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed, M., M.S. Alsalhi, and M.K. Siddiqui. 2010. Silver nanoparticle applications and human health. Clinica Chimica Acta 411: 1841–1848.
Bar-Ilan, O., R.M. Albrecht, V.E. Fako, and D.Y. Furgeson. 2009. Toxicity assessments of multisized gold and silver nanoparticles in zebrafish embryos. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 5: 1897–1910.
Bielmyer, G.K., M. Grosell, and K.V. Brixti. 2006. Toxicity of silver, zinc, copper, and nickel to the copepod Acartia tonsa exposed via a phytoplankton diet. Environmental Science and Technology 40: 2063–2068.
Bilberg, K., H. Malte, T. Wang, and E. Baatrup. 2010. Silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate cause respiratory stress in Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis). Aquatic Toxicology 96: 159–165.
Bilberg, K., M.B. Hovgaard, F. Besenbacher, and E. Baatrup. 2012. In vivo toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions in zebrafish (Danio rerio), 1–9. Article: Journal of Toxicology.
Chen, K.L., and M. Elimelech. 2006. Aggregation and deposition kinetics of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles. Langmuir 22: 10994–11001.
El Badawy, A.M., T.P. Luxton, R.G. Silva, K.G. Scheckel, M.T. Suidan, and T.M. Tolaymat. 2010. Impact of environmental conditions (pH, ionic strength, and electrolyte type) on the surface charge and aggregation of silver nanoparticles suspensions. Environmental Science and Technology 44: 1260–1266.
Fabrega, J., S.N. Luoma, C.R. Tyler, T.S. Galloway, and J.R. Lead. 2011. Silver nanoparticles: behaviour and effects in the aquatic environment. Environment International 37: 517–531.
Griffitt, R.J., J. Luo, J. Gao, J.C. Bonzongo, and D.S. Barber. 2008. Effects of particle composition and species on toxicity of metallic nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 27: 1972–1978.
Harper, S.L., C.Y. Usenko, J. Hutchison, B.L.S. Maddux, and R.L. Tanguay. 2008. In vivo biodistribution and toxicity depends on nanomaterial composition, size, surface functionalization and route of exposure. Journal of Experimental Nanoscience 3: 195–206.
Harper, S.L., J. Hutchison, B.L.S. Maddux, and R.L. Tanguay. 2010. Integrative strategies to understand nanomaterial-biological interactions. International Perspectives on Environmental Nanotechnology: Applications and Implications. 2: 51–56.
Kim, Y.S., J.S. Kim, H.S. Cho, D.S. Rha, J.M. Kim, J.D. Park, B.S. Choi, R. Lim, H.K. Chang, Y.H. Chung, I.H. Kwon, J. Jeong, B.S. Han, and I.J. Yu. 2008. Twenty-eight-day oral toxicity, genotoxicity, and gender-related tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles in Sprague-Dawley rats. Inhalation Toxicology 20: 575–583.
Kimmel, C.B., W.W. Ballard, S.R. Kimmel, B. Ullmann, and T.F. Schilling. 1995. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Developmental Dynamics 203: 253–310.
Lee, K.J., P.D. Nallathamby, L.M. Browning, C.J. Osgood, and X.H. Xu. 2007. In vivo imaging of transport and biocompatibility of single silver nanoparticles in early development of zebrafish embryos. ACS Nano 1: 133–143.
Park, E.J., J. Yi, Y. Kim, K. Choi, and K. Park. 2010. Silver nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity by a Trojan-horse type mechanism. Toxicology In Vitro 24: 872–878.
Powers, C.M., T.A. Slotkin, F.J. Seidler, A.R. Badireddy, and S. Padilla. 2011. Silver nanoparticles alter zebrafish development and larval behavior: distinct roles for particle size, coating and composition. Neurotoxicology and Teratology 33: 708–714.
Roh, J.Y., S.J. Sim, J. Yi, K. Park, K.H. Chung, D.Y. Ryu, and J. Choi. 2009. Ecotoxicity of silver nanoparticles on the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans using functional ecotoxicogenomics. Environmental Science and Technology 43: 3933–3940.
Römer, I., T.A. White, M. Baalousha, K. Chipman, M.R. Viant, and J.R. Lead. 2011. Aggregation and dispersion of silver nanoparticles in exposure media for aquatic toxicity tests. Journal of Chromatography A 1218: 4226–4233.
Scown, T.M., E.M. Santos, B.D. Johnston, B. Gaiser, M. Baalousha, S. Mitov, J.R. Lead, V. Stone, T.F. Fernandes, M. Jepson, R. van Aerle, and C.R. Tyler. 2010. Effects of aqueous exposure to silver nanoparticles of different sizes in rainbow trout. Toxicological Sciences 115: 521–534.
Sung, J.H., J.H. Ji, J.D. Park, J.U. Yoon, D.S. Kim, K.S. Jeon, M.Y. Song, J. Jeong, B.S. Han, J.H. Han, Y.H. Chung, H.K. Chang, J.H. Lee, M.H. Cho, B.J. Kelman, and I.J. Yu. 2009. Subchronic inhalation toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicological Sciences 108: 452–461.
Truong, L., S.L. Harper, and R.L. Tanguay. 2011. Evaluation of embryotoxicity using the zebrafish model. Methods in Molecular Biology 691: 271–279.
Usenko, C.Y., S.L. Harper, and R.L. Tanguay. 2007. In vivo evaluation of carbon fullerene toxicity using embryonic zebrafish. Carbon 45: 1891–1898.
Usenko, C.Y., S.L. Harper, and R.L. Tanguay. 2008. Fullerene C60 exposure elicits an oxidative stress response in embryonic zebrafish. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 229: 44–55.
Yen, H.J., S.H. Hsu, and C.L. Tsai. 2009. Cytotoxicity and immunological response of gold and silver nanoparticles of different sizes. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 5: 1553–1561.
Yeo, M.K., and S.W. Pak. 2008. Exposing zebrafish to silver nanoparticles during caudal fin regeneration disrupts caudal fin growth and p53 signaling. Molecular and Cellular Toxicology 4: 311–317.
Yeo, M.K., and J.W. Yoon. 2009. Comparison of the effects of nano-silver antibacterial coatings and silver ions on zebrafish embryogenesis. Molecular and Cellular Toxicology 5: 23–31.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2010-013-E00035). Support to SLH was provided in part by National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) grants ES017552-01A2, ES016896-01 and P30 ES03850, and the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) FA8650-05-1-5041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, K., Tuttle, G., Sinche, F. et al. Stability of citrate-capped silver nanoparticles in exposure media and their effects on the development of embryonic zebrafish (Danio rerio). Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 125–133 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0005-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0005-x