Abstract
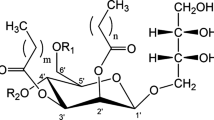
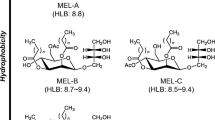
Mannosylerythritol lipids (MEL) are surface active compounds produced by fungi with potential as biosurfactans in personal care and cosmetic applications. Within this work the microbial synthesis of MEL was investigated using several Pseudozymastrains. Each strain produced a specific MEL composition. The obtained biosurfactants showed good emulsifier properties and high surface activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Transparency Market Research (2011) Specialty Surfactants Market And BioSurfactants Market: Global Scenario, Raw Material And Consumption Trends, Industry Analysis, Size, Share & Forecast 2010–2018. www.transparencymarketresearch.com/specialty-and-biosurfactants-market.html
Fabry B (1991) Tenside. Eigenschaften, Rohstoffe, Produktion, Anwendungen. Chemie in unserer Zeit 25:214–222
Koh LP, Wilcove DS (2008) Is oil palm agriculture really destroying tropical biodiversity? Conserv Lett 1:60–64
Ron EZ, Rosenberg E (2001) Natural roles of biosurfactants. Environ Microbiol 3:229–236
Marchant R, Banat IM (2012) Microbial biosurfactants: challenges and opportunities for future exploitation. Trends Biotechnol 30:558–565
Yamamoto S, Morita T, Fukuoka T et al. (2012) The moisturizing effects of glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, on human skin. J Oleo Sci 61:407–412
Isoda H, Kitamoto D, Shinmoto H et al. (1997) Microbial extracellular glycolipid induction of differentiation and inhibition of the protein kinase C activity of human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL60. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:609–614
Arutchelvi JI, Bhaduri S, Uppara PV et al. (2008) Mannosylerythritol lipids: a review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1559–1570
Morita T, Ogura Y, Takashima M et al. (2011) Isolation of Pseudozyma churashimaensis sp. nov., a novel ustilaginomycetous yeast species as a producer of glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids. J Biosci Bioeng 112:137–144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Günther, M., Hirth, T., Zibek, S. et al. Produktion von Biotensiden mit Pseudozyma-Stämmen. Biospektrum 19, 813–815 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-013-0393-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-013-0393-y