Abstract
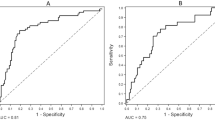
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with increased coronary artery disease (CAD) and coronary artery calcification. We hypothesized that the osteogenic factor, bone morphogenetic protein-4 (sBMP-4), is elevated in subjects with both CKD and CAD. Serum was collected from 79 subjects undergoing diagnostic angiography and stratified according to CAD and CKD status. Subjects with both CAD and CKD had significantly elevated sBMP-4 compared to those with only one or no disease. sBMP-4 continued to be associated with the presence of both diseases after adjustment for other risk factors. To determine if sBMP-4 is associated with coronary artery calcification, we compared coronary artery calcium scores (CAC) to sBMP-4 in 22 subjects. A positive correlation between CAC and sBMP-4 was seen. In conclusion, sBMP-4 is elevated in patients with both CAD and CKD and positively correlates with CAC, suggesting a role for sBMP-4 in the increased CAD seen in CKD patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shulman, N. B., Ford, C. E., Hall, W. D., Blaufox, M. D., Simon, D., Langford, H. G., et al. (1989). Prognostic value of serum creatinine and effect of treatment of hypertension on renal function. Results from the hypertension detection and follow-up program. The Hypertension Detection and Follow-up Program Cooperative Group. Hypertension, 13, I80–I93.
Lloyd-Jones, D., Adams, R., Carnethon, M., De Simone, G., Ferguson, T. B., Flegal, K., et al. (2009). Heart disease and stroke statistics—2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation, 119, e21–e181.
Chonchol, M., Whittle, J., Desbien, A., Orner, M. B., Petersen, L. A., & Kressin, N. R. (2008). Chronic kidney disease is associated with angiographic coronary artery disease. American Journal of Nephrology, 28, 354–360.
Weiner, D. E., Tighiouart, H., Elsayed, E. F., Griffith, J. L., Salem, D. N., Levey, A. S., et al. (2007). The Framingham predictive instrument in chronic kidney disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 50, 217–224.
Kestenbaum, B. R., Adeney, K. L., de Boer, I. H., Ix, J. H., Shlipak, M. G., & Siscovick, D. S. (2009). Incidence and progression of coronary calcification in chronic kidney disease: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Kidney International, 76, 991–998.
Nakano, T., Ninomiya, T., Sumiyoshi, S., Fujii, H., Doi, Y., Hirakata, H., et al. (2010). Association of kidney function with coronary atherosclerosis and calcification in autopsy samples from Japanese elders: the Hisayama study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 55, 21–30.
Russo, D., Palmiero, G., De Blasio, A. P., Balletta, M. M., & Andreucci, V. E. (2004). Coronary artery calcification in patients with CRF not undergoing dialysis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 44, 1024–1030.
Mesquita, M., Demulder, A., Damry, N., Melot, C., Wittersheim, E., Willems, D., et al. (2009). Plasma osteoprotegerin is an independent risk factor for mortality and an early biomarker of coronary vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, 47, 339–346.
Kiyono, M., & Shibuya, M. (2003). Bone morphogenetic protein 4 mediates apoptosis of capillary endothelial cells during rat pupillary membrane regression. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 23, 4627–4636.
Graff, J. M. (1997). Embryonic patterning: to BMP or not to BMP, that is the question. Cell, 89, 171–174.
Dhore, C. R., Cleutjens, J. P., Lutgens, E., Cleutjens, K. B., Geusens, P. P., Kitslaar, P. J., et al. (2001). Differential expression of bone matrix regulatory proteins in human atherosclerotic plaques. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 21, 1998–2003.
Schluesener, H. J., & Meyermann, R. (1995). Immunolocalization of BMP-6, a novel TGF-beta-related cytokine, in normal and atherosclerotic smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis, 113, 153–156.
Bostrom, K., Watson, K. E., Horn, S., Wortham, C., Herman, I. M., & Demer, L. L. (1993). Bone morphogenetic protein expression in human atherosclerotic lesions. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 91, 1800–1809.
Yao, Y., Bennett, B. J., Wang, X., Rosenfeld, M. E., Giachelli, C., Lusis, A. J., et al. (2010). Inhibition of bone morphogenetic proteins protects against atherosclerosis and vascular calcification. Circulation Research, 107, 485–494.
Panizo, S., Cardus, A., Encinas, M., Parisi, E., Valcheva, P., Lopez-Ongil, S., et al. (2009). RANKL increases vascular smooth muscle cell calcification through a RANK-BMP4-dependent pathway. Circulation Research, 104, 1041–1048.
Sorescu, G. P., Sykes, M., Weiss, D., Platt, M. O., Saha, A., Hwang, J., et al. (2003). Bone morphogenic protein 4 produced in endothelial cells by oscillatory shear stress stimulates an inflammatory response. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 31128–31135.
Miriyala, S., Gongora Nieto, M. C., Mingone, C., Smith, D., Dikalov, S., Harrison, D. G., et al. (2006). Bone morphogenic protein-4 induces hypertension in mice: role of noggin, vascular NADPH oxidases, and impaired vasorelaxation. Circulation, 113, 2818–2825.
Wong, W. T., Tian, X. Y., Chen, Y., Leung, F. P., Liu, L., Lee, H. K., et al. (2010). Bone morphogenic protein-4 impairs endothelial function through oxidative stress-dependent cyclooxygenase-2 upregulation: implications on hypertension. Circulation Research, 107, 984–991.
National Kidney Foundation. (2002). K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 39, S1–S266.
Oh, J., Wunsch, R., Turzer, M., Bahner, M., Raggi, P., Querfeld, U., et al. (2002). Advanced coronary and carotid arteriopathy in young adults with childhood-onset chronic renal failure. Circulation, 106, 100–105.
Goodman, W. G., Goldin, J., Kuizon, B. D., Yoon, C., Gales, B., Sider, D., et al. (2000). Coronary-artery calcification in young adults with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing dialysis. The New England Journal of Medicine, 342, 1478–1483.
Braun, J., Oldendorf, M., Moshage, W., Heidler, R., Zeitler, E., & Luft, F. C. (1996). Electron beam computed tomography in the evaluation of cardiac calcification in chronic dialysis patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 27, 394–401.
Schwarz, U., Buzello, M., Ritz, E., Stein, G., Raabe, G., Wiest, G., et al. (2000). Morphology of coronary atherosclerotic lesions in patients with end-stage renal failure. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 15, 218–223.
Moe, S. M., & Chen, N. X. (2004). Pathophysiology of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Circulation Research, 95, 560–567.
Nitta, K., Akiba, T., Uchida, K., Kawashima, A., Yumura, W., Kabaya, T., et al. (2003). The progression of vascular calcification and serum osteoprotegerin levels in patients on long-term hemodialysis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 42, 303–309.
Morena, M., Terrier, N., Jaussent, I., Leray-Moragues, H., Chalabi, L., Rivory, J. P., et al. (2006). Plasma osteoprotegerin is associated with mortality in hemodialysis patients. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 17, 262–270.
Gonnelli, S., Montagnani, A., Caffarelli, C., Cadirni, A., Campagna, M. S., Franci, M. B., et al. (2005). Osteoprotegerin (OPG) and receptor activator of NF-kB ligand (RANK-L) serum levels in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, 28, 534–539.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by grants from the National Center for Research Resources (5 P20 RR018766-10) and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (8 P20 GM103514-10) from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
(DOCX 207 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stahls, P.F., Lightell, D.J., Moss, S.C. et al. Elevated Serum Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Coronary Artery Disease. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 6, 232–238 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-012-9429-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-012-9429-9