Abstract
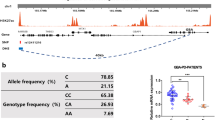
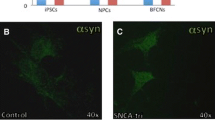
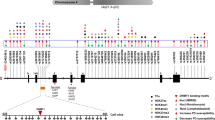
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder affecting millions of people worldwide, but its cause and pathogenesis are still not fully understood. Earlier studies have shown that SNCA, which encodes α-synuclein, is one of the key genes associated with PD. Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) variants of SNCA are thought to be correlated with disease onset. The underlying mechanisms however are enigmatic. A recent study published in Nature revealed that one of the SNP variants in the SNCA non-coding element elevated α-synuclein expression in human neurons by reducing the binding efficiency of transcription factors, demonstrating a previously uncharted role for SNPs in the pathogenesis of PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tatton WG, Chalmers-Redman R, Brown D, Tatton N. Apoptosis in Parkinson’s disease: signals for neuronal degradation. Ann Neurol 2003, 53 Suppl 3: S61–70; discussion S70–62.
Manolio TA. Genomewide association studies and assessment of the risk of disease. N Engl J Med 2010, 363: 166–176.
Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Lill CM, Do CB, Hernandez DG, Saad M, et al. Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 2014, 46: 989–993.
Soldner F, Stelzer Y, Shivalila CS, Abraham BJ, Latourelle JC, Barrasa MI, et al. Parkinson-associated risk variant in distal enhancer of alpha-synuclein modulates target gene expression. Nature 2016, 533: 95–99.
Abeliovich A, Rhinn H. Parkinson’s disease: guilt by genetic association. Nature 2016, 533: 40–41.
Devine MJ, Gwinn K, Singleton A, Hardy J. Parkinson’s disease and alpha-synuclein expression. Mov Disord 2011, 26: 2160–2168.
Roadmap Epigenomics C, Kundaje A, Meuleman W, Ernst J, Bilenky M, Yen A, et al. Integrative analysis of 111 reference human epigenomes. Nature 2015, 518: 317–330.
Kilpinen H, Waszak SM, Gschwind AR, Raghav SK, Witwicki RM, Orioli A, et al. Coordinated effects of sequence variation on DNA binding, chromatin structure, and transcription. Science 2013, 342: 744–747.
Schaffer AE, Freude KK, Nelson SB, Sander M. Nkx6 transcription factors and Ptf1a function as antagonistic lineage determinants in multipotent pancreatic progenitors. Dev Cell 2010, 18: 1022–1029.
Mariani J, Favaro R, Lancini C, Vaccari G, Ferri AL, Bertolini J, et al. Emx2 is a dose-dependent negative regulator of Sox2 telencephalic enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40: 6461–6476.
Ligon KL, Echelard Y, Assimacopoulos S, Danielian PS, Kaing S, Grove EA, et al. Loss of Emx2 function leads to ectopic expression of Wnt1 in the developing telencephalon and cortical dysplasia. Development 2003, 130: 2275–2287.
Soldner F, Jaenisch R. Medicine. iPSC disease modeling. Science 2012, 338: 1155–1156.
Rhinn H, Qiang L, Yamashita T, Rhee D, Zolin A, Vanti W, et al. Alternative alpha-synuclein transcript usage as a convergent mechanism in Parkinson’s disease pathology. Nat Commun 2012, 3: 1084.
Chen BC, Legant WR, Wang K, Shao L, Milkie DE, Davidson MW, et al. Lattice light-sheet microscopy: imaging molecules to embryos at high spatiotemporal resolution. Science 2014, 346: 1257998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, S., Zhou, J. Finding the ‘Guilty’ Gene Variant of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease Via CRISPR/Cas9. Neurosci. Bull. 33, 115–117 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0065-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0065-2