Abstract
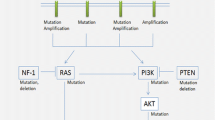
Slit2/Robo1 is a conserved ligand-receptor system, which greatly affects the distribution, migration, axon guidance and branching of neuron cells. Slit2 and its transmembrane receptor Robo1 have different distribution patterns in gliomas. The expression of Slit2 is at very low levels in pilocytic astrocytoma, fibrillary astrocytoma and glioblastoma, while Robo1 is highly expressed in different grades of gliomas at both mRNA and protein levels. Acquisition of insidious invasiveness by malignant glioma cells involves multiple genetic alterations in signaling pathways. Although the specific mechanisms of tumor-suppressive effect of Slit2/Robo1 have not been elucidated, it has been proved that Slit2/Robo1 signaling inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by inactivation of Cdc42-GTP. With the research development on the molecular mechanisms of Slit2/Robo1 signaling in glioma invasion and migration, Slit2/Robo1 signaling may become a potential target for glioma prevention and treatment.
摘要
Slit2/Robo1 信号通路是一个进化保守的配体受体系统。该信号通路对神经细胞的分布、 迁移、 轴突导向起着重要作用。 Slit2 及其跨膜受体Robo1蛋白在胶质瘤中的分布是不同的。 Slit2在毛细胞性星形细胞瘤及胶质母细胞瘤中是低表达的, 而Robo1 在各级别的胶质瘤中均有高表达。 恶性胶质瘤细胞的浸润侵袭机制包括多条信号通路的多种基因的改变。 虽然Slit2/Robo1信号通路抑制肿瘤的分子机制尚不清楚, 但已有研究报道其抑制胶质瘤细胞侵袭的作用是通过抑制Cdc42-GTP的活性来实现的。 本文主要就Slit2/Robo1信号通路在胶质瘤中的作用进行详尽探讨。 伴随Slit2/Robo1信号通路分子机制研究的不断深入, 将会为有效治疗恶性胶质瘤提供新的策略和思路。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dallol A, Krex D, Hesson L, Eng C, Maher ER, Latif F. Frequent epigenetic inactivation of the SLIT2 gene in gliomas. Oncogene 2003, 22: 4611–4616.
Kleihues P, Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, Rorke LB, Reifenberger G, Burger PC, et al. The WHO classification of tumors of the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2002, 61: 215–225; discussion 226-219.
Louis DN, Pomeroy SL, Cairncross JG. Focus on central nervous system neoplasia. Cancer Cell 2002, 1: 125–128.
Holland EC. Gliomagenesis, genetic alterations and mouse models. Nat Rev Genet 2001, 2: 120–129.
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev 2007, 21: 2683–2710.
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 2007, 114: 97–109.
Dickson BJ, Gilestro GF. Regulation of commissural axon pathfinding by slit and its Robo receptors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2006, 22: 651–675.
Wong K, Park HT, Wu JY, Rao Y. Slit proteins: molecular guidance cues for cells ranging from neurons to leukocytes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2002, 12: 583–591.
Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, Arnott D, Henzel W, Goodman CS, et al. Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell 1999, 96: 795–806.
Wang B, Xiao Y, Ding BB, Zhang N, Yuan X, Gui L, et al. Induction of tumor angiogenesis by Slit-Robo signaling and inhibition of cancer growth by blocking Robo activity. Cancer Cell 2003, 4: 19–29.
Plump AS, Erskine L, Sabatier C, Brose K, Epstein CJ, Goodman CS, et al. Slit1 and Slit2 cooperate to prevent premature midline crossing of retinal axons in the mouse visual system. Neuron 2002, 33: 219–232.
Mambetisaeva ET, Andrews W, Camurri L, Annan A, Sundaresan V. Robo family of proteins exhibit differential expression in mouse spinal cord and Robo-Slit interaction is required for midline crossing in vertebrate spinal cord. Dev Dyn 2005, 233: 41–51.
Fouquet C, Di Meglio T, Ma L, Kawasaki T, Long H, Hirata T, et al. Robo1 and robo2 control the development of the lateral olfactory tract. J Neurosci 2007, 27: 3037–3045.
Grieshammer U, Le M, Plump AS, Wang F, Tessier-Lavigne M, Martin GR. SLIT2-mediated ROBO2 signaling restricts kidney induction to a single site. Dev Cell 2004, 6: 709–717.
Sabatier C, Plump AS, Le M, Brose K, Tamada A, Murakami F, et al. The divergent Robo family protein rig-1/Robo3 is a negative regulator of slit responsiveness required for midline crossing by commissural axons. Cell 2004, 117: 157–169.
Huminiecki L, Gorn M, Suchting S, Poulsom R, Bicknell R. Magic roundabout is a new member of the roundabout receptor family that is endothelial specific and expressed at sites of active angiogenesis. Genomics 2002, 79: 547–552.
Wong K, Ren XR, Huang YZ, Xie Y, Liu G, Saito H, et al. Signal transduction in neuronal migration: roles of GTPase activating proteins and the small GTPase Cdc42 in the Slit-Robo pathway. Cell 2001, 107: 209–221.
Park KW, Morrison CM, Sorensen LK, Jones CA, Rao Y, Chien CB, et al. Robo4 is a vascular-specific receptor that inhibits endothelial migration. Dev Biol 2003, 261: 251–267.
Sawamoto K, Wichterle H, Gonzalez-Perez O, Cholfin JA, Yamada M, Spassky N, et al. New neurons follow the flow of cerebrospinal fluid in the adult brain. Science 2006, 311: 629–632.
Liu D, Hou J, Hu X, Wang X, Xiao Y, Mou Y, et al. Neuronal chemorepellent Slit2 inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell migration by suppressing small GTPase Rac1 activation. Circ Res 2006, 98: 480–489.
Mertsch S, Schmitz N, Jeibmann A, Geng JG, Paulus W, Senner V. Slit2 involvement in glioma cell migration is mediated by Robo1 receptor. J Neurooncol 2008, 87: 1–7.
Dickinson RE, Dallol A, Bieche I, Krex D, Morton D, Maher ER, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of SLIT3 and SLIT1 genes in human cancers. Br J Cancer 2004, 91: 2071–2078.
Guan H, Zu G, Xie Y, Tang H, Johnson M, Xu X, et al. Neuronal repellent Slit2 inhibits dendritic cell migration and the development of immune responses. J Immunol 2003, 171: 6519–6526.
Yiin JJ, Hu B, Jarzynka MJ, Feng H, Liu KW, Wu JY, et al. Slit2 inhibits glioma cell invasion in the brain by suppression of Cdc42 activity. Neuro Oncol 2009, 11: 779–789.
Rhee J, Buchan T, Zukerberg L, Lilien J, Balsamo J. Cables links Robo-bound Abl kinase to N-cadherin-bound β-catenin to mediate Slit-induced modulation of adhesion and transcription. Nat Cell Biol 2007, 9: 883–892.
Rhee J, Mahfooz NS, Arregui C, Lilien J, Balsamo J, VanBerkum MF. Activation of the repulsive receptor Roundabout inhibits N-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion. Nat Cell Biol 2002, 4: 798–805.
Prasad A, Paruchuri V, Preet A, Latif F, Ganju RK. Slit-2 induces a tumor-suppressive effect by regulating beta-catenin in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2008, 283: 26624–26633.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Wen-Liang, L., Li, F. et al. Slit2/Robo1 signaling in glioma migration and invasion. Neurosci. Bull. 26, 474–478 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-010-0730-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-010-0730-9