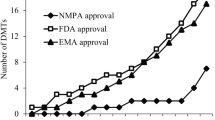
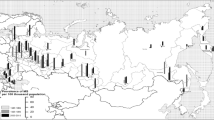
Abstract
This review focused on the diagnosis and clinical features of multiple sclerosis (MS) in China. We have identified the published researching information from 1976 to 2008 in China. The key issues related to the diagnosis and clinical features of MS in China were summarized. The first patient with MS in China was reported in 1926 from Xiehe hospital. Case reports on MS has been increasing during recent decades. Almost all the patients with MS were confirmed by the McDonald criteria (1977) before 1984. After the year of 1992, even to this day, the Poser criteria were widely used in China. Although the new diagnostic criteria, McDonald criteria (2001), were presented in 2001, only few papers published in Chinese were reported. The most frequent initial symptoms or signs of the patients with MS were optic nerve, motor weakness and sensory symptoms. The most frequent location of MS lesions over the course was found to be the spinal cord, followed by the cerebrum and optic nerves. Almost all patients had been treated with corticosteroids. This review supported previous observations in Chinese patients with MS. However, further studies are needed to understand epidemiologic features of MS in China.
摘要
本文对中国多发性硬化诊断标准的使用及疾病特征进行综述。收集1976∼2008年期间关于中国多发性硬化疾病研究的文献, 分析其中的诊断信息及临床特征。中国首例多发性硬化患者于1926 年在协和医院诊断之后的几十年, 关于多发性硬化的报道日益增多。1984 年前, 几乎所有患者的诊断均依据McDonald 诊断标准(1977)。1992年后至今, Poser 诊断标准在国内得到了广泛的应用。尽맜2001 年推出新的诊断标准McDonald criteria (2001), 但以该诊断确诊多发性硬化的报道并不多。可见国内在多发性硬化诊断中存在诊断标准滞后的现象。中国多发性硬化患者的首发症状以视神经受累最常见, 其次为肢体无力和感觉障碍。病程中病变最常累及的部位为脊髓, 其次为大脑和视神经。大多数患者均接受过皮质激素的治疗。本文支持了以往关于中国多发性硬化疾病的研究结果。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guan YT, Zhang GX, Rostami A. Cell-bases remyelinating therapy in inflammatory demyelinating injury of the CNS. Neurosci Bull 2005, 21: 364–369.
Guo MF, Ji N, Ma CG. Immunologic pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Neurosci Bull 2008, 24: 381–386.
Owens T. The enigma of multiple sclerosis inflammation and neurodegeneration cause heterogeneous dysfunction and damage. Curr Opin Neurol 2003, 16: 259–265.
Chen ZL, Wang DM, Duan JF, Wen SQ, Tang YF, Li ZX. Leptin enhances the release of cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from acute multiple sclerosis patients. Neurosci Bull 2006, 22: 115–117.
Zhao BX. Multiple sclerosis and acute demyelinating diseases (Review). Chin J Neurology Psychiatry 1981, 14: 101–104.
Xu ZC, Wang WZ, Tong MX, Zhang ZL. Clinical analysis of 151 patients with multiple sclerosis. Chin J Neurology Psychiatry 1984, 17: 377–381.
Zhao BX, Liu XQ, Guo YP, Yang YC, Huang HF. Clinical feature of patients with multiple sclerosis in China. Chin J Neurology Psychiatry 1979, 12: 169–173.
Zhao F, Liu ZJ. Multiple sclerosis — autopsy of 3 patients and clinical analysis of 22 patients. Chin J Neurology Psychiatry 1979, 12: 179–182.
Xu J, Xiao ZX, Hu WM, Ge MZ, Wang WY, Tian JX, et al. Clinical features of patients with multiple sclerosis. Chin J Neurology Psychiatry 1981, 14: 105–108.
Zhao BX, Liu XQ, Guo YP, Yang YC, Huang HF. Multiple Sclerosis. A clinical study of 70 cases. Eur Neurol 1981, 20: 394–400.
Zhao BX, Liu XQ, Yang YC, Huang HF, Liu DS, Lin SH, et al. Clinical analysis of 256 patients with multiple sclerosis. Chin Med J 1983, 63: 610–613.
Poser CM, Paty DW, Scheinberg L, McDonald WI, Davis FA, Ebers GC, et al. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol 1983, 13: 227–231.
Gao ZL, Zhou N, Chen J, Zhang CH. Clinical analysis of 130 patients with multiple sclerosis. Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Anhui 1995, 30: 147–149.
Li HP, Zhan QM, Wang YZ, Sun B. MRI, EP and clinical study in multiple sclerosis. Med J Chin Peoples Liberation Army 1995, 20: 465–467.
Zheng JZ, Liu ZQ. Multiple sclerosis. J Apoplexy Nerv Dis 1990, 7: 139–141.
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung HP, Lublin FD, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guideline from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2001; 50: 121–127.
Xue CH, Wu J, Hong JH, Chen Y. Clinical analysis of 32 patients with multiple sclerosis. Shaanxi Med J 2007, 36: 1260–1261.
Cheng Q, Miao L, Zhang J, Guan YT, Liu ZG, Wang X, et al. Clinical features of multiple sclerosis in patients from a survey in Shanghai, China. Multiple Sclerosis 2008, 14: 671–678.
Liu HY, Shao FY. Clinical analysis of 168 patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Med 2007, 27: 35–36.
Chen KM, Zhang X, Xia JH. Clinical characteristic of 158 patients with multiple sclerosis. Chin J Pract Nerv Dis 2008, 11:69–71.
Liu GZ, Xu XH, Wang XQ, Fang LB, Zhang H, Guo H, et al. The comparison of two diagnostic criteria of multiple sclerosis. Clin J Neuroimmunol Neurol 2001, 8: 129–141.
Liu JL, Ma CG, Cheng DB, Qin C, Li JP. The Comparison of new and old diagnostic criteria of multiple sclerosis — Clinical analysis of 60 patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Focus 2006, 21:1113–1114.
Cheng Q, Miao L, Zhang J, Ding SJ, Liu ZG, Wang X, et al. A population-based survey of multiple sclerosis in Shanghai, China. Neurology 2007, 68: 1495–1500.
Xu Q, Liu Z, Zheng HM. MRI appearance in multiple sclerosis. Ti Erh Chun i Ta Hsueh Hsueh Pao 1992; 13: 392–394.
Lau KK, Wong LK, Li LS, Chan YW, Li HL, Wong V. Epidemiological study of multiple sclerosis in Hong Kong Chinese: questionnaire survey. Hong Kong Med J 2002, 8: 77–80.
Guo YP. Pathological study of multiple sclerosis in China. Chin J Neurology Psychiatry 1979, 12: 174–178.
Kira J. Multiple sclerosis in the Japanese population. Lancet Neurol 2003, 2: 117–127.
Hung TP, Landsborough D, Hsi MS. Multiple sclerosis amongst Chinese in Taiwan. J Neurol Sci 1976, 27: 459–484.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, XJ., Xu, LZ. Review of the diagnosis and clinical features of multiple sclerosis in China. Neurosci. Bull. 25, 38–42 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-1212-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-1212-9