Abstract
Liver transplantation is a therapeutic option of choice for acute and chronic end-stage liver disease. Indications, contraindications, and surgical procedures for the liver transplantation have become well established. In most part of the world, the main source of liver for transplantation remains the donation after brain death (DBD), but in view of increasing death on the waiting list due to shortage of brain dead organs other options such as split liver transplantation, living donor liver transplantation (LDLT), and donation after cardiac death (DCD) have been used. In the pretransplantation era, liver failure was nearly universally fatal, with mortality from fulminant hepatic failure of 80–90 %, and 1-year mortality in decompensated cirrhosis of more than 50 %. In contrast, liver transplantation patient survival is presently more than 85 % at 1 year and more than 70 % at 5 years, emphasizing the clinical benefit of liver transplantation for either acute or chronic liver failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riordan SM, Williams R (2008) Perspectives on liver failure: past and future. Semin Liver Dis 28:137–141
Benhamou JP (1991) Fulminant and sub-fulminant hepatic failure: definition and causes. In: Williams R, Hughes RD (eds) Acute liver failure: improved understanding and better therapy. Mitre, London, pp 6–10
O’Grady JG, Alexander GJ, Hayllar KM et al (1989) Early indicators of prognosis in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 97:439–445
Bernuau J, Rueff B, Benhamou JP (1986) Fulminant and subfulminant liver failure: definitions and causes. Semin Liver Dis 6:97–106
Ascher NL, Lake JR, Emond JC et al (1993) Liver transplantation for fulminant hepatic failure. Arch Surg 128:677–682
Mazzaferro V, Regalia E, Doci R et al (1996) Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 334(11):693–699
Pfitzmann R, Schwenzer J, Rayes N, Seehofer D, Neuhaus R, Nüssler NC (2007) Long-term survival and predictors of relapse after orthotopic liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. Liver Transpl 13:197–205
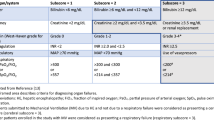
Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremers W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, D’Amico G, Dickson ER, Kim WR (2001) A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology 33:464–470
Chari RS, Gan TJ, Robertson KM, Bass K, Camargo CA Jr, Greig PD et al (1998) Venovenous bypass in adult orthotopic liver transplantation: routine or selective use? J Am Coll Surg 186:683–690
Jovine E, Mazziotti A, Grazi GL, Ercolani G, Masetti M, Morganti M et al (1997) Piggy-back versus conventional technique in liver transplantation: report of a randomized trial. Transpl Int 10:109–112
Broelsch CE, Emond JC, Whitington PF et al (1990) Application of reduced-size liver transplants as split grafts, auxiliary orthotopic grafts, and living related segmental transplants. Ann Surg 212:368–375, discussion 375–377
Reyes J, Gerber D, Mazariegos GV et al (2000) Split-liver transplantation: a comparison of ex vivo and in situ techniques. J Pediatr Surg 35:283–289
Greig PD, Woolf GM, Sinclair SB et al (1989) Treatment of primary liver graft nonfunction with prostaglandin E1. Transplantation 48:447–453
Langnas AN, Marujo W, Stratta RJ, Wood RP, Shaw BW Jr (1991) Vascular complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. Am J Surg 161:76–82
Abbasoglu O, Levy MF, Testa G et al (1998) Does intraoperative hepatic artery flow predict arterial complications after liver transplantation? Transplantation 66:598–601
Todo S, Furukawa H, Kamiyama T (2005) How to prevent and manage biliary complications in living donor liver transplantation? J Hepatol 43:22–27
Douzdjian V, Abecassis MM, Johlin FC (1994) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction following liver transplantation: screening by bed-side manometry and definitive manometric evaluation. Dig Dis Sci 39:253–256
Taylor AL, Watson CJ, Bradley JA (2005) Immunosuppressive agents in solid organ transplantation: mechanisms of action and therapeutic efficacy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 56:23–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, R. Liver Transplantatation- an Overview. Indian J Surg 75, 185–191 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-012-0643-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-012-0643-0